Abstract
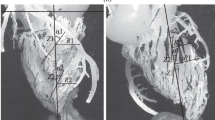
There have been several reports on novel threadlike structures (NTSs) on the surfaces of the internal organs of rats and rabbits since their first observation by Bonghan Kim in 1963. To confirm this novel circulatory function, it is necessary to observe the flow of liquid through the NTS as well as the structurally corroborating channels in the NTS. In this article, we report on the measurement of the flow speed of Alcian blue solution in the NTSs on the organ surfaces of rabbits, and we present electron microscopic images depicting the cribrous cross-section with channels. The speed was measured as 0.3 ± 0.1 mm/s, and the flow distance was up to 12 cm. The flow was unidirectional, and the phase contrast microscopic images showed that the NTSs were strongly stained with Alcian blue. The ultrastructure of the NTSs revealed by cryo-scanning electron microscopy and high-voltage electron microscopy showed that (1) there were cell-like bodies and globular clumps of matter inside the sinus of the channel with thin strands of segregated zones which is a microscopic evidence of the liquid flow, (2) the sinuses have wall structures surrounded with extracellular matrices of collagenous fibers, and (3) there exists a cribriform structure of sinuses. To understand the mechanism for the circulation, a quantitative analysis of the flow speed has been undertaken applying a simplified windkessel model. In this analysis, it was shown that the liquid flow through the NTSs could be due to peristaltic motion of the NTS itself.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baik KY, Lee J, Lee B-C, Johng H-M, Nam TJ, Sung B, Cho S, Soh K-S (2005) Acupuncture meridian and intravascular Bonghan duct. Key Eng Mater 277–279:125–129
Chan SHH (1984) What is being stimulated in acupuncture: evaluation of the existence of a specific substrate. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 8:25–33
Cho SJ, Kim BS, Park YS (2004) Threadlike structures in the aorta and coronary artery of swine. J Intl Soc Life Info Sci 22:609–611
Griffiths DJ (1987) Dynamics of the upper urinary track: I. Peristaltic flow through a distensible tube of limited length. Phys Med Biol 32(7):813–822
Hwang YC (1992) Anatomy and classification of acupoints. Probl Vet Med 4(1):12–15
Ifrim-Chen F, Ifrim M (2005) Acupuncture and meridians: a histochemical study. Ital J Anat Embryol 110:51–57
Järvinen E, Lyly M, Ruokolainen J, Råback P (2001) Three-dimensional fluid–structure interaction modeling of blood flow in elastic arteries. ECCOMAS Comp Fluid Dynamics Conference, Swansea, Wales, UK (http://www.csc.fi/elmer/papers/)
Johng H-M, Shin H-S, Yoo JS, Lee B-C, Baik K-Y, Soh K-S (2004) Bonghan ducts on the surfaces of rat liver. J Intl Soc Life Info Sci 22(2):469–472
Johng H-M, Yoo JS, Yoon T-J, Shin H-S, Lee B-C, Lee C, Choi C, Sohn Y, Lee J-K, Soh K-S (2007) Use of magnetic nanoparticles to visualize threadlike structures inside lymphatic vessels of rats. eCAM 4(1):77–82
Kim BH (1963) On the Kyungrak system. J Acad Med Sci DPR Kor 90:1–35
Kim BH (1965) Sanal theory. J Acad Med Sci DPR Kor 168:5–38
Kim MS, Ogay V, Shin H-S, Lee B-C, Soh K-S (2006) An Alcian blue staining technique for tracing the governing vessel (GV) meridian in rats. IFMBE Proc. Vol. 14 (World Congress on Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering, Seoul, Korea, 2006) pp 3442–3445
Lee B-C, Baik KY, Johng H-M, Nam TJ, Lee J, Sung B, Choi C, Park W-M, Park E-S, Park D-H, Yoon Y-S, Soh K-S (2004a) Acridine orange staining method to reveal characteristic features of intravascular threadlike structure. Anat Rec 278B:27–30
Lee KJ, Kim S, Jung TE, Jin D, Kim DH, Kim HW (2004b) Unique duct system and the corpuscle-like structures found on the surface of the liver. J Intl Soc Life Info Sci 22:460–462
Lee B-C, Yoo JS, Baik K-Y, Kim KW, Soh K-S (2005a) Novel threadlike structures (Bonghan ducts) inside lymphatic vessels of rabbits visualized with a Janus Green B staining method. Anat Rec 286B:1–7
Lee C, Yoo JS, Kim HH, Kwon J, Soh KS (2005b) Flow of nanoparticles inside organs-surface Bonghan ducts. Proc 23th Symp Kor Soc Jungshin Sci 23:129–134 (in Korean)
Lee BC, Yoo JS, Ogay V, Kim KW, Dobberstein H, Soh K-S, Chang B-S (2007) Electron microscopic study of novel threadlike structures on the surfaces of mammalian organs. Microsc Res Tech 70:34–43
Li J K-J (2000) The arterial circulation. Humana Press, New Jersey
Mazumdar JN (1992) Biofluid mechanics. World Scientific, Singapore
Metry S, Arhan P, Chauvet G (1995) A mathematical analysis of intestinal peristaltic waves. Med Eng Phys 17(9):204–214
Noordergraaf A (1978) Circulatory system dynamics. Academic, New York
Ogay V, Baik KY, Lee BC, Soh K-S (2006) Characterization of DNA-containing granules flowing through the meridian-like system on the internal organs of rabbits. Acupunc Electro Therap Res 31:13–31
Read ND (1991) Low-temperature scanning electron microscopy of fungi and fungus-plant interactions. In: Mendgen K, Lesemann DE (eds) Electron microscopy of plant pathogens. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 17–29
Shin H-S, Johng H-M, Lee B-C, Cho S-I, Soh K-S, Baik K Y, Yoo J-S, Soh K-S (2005) Feulgen reaction study of novel threadlike structures (Bonghan ducts) on the surface of mammalian organs. Anat Rec 284B(1):35–40
Soh K-S, Hong S, Hong J-Y, Lee B-C, Yoo JS (2006) Immunohistochemical characterization of intravascular Bonghan duct. Microcirculation 13:166
Sung B (2005) Effects of UV-A irradiation on the motion of BH-Granules. M.Sc. thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul
Yoo JS, Choi K, Baik KY, Chung DS, Soh K-S (2005) Liquid-phase microextraction method in capillary electrophoresis to detect adrenaline in Bonghan liquid. J Intl Soc Life Info Sci 23(2):292–296
Yoo JS, Johng H-M, Yoon T-J, Shin H-S, Lee B-C, Lee C, Ahn BS, Kang D-I, Lee J-K, Soh K-S (2007) In vivo fluorescence imaging of threadlike tissues (Bonghan ducts) inside lymphatic vessels with nanoparticles. Curr Appl Phys 7:342–348
Zhai N (1989) The research of the histo-physiological relation of mastocyte and meridian. Chin Acupunct Moxi 8:274–277
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by NRL (M1-0300-00-0324) and Ministry of Science and Technology of Korea through the Cavendish-KAIST Cooperative Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Baeckkyoung Sung and Min Su Kim contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, B., Kim, M.S., Lee, BC. et al. Measurement of flow speed in the channels of novel threadlike structures on the surfaces of mammalian organs. Naturwissenschaften 95, 117–124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-007-0300-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-007-0300-9