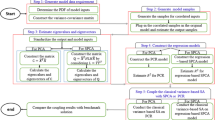
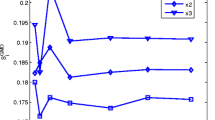
Abstract
Global sensitivity analysis (GSA) plays an important role to quantify the relative importance of uncertain parameters to the model response. However, performing quantitative GSA directly is still a challenging problem for complex models with dependent inputs. A novel method is proposed for screening dependent inputs in the study. The proposed method inherits the capability of easily handing multivariate dependence from the distance correlation. With the help of a projection operator in the Hilbert space, it can work without knowing the specific conditional distribution of inputs. The advantages of the proposed method are discussed and demonstrated through applications to numerical and environmental modeling examples containing many dependent variables. Compared to classical GSA methods with dependent variables, the proposed method can be easily used, while the accuracy of inputs screening is well maintained.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgonovo E (2007) A new uncertainty importance measure. Reliab Eng Syst Saf. 92(6):771–784
Botev ZI, Grotowski JF, Kroese DP (2010) Kernel density estimation via diffusion. Ann Stat 38(5):2916–2957
Brell G, Li G, Rabitz H (2010) An efficient algorithm to accelerate the discovery of complex material formulations. J Chem Phys 132(17):174103
Campolongo F, Cariboni J, Saltelli A (2007) An effective screening design for sensitivity analysis of large models. Environ Model Softw 22(10):1509–1518
Campolongo F, Saltelli A, Cariboni J (2011) From screening to quantitative sensitivity analysis. A Unifi- Approach. Comput Phys Commun 182(4):978–988
Da Veiga S (2015) Global sensitivity analysis with dependence measures. J Stat Comput Simul 85(7):1283–1305
Da Veiga S, Wahl F, Gamboa F (2009) Local polynomial estimation for sensitivity analysis on models with correlated inputs. Technometrics. 51(4):452–463
De Lozzo M, Marrel A (2016) New improvements in the use of dependence measures for sensitivity analysis and screening. J Stat Comput Simul 86(15):3038–3058
De Lozzo M, Marrel A (2017) Sensitivity analysis with dependence and variance-based measures for spatio-temporal numerical simulators. Stoch Env Res Risk A 31(6):1437–1453
Feng K, Lu Z, Yun W (2018) Aircraft icing severity analysis considering three uncertainty types. AIAA J. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J057529. Accessed 25 March 2019
Ge Q, Menendez M (2014) An efficient sensitivity analysis approach for computationally expensive microscopic traffic simulation models. Int J Transp 2(2):49–64
Ge Q, Menendez M (2017) Extending Morris method for qualitative global sensitivity analysis of models with dependent inputs. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 162:28–39
Ge Q, Ciuffo B, Menendez M (2014) An exploratory study of two efficient approaches for the sensitivity analysis of computationally expensive traffic simulation models. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 15(3):1288–1297
Gretton A, Bousquet O, Smola A, Schölkopf B (2005) Measuring statistical dependence with Hilbert-Schmidt norms. In: Jain S, Simon H, Tomita E (eds) Algorithmic learning theory. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3734. Springer, Berlin, pp 63–77
Hamilton AS, Hutchinson DG, Moore RD (2000) Estimating winter streamflow using conceptual streamflow model. J Cold Reg Eng 14(4):158–175
Huo X, Székely GJ (2016) Fast computing for distance covariance. Technometrics. 58(4):435–447
Iman RL (2008) Latin hypercube sampling. Encyclopedia of Quantitative Risk Analysis and Assessment. Wiley, Hoboken
Iman RL, Conover WJ (1982) A distribution-free approach to inducing rank correlation among input variables. Commun Stat Simul Comput 11(3):311–334
Janon A, Klein T, Lagnoux A, Nodet M, Prieur C (2014) Asymptotic normality and efficiency of two Sobol’ index estimators. ESAIM-Probab Stat 18:342–364
Joeph H, Pierre G (2018) An approximation theoretic perspective of the Sobol’ indices with dependent variables. Int J Uncertain Quan 8(6):483–493
Kala Z, Valeš J (2017) Global sensitivity analysis of lateral-torsional buckling resistance based on finite element simulations. Eng Struct 134:37–47
Kala Z, Valeš J (2018) Imperfection sensitivity analysis of steel columns at ultimate limit state. Arch Civ Mech Eng 18:1207–1218
Kollat JB, Reed PM, Wagener T (2012) When are multiobjective calibration trade-offs in hydrologic models meaningful? Water Resour Res 48(3)
Kucherenko S (2009) Derivative based global sensitivity measures and their link with global sensitivity indices. Math Comput Simul 79(10):3009–3017
Lambert RS, Lemke F, Kucherenko SS, Song S, Shah N (2016) Global sensitivity analysis using sparse high dimensional model representations generated by the group method of data handling. Math Comput Simul 128:42–54
Li R, Zhong W, Zhu L (2012) Feature screening via distance correlation learning. J Am Stat 107(499):1129–1139
Lindström G (1997) A simple automatic calibration routine for the HBV model. Hydrol Res 28(3):153–168
