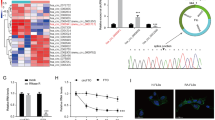
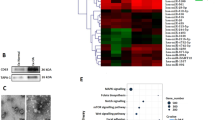
Abstract
Fibroblast-derived exosomes have been reported to transfer microRNAs to recipient cells, where they regulate target gene expression, which is of interest for understanding the basic biology of inflammation, tissue homeostasis, and development of therapeutic approaches. Initial microarray-based analysis carried out in this study identified the rheumatoid arthritis (RA)–related differentially expressed gene pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4). Subsequently, the upstream regulatory microRNA-106b (miR-106b) of PDK4 was predicted with bioinformatic analyses. A collagen-induced arthritis (CIA)-induced mouse model was established, and exosomes were isolated from synovial fibroblasts (SFs) and transferred into chondrocytes to identify the role of exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We found that PDK4 was poorly expressed in RA cartilage tissues and chondrocytes, while miR-106b was highly expressed in RA SFs and SF-derived exosomes. Notably, PDK4 was confirmed as a target gene of miR-106b. Over-expression of PDK4 promoted the proliferation and migration abilities of chondrocytes and inhibited their apoptosis as well as affected the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin (OPG) system. Meanwhile, miR-106b was delivered from SFs to chondrocytes through exosomes, which suppressed chondrocyte proliferation and migration and accelerated apoptosis as well as affected the RANKL/RANK/OPG system via down-regulation of PDK4. Furthermore, in vivo results validated that miR-106b inhibition could relieve CIA-induced RA. Taken together, SF-derived exosomal miR-106b stimulates RA initiation by targeting PDK4, indicating a physiologically validated potential approach for the prevention and treatment of RA.
Key messages
-
PDK4 is decreased in chondrocytes of RA, while miR-106b is increased in SFBs.
-
PDK4 promotes proliferation and migration of chondrocytes.
-
miR-106b could target 3′UTR of PDK4 gene.
-
SFB-exosomal miR-106b inhibits proliferation and migration of chondrocytes.
-
Inhibition of miR-106b attenuates RA progression in a CIA mouse model.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Myasoedova E, Davis JM 3rd, Crowson CS, Gabriel SE (2010) Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis: rheumatoid arthritis and mortality. Curr Rheumatol Rep 12:379–385
Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376:1094–1108
Marrelli K, Cheng AJ, Brophy JD, Power GA (2018) Perceived versus performance fatigability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Physiol 9:1395
Gibofsky A (2012) Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Manag Care 18:S295–S302
Bartok B, Firestein GS (2010) Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 233:233–255
Alam J, Jantan I, Bukhari SNA (2017) Rheumatoid arthritis: recent advances on its etiology, role of cytokines and pharmacotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother 92:615–633
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay S, Pap T (2006) Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45:669–675
Sode J, Krintel SB, Carlsen AL, Hetland ML, Johansen JS, Horslev-Petersen K, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Ellingsen T, Burton M, Junker P, Ostergaard M, Heegaard NHH (2018) Plasma MicroRNA profiles in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis responding to adalimumab plus methotrexate vs methotrexate alone: a placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Rheumatol 45:53–61
Soltanzadeh-Yamchi M, Shahbazi M, Aslani S, Mohammadnia-Afrouzi M (2018) MicroRNA signature of regulatory T cells in health and autoimmunity. Biomed Pharmacother 100:316–323
Yu S, Qin X, Chen T, Zhou L, Xu X, Feng J (2017) MicroRNA-106b-5p regulates cisplatin chemosensitivity by targeting polycystic kidney disease-2 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 28:852–860
Sun C, Yao X, Jiang Q, Sun X (2018) miR-106b targets DAB2 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis. Oncol Lett 16:3063–3069
He QY, Wang GC, Zhang H, Tong DK, Ding C, Liu K, Ji F, Zhu X, Yang S (2016) miR-106a-5p suppresses the proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by targeting HMGA2. DNA Cell Biol 35:506–520
Tao Y, Wang Z, Wang L, Shi J, Guo X, Zhou W, Wu X, Liu Y, Zhang W, Yang H, Shi Q, Xu Y, Geng D (2017) Downregulation of miR-106b attenuates inflammatory responses and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56:1804–1813
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659
Zhang HG, Grizzle WE (2014) Exosomes: a novel pathway of local and distant intercellular communication that facilitates the growth and metastasis of neoplastic lesions. Am J Pathol 184:28–41
Becker A, Thakur BK, Weiss JM, Kim HS, Peinado H, Lyden D (2016) Extracellular vesicles in cancer: cell-to-cell mediators of metastasis. Cancer Cell 30:836–848
Zappulli V, Friis KP, Fitzpatrick Z, Maguire CA, Breakefield XO (2016) Extracellular vesicles and intercellular communication within the nervous system. J Clin Invest 126:1198–1207
Leclerc D, Pham DN, Levesque N, Truongcao M, Foulkes WD, Sapienza C, Rozen R (2017) Oncogenic role of PDK4 in human colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer 116:930–936
Zhao Y, Yan X, Li X, Zheng Y, Li S, Chang X (2016) PGK1, a glucose metabolism enzyme, may play an important role in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res 65:815–825
Tanaka Y, Ohira T (2018) Mechanisms and therapeutic targets for bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis, in particular the RANK-RANKL system. Curr Opin Pharmacol 40:110–119
Remuzgo-Martinez S, Genre F, Lopez-Mejias R et al (2016) Expression of osteoprotegerin and its ligands, RANKL and TRAIL, in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep 6:29713
Broeren MG, de Vries M, Bennink MB, Arntz OJ, Blom AB, Koenders MI, van Lent P, van der Kraan P, van den Berg W, van de Loo F (2016) Disease-regulated gene therapy with anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 under the control of the CXCL10 promoter for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Gene Ther 27:244–254
Kang K, Park SH, Chen J et al (2017) Interferon-gamma represses M2 gene expression in human macrophages by disassembling enhancers bound by the transcription factor MAF. Immunity 47(235–250):e234
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy--analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20:307–315
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3:Article3
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A, Tsafou KP, Kuhn M, Bork P, Jensen LJ, von Mering C (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D447–D452
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Menard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovsky J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Hou C, Meng F, Zhang Z, Kang Y, Chen W, Huang G, Fu M, Sheng P, Zhang Z, Liao W (2015) The role of microRNA-381 in chondrogenesis and interleukin-1-beta induced chondrocyte responses. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:1753–1766
Wade SM, Trenkmann M, McGarry T, Canavan M, Marzaioli V, Wade SC, Veale DJ, Fearon U (2019) Altered expression of microRNA-23a in psoriatic arthritis modulates synovial fibroblast pro-inflammatory mechanisms via phosphodiesterase 4B. J Autoimmun 96:86–93
Rojo AI, Medina-Campos ON, Rada P, Zuniga-Toala A, Lopez-Gazcon A, Espada S, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Cuadrado A (2012) Signaling pathways activated by the phytochemical nordihydroguaiaretic acid contribute to a Keap1-independent regulation of Nrf2 stability: role of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Free Radic Biol Med 52:473–487
Zhang H, Huