Abstract
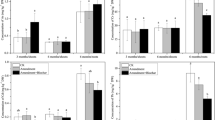
Three different types of low cost soil amendments, namely, EDTA, elemental S and N-fertilizer, were investigated with Vetiver grass, Vetiveria zizanioides (Linn.) Nash growing under highly mixed Cd–Pb contamination conditions. A significant increase (p < 0.05) in Cd and Pb accumulation were recorded in the shoots of all EDTA and N-fertilizer assisted treatments. The accumulation of Cd in 25 mmol EDTA/kg soil and 300 mmol N/kg soil showed relatively higher translocation factor (1.72 and 2.15) and percentage metal efficacy (63.25 % and 68.22 %), respectively, compared to other treatments. However, it was observed that the increased application of elemental S may inhibit the availability of Pb translocation from soil-to-root and root-to-shoot. The study suggests that viable application of 25 mmol EDTA/kg, 300 mmol N/kg and 20 mmol S/kg soil have the potential to be used for soil amendment with Vetiver grass growing under contaminated mixed Cd–Pb soil conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali H, Khan E, Anwar M (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals: concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91(7):869–881
Alloway BJ (2013) Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. (3rd ed.). Environ Pollut 22. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. Springer, London, pp 11–50
Bradl HB (2005) Heavy metals in the environment. In: Bradl HB (ed) Sources and origins of heavy metals, Elsevier Academic Press, pp 1–27
CCME Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (1999a) Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health: Canadian environmental quality guidelines—Cadmium. http://ceqg-rcqe.ccme.ca/download/en/261. Accessed Dec 2015
CCME Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (1999b) Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health: Canadian environmental quality guidelines—Lead. http://ceqg-rcqe.ccme.ca/download/en/269. Accessed Dec 2015
Chen Y, Shen Z, Li X (2004) The use of Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) in the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Appl Geochem 19(10):1553–1565
Chen KF, Yeh TY, Lin CF (2012) Phytoextraction of Cu, Zn and Pb enhanced by chelators with Vetiver (Vetiveria zizanioides) in hydroponic and pot experiments. ISRN Ecol. doi:10.5402/2012/729693
Chiu KK, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2005) Enhanced uptake of As, Zn and Cu byVetiveria zizanioides and Zea maysusing chelating agents. Chemosphere 60(10):1365–1375
Chiu KK, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2006) Growth ofVetiveria zizanioides andPhragmities australison Pb/Zn and Cu mine tailings amended with manure compost and sewage sludge: a greenhouse study. Bioresource Technol 97(1):158–170
Danh LT, Truong P, Mammucari R, Tran T, Foster N (2009) Vetiver grass (Vetiveria Zizanioides) a choice plant for phytoremediation of heavy metals and organic wastes. Int J Phytoremediat 11(8):664–691
Dede G, Ozdemir S (2016) Effects of elemental sulphur on heavy metal uptake by plants growing on municipal sewage sludge. J Environ Manage 166:103–108
DOE Department of Environment, Malaysia (2009) Contaminated land management and control guidelines no. 1: Malaysian recommended site screening levels for contaminated land. http://www.doe.gov.my/portalv1/wp-content/uploads/Contaminated-Land-Management-and-Control-Guidelines-No-1_Malaysian-Recommended-Site-Screening-Levels-for-Contaminated-Land.pdf. Accessed Dec 2015
Feng Q, Tai P, Li P, Guo Y, Fu S (2009) Role of sulfur in cadmium accumulation of Tagetes erecta L. J Plant Nutr 32(6):919–928
Karami N, Clemente R, Moreno-Jiménez E, Lepp NW, Beesley L (2011) Efficiency of green waste compost and biochar soil amendments for reducing lead and copper mobility and uptake to ryegrass. J Hazard Mater 191(1):41–48
Motior MR, Abdou AS, Al Darwish FH, El-Tarabily KA, Awad MA, Golam F, Sofian-Azirun M (2011) Influence of elemental sulfur on nutrient uptake, yield and quality of cucumber grown in sandy calcareous soil. Aust J Crop Sci 5(12):1610–1615
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8(3):199–216
Nascimento CWA, Amarasiriwardena D, Xing B (2006) Comparison of natural organic acids and synthetic chelates at enhancing phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 140(1):114–123
Ng CC, Law SH, Amru NB, Motior MR, Radzi BM (2016a) Phyto-assessment of soil heavy metal accumulation in tropical grasses. J Anim Plant Sci 26(3):686–696
Ng CC, Rahman MM, Boyce AN, Abas MR (2016b) Heavy metals phyto-assessment in commonly grown vegetables: water spinach (I. aquatica) and okra (A. esculentus). Springer Plus 5(1):469
Prasad A, Chand S, Kumar S, Chattopadhyay A, Patra DD (2014) Heavy metals affect yield, essential oil compound and rhizosphere microflora of Vetiver (Vetiveria zizanioides) grass. Commun Soil Sci Plan 45(11):1511–1522
Rahman MM, Soaug AA, Darwish FHA, Golam F, Sofian-Azirun M (2011) Growth and nutrient uptake of maize plants as affected by elemental sulfur and nitrogen fertilizer in sandy calcareous soil. Afr J Biotechnol 10(60):12882–12889
Rahman MM, Azirun SM, Boyce AN (2013) Enhanced accumulation of copper and lead in Amaranth (Amaranthus paniculatus), Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea) and Sunflower (Helianthus annuus). PLoS One 8(5):e62941
Singh V, Thakur L, Mondal P (2015) Removal of lead and chromium from synthetic wastewater using Vetiveria zizanioides. Clean Soil Air Water 43(4):538–543
Truong P, Danh LT (2015) The Vetiver system for improving water quality: prevention and treatment of contaminated water and land, 2nd edn. The Vetiver Network International
Truong P, Van TT, Pinners E (2008) Vetiver system applications technical reference manual, 2nd edn. The Vetiver Network International
US EPA (1996) Method 3050B Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soils, United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/epa-3050b.pdf. Accessed Dec 2015
US EPA (2007a) The use of soil amendments for remediation revitalization and reuse. United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-05/documents/the_use_of_soil_amendments_for_remediation_revitalization_and_reule.pdf. Accessed Dec 2015
US EPA (2007b) Method 7000B Flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry, United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/7000b.pdf. Accessed Dec 2015
Acknowledgments
This research work is made possible through funding provided by the University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur (PG006-2013A and RK001-2016) and the Malaysia Toray Science Foundation (STRG15/G251) grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Malaysia Toray Science Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, C.C., Boyce, A.N., Rahman, M.M. et al. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Mixed Heavy Metals Contamination in Vetiver Grass. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97, 695–701 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1921-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1921-5