Lyons R (2013) Distance covariance in metric spaces. Ann Probab 41(5):3284–3305
Malte K. Vine copula MATLAB toolbox, version 1.2, 2016, https://github.com/MalteKurz/VineCopulaMatlab.git. Accessed 25 Mar 2019
Mara TA, Tarantola S (2012) Variance-based sensitivity indices for models with dependent inputs. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 107:115–121
Mara TA, Tarantola S, Annoni P (2015) Non-parametric methods for global sensitivity analysis of model output with dependent inputs. Environ Model Softw 72:173–183
Morris MD (1991) Factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments. Technometrics. 33(2):161–174 https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00401706.1991.10484804. Accessed 25 March 2019
Nelsen RB (2007) An introduction to copulas. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Owen AB (2013) Better estimation of small Sobol’ sensitivity indices. ACM T Model Comput S (TOMACS) 23(2):11
Pianosi F, Sarrazin F, Wagener T (2015) A Matlab toolbox for global sensitivity analysis. Environ Model Softw 70:80–85
Plischke E, Borgonovo E, Smith CL (2013) Global sensitivity measures from given data. Eur J Oper Res 226(3):536–550
Rizzo ML, Székely GJ (2016) Energy distance. WIREs Comput Stat 8:27–38
Saltelli A (2002) Sensitivity analysis for importance assessment. Risk Anal 22(3):579–590
Saltelli A, Tarantola S (2002) On the relative importance of input factors in mathematical models: safety assessment for nuclear waste disposal. J Am Stat Assoc 97(459):702–709
Saltelli A, Ratto M, Andres T, Campolongo F, Cariboni J, Gatelli D, Saisana M, Tarantola S (2008) Global sensitivity analysis: the primer. Wiley, Hoboken
Saltelli A, Campolongo F, Cariboni J (2009) Screening important inputs in models with strong interaction properties. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 94(7):1149–1155
Sobol IM (1976) Uniformly distributed sequences with an additional uniform property. USSR Comput Math Math Phys 16(5):236–242
Sobol’ IM (1993) Sensitivity estimates for nonlinear mathematical models. Math Modeling Comput Exp 1(4):407–414
Székely GJ, Rizzo ML (2013) The distance correlation t-test of independence in high dimension. J Multivar Anal 117:193–213
Szekely GJ, Rizzo ML (2014) Partial distance correlation with methods for dissimilarities. Ann Stat 42(6):2382–2412
Székely GJ, Rizzo ML, Bakirov NK (2007) Measuring and testing dependence by correlation of distances. Ann Stat:2769–2794
Xiao S, Lu Z, Wang P (2018) Multivariate global sensitivity analysis for dynamic models based on energy distance. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57:279–291
Xu C (2013) Decoupling correlated and uncorrelated parametric uncertainty contributions for nonlinear models. Appl Math Model 37(24):9950–9969
Xu L, Lu Z, Xiao S (2019) Generalized sensitivity indices based on vector projection with multivariate outputs. Appl Math Model 66:592–610
Yun W, Lu Z, Jiang X, Zhang L (2018) Borgonovo moment independent global sensitivity analysis by Gaussian radial basis function meta-model. Appl Math Model 54:378–392
Yun W, Lu Z, Jiang X (2018) An efficient method for moment-independent global sensitivity analysis by dimensional reduction technique and principle of maximum entropy. Reliab Eng Syst Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2018.03.029. Accessed 25 March 2019
Zadeh FK, Nossent J, Sarrazin F, Pianosi F, van Griensven A, Wagener T, Bauwens W (2017) Comparison of variance-based and moment-independent global sensitivity analysis approaches by application to the SWAT model. Environ Model Softw 91:210–222
Zhang K, Lu Z, Wu D, Zhang Y (2017) Analytical variance based global sensitivity analysis for models with correlated variables. Appl Math Model 45:748–767
Zhou C, Lu Z, Zhang L, Hu J (2014) Moment independent sensitivity analysis with correlations. Appl Math Model 38(19–20):4885–4896
Zhou C, Lu Z, Li W (2015) Sparse grid integration based solutions for moment-independent importance measures. Probabilist Eng Mech 39:46–55
Zhou Y, Lu Z, Cheng K (2019a) Sparse polynomial chaos expansions for global sensitivity analysis with partial least squares and distance correlation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 59(1):229–247
Zhou Y, Lu Z, Cheng K, Yun W (2019b) A Bayesian Monte Carlo-based method for efficient computation of global sensitivity indices. Mech Syst Signal Process 117(15):498–516
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. NSFC 51775439).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nestor V Queipo
Appendix
Appendix
If none of the Xs, Y, and X~s are constant convergence and \( \mid {P}_{{X_{\sim s}}^{\perp }}\left({X}_s\right)\mid >0 \). We have
Similarly,
Combining (A.1) and (A.2), we have
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Lu, Z., Xiao, S. et al. Distance correlation-based method for global sensitivity analysis of models with dependent inputs. Struct Multidisc Optim 60, 1189–1207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02257-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02257-z