Abstract
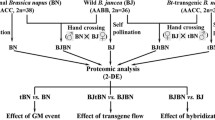
In spite of commercial use of heterosis in agriculture, the molecular basis of heterosis is poorly understood. To gain a better understanding of the molecular basis of wheat heterosis, we carried out a comparative proteomic analysis in seedling leaves between wheat hybrid and parents. Common wheat (Triticum aestivum L., 2n = 6x = 42, AABBDD) Line 3338 and spelt wheat (Triticum spelta L., 2n = 6x = 42, AABBDD) Line 2463 were used to produce a heterotic F1 hybrid. The expression patterns of the total proteins were compared in seedling leaves between hybrid and its parents by using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis with two pH ranges for the first dimension separation. Among ~900 protein spots reproducibly detected, 49 protein spots were identified as being differentially expressed between hybrid and its parental lines (P < 0.05) for more than 1.5-folds. Six possible modes of differential expression were observed, including high- and low-parent dominance, underdominance, and overdominance, uniparent silencing and uniparent dominance. Moreover, 30 of the 49 differentially expressed protein spots were identified, which were involved in metabolism, signal transduction, energy, cell growth and division, disease and defense, secondary metabolism. These results indicated that wheat hybridization can cause protein expression differences between hybrid and its parents; these proteins were involved in diverse physiological process pathways, which might be responsible for the observed heterosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
Acetonitrile
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BPH:
-
Best-parent heterosis
- CHA:
-
Chemical hybridizing agent
- CHAPS:
-
3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl)-dimethylammonio]-1-propane sulfonate
- CHCA:
-
A-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid
- DDRT:
-
Differential display reverse transcript
- DRH:
-
Down-regulated in hybrid
- DTT:
-
1,4-Dithio-DL-threitol
- FBA:
-
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- HDH:
-
High-dominant in hybrid
- IEF:
-
Isoelectric focusing
- LDH:
-
Low-dominant in hybrid
- LDW:
-
Leaf dry weight
- LFW:
-
Leaf fresh weight
- LRR:
-
Leucine-rich repeat protein
- MPH:
-
Mid-parent heterosis
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- PMF:
-
Peptide map fingerprinting
- PTM:
-
Post translational modification
- RcbA:
-
Rubisco activase
- RcbL:
-
Rubisco large subunit
- SSH:
-
Suppression subtractive hybridization
- 2DE:
-
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- TIR:
-
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor
- TLN:
-
Total leaf number
- TTN:
-
Total tiller number
- UPF1:
-
Dominant expression of uniparental proteins in hybrids
- UPnF1:
-
Dominant expression of uniparental proteins but not in hybrids
- URH:
-
Up-regulated in hybrid
References
Anderson L, Seilhamer J (1997) A comparison of selectedmRNA and protein abundances in human liver. Electrophoresis 18:533–537
Baginsky S, Kleffmann T, von Zychlinski A, Gruissem W (2005) Analysis of shotgun proteomics and RNA profiling data from Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts. J Proteome Res 4:637–640
Bevan M, Bancroft I, Bent E, Love K, Goodman H, Dean C, Bergkamp R, Dirkse W (1998) Analysis of 1.9 Mb of contiguous sequence from chromosome 4 of the Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 391:485–488
Broughton W-J, Dilworth M-J (1971) Control of leghaemoglobin synthesis in snake beans. Biochem J 125:1075–1080
Corbin R-W, Paliy O, Yang F, Shabanowitz J, Platt M, Lyons C-E, Root K, McAuliffe J, Jordan M-I, Kustu S, Soupene E, Hunt D-F (2003) Toward a protein profile of Escherichia coli: comparison to its transcription profile. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9232–9237
Damerval C, Hebert Y, De Vienne D (1987) Is the polymorphism of protein amounts related to phenotypic variability? A comparison of two-dimensional electrophoresis data with morphological traits in maize. Theor Appl Genet 74:194–202
Day D-A, Tuite M-F (1998) Post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanisms in eukaryotes: an overview. J Endocrinol 157:361–371
Donnelly B-E, Madden R-D, Ayoubi P, Porter D-R, Dillwith J-W (2005) The wheat(Triticum aestivum L.) leaf proteome. Proteomics 5:1624–1633
Dunne A, Ejdebäck M, Ludidi P-L, O’Neill L-A, Gay N-J (2003) Structural complementarity of Toll/Interleukin-1 Receptor domains in Toll-like Receptors and the adaptors Mal and MyD88. J Biol Chem 278:41443–41451
Fedoroff N (2000) Transposons and genome evolution in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:7002–7007
Forsthoefel N-R, Cutler K, Port M-D, Yamamoto T, Vernon D-M (2005) PIRLs: a novel class of plant intracellular leucine-rich repeat proteins. Plant Cell Physiol 46:913–922
Frost D, Way H, Howles P, Luck J, Manners J, Hardham A, Finnegan J, Ellis J (2004) Tobacco Transgenic for the flax rust resistance gene L expresses allele-specific activation of defense responses. MPMI 17:224–232
Gonella J-A, Peterson P-A (1978) Isozyme relatedness of inbred lines of maize and performance of their hybrids. Maydica 23:55–61
Guo M, Rupe M-A, Zinselmeier C, Habben J, Bowen B-A, Smith O-S (2004) Allelic variation of gene expression in maize hybrids. Plant Cell 16:1707–1716
Gygi S-P, Rochon Y, Franza B-R, Aebersold R (1999) Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol Cell Biol 19:1720–1730
Hadjinov M-I, Scherbok V-S, Benko N-I, Gusev V-P, Sukhorzhevokaya T-B, Voronova L-P (1982) Interrelationships between isozymic diversity and combining ability in maize lines. Maydica 27:135–149
Heidrich-Sobrinho E, Cordeiro A-R (1975) Codominant isoenzymic allela as markers of genetic diversity correlated with heterosis in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 46:197–199
Holmes-Davis R, Tanaka C-K, Vensel W-H, HurkmanW-J McCormick S (2005) Proteome mapping of mature pollen of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proteomics 5:4864–4884
Huang Y, Li L-H, Chen Y, Li X-H, Xu C-G, Wang S-P, Zhang Q-F (2006) Comparative analysis of gene expression at early seedling stage between a rice hybrid and its parents using a cDNA microarray of 9198 uni-sequences. Sci China 49:519–529
Hunter R-B, Kannenberg L-W (1971) Isozyme characterization of corn (Zea mays) inbreds and its relationship to single cross hybrid performance. Can J Genet Cytol 13:197–199
Kashkush K, Feldman M, Levy A-A (2003) Transcriptional activation of retrotransposons alters the expression of adjacent genes in wheat. Nature Genet 33:102–106
Kumar A, Bennetzen J-L (1999) Plant retrotransposon. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Leonardi A, Damerval C, De Vienne D (1987) Inheritance of protein amounts: comparison of two-dimensional electrophoresis patterns of leaf sheath of two maize lines (Zeamays L.) and their hybrids. Genet Res 50:1–5
Mack P-D, Kapelnikov A, Heifetz Y, Bender M (2006) Mating-responsive genes in reproductive tissues of female Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103:10358–10363
Martin T, Frommer W-B, Salanoubat M, Willmitzer L (1993) Expression of an Arabidopsis sucrose synthase gene indicates a role in metabolization of sucrose both during phloem loading and in sink organs. Plant J. 4:367–377
Matuschke I, Mishra RR, Qaim M (2007) Adoption and impact of hybrid wheat in India. World Dev 35:1422–1435
Mills D-A, Richter M-L (1991) Nucleotide binding to the isolated β subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase. J Biol Chem 266:7440–7444
Mooney B-P, Miernyk J-A, Greenlief C-M, Thelen J-J (2006) Using quantitative proteomics of Arabidopsis roots and leaves to predict metabolic activity. Physiol Plant 128:237–250
Nature Signaling Gateway (2007) Nature publishing group. http://www.signaling-gateway.org. Cited 29 Oct 2007
Ni Z-F, Sun Q-X, Wu L-M, Xie C-J (2002) Differential gene expression between wheat hybrids and their parental inbreds in primary roots. Acta Bot Sin 44:457–462
Ni Z-F, Sun Q-X, Liu Z-Y (2000) Identification of a hybrid-specific expressed gene encoding novel RNA-binding protein in wheat seedling leaves using differential display of mRNA. Mol Gen Genet 263:934–938
Noir S, Brautigam A, Colby T, Schmidt J, Panstruga R (2005) A reference map of the Arabidopsis thaliana mature pollen proteome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337:1257–1266
Porubleva L, Velden K-V, Kothari S, Oliver D-J, Chitnis P-R (2001) The proteome of maize leaves: use of gene sequences and expressed sequence tag data for identification of proteins with peptide mass fingerprints. Electrophoresis 22:1724–1738
Ramagli L-S (1999) Quantifying protein in 2-D PAGE solubilization buffers. Methods Mol Biol 112:99–103
Romagnoli S, Maddaloni M, Livini C, Motto M (1990) Relationship between gene expression and hybrid vigor in primary root tips of young maize. Theor Appl Genet 80:769–775
Seo Y-S, Jeon J-SE, Rojas M-R, Gilbertson R-L (2007) Characterization of a novel Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR)-TIR gene differentially expressed in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Othello) undergoing a defence response to the geminivirus Bean dwarf mosaic virus. Mol Plant Pathol 8:151–162
Song X, Ni Z-F, Yao Y-Y, Xie C-J, Li Z-X, Wu H-Y, Zhang Y-H, Sun Q-X (2007) Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root proteome and differentially expressed root proteins between hybrid and parents. Proteomics 7:3538–3557
Sun Q-X, Ni Z-F, Liu Z-Y (1999) Differential gene expression between wheat hybrids and their parental inbreds in seedling leaves. Euphytica 106:117–123
Sun Q-X, Wu L-M, Ni Z-F, Meng F-R, Wang Z-K, Lin Z (2004) Differential gene expression patterns in leaves between hybrids and their parental inbreds are correlated with heterosis in a wheat diallel cross. Plant Sci 166:651–657
Swanson-Wagner R-A, Jia Y, DeCook R, Borsuk L-A, Nettleton D, Schnable P-S (2006) All possible modes of gene action are observed in a global comparison of gene expression in a maize F 1 hybrid and its inbred parents. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:6805–6810
Tsaftaris A-S (1987) Isozymes in plant breeding. In: Rattazzi MC, Scandalios GJ, Whitt GS (eds) Isozymes: current topics in biological and medical research. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 103–119
Tsuyoshi M, Nobuaki H, Kazuko Y-S, Hiroshi K, Kazuo S (1994) Cloning and sequencing of a nove1 serine/threonine protein kinase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 106:1229–1230
Wang Z-K, Ni Z-F, Wu H-L, Nie X-L, Sun Q-X (2006) Heterosis in root development and differential gene expression between hybrids and their parental inbreds in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:1283–1294
Wu L-M, Ni Z-F, Meng F-R, Lin Z, Sun Q-X (2003) Cloning and characterization of leaf cDNAs that are differentially expressed between wheat hybrids and their parents. Mol Gen Genet 270:281–286
Xia Q, Hendrickson E-L, Zhang Y, Wang T, Taub F, Moore B-C, Porat I, Whitman W-B, Hackett M, Leigh J-A (2006) Quantitative proteomics of the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis validated by microarray analysis and real time PCR. Mol Cell Proteomics Feb 24:868–881
Xiong L-Z, Yang G-P, Xu C-G, Zhang Q-F, Maroof M-A-S (1998) Relationships of differential gene expression in leaves with heterosis and heterozygosity in a rice diallel cross. Mol Breed 4:129–136
Yao Y-Y, Ni Z-F, Zhang Y-H, Chen Y, Ding Y-H, Han Z-F, Liu Z-Y, Sun Q-X (2005) Identification of differentially expressed genes in leaf and root between wheat hybrid and its parental inbreds using PCR-based cDNA subtraction. Plant Mol Biol 58:367–384
Zhang Y-H, Ni Z-F, Yao Y-Y, Zhao J, Sun Q-X (2006) Analysis of genome-wide gene expression in root of wheat hybrid and its parents inbreds using Barley1 GeneChip. Prog Nat Sci 16:712–720
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mr. Jidong Feng for his assistance in mass spectrometry analysis. This work was financially supported by National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB109000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30671297), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-05-0131) and 863 Project of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kearsey.
X. Song and Z. Ni have equally contributed to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2008_890_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary Table 1 t-test for the protein spot accumulation differences between wheat hybrid and parents (DOC 592 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Ni, Z., Yao, Y. et al. Identification of differentially expressed proteins between hybrid and parents in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedling leaves. Theor Appl Genet 118, 213–225 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0890-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0890-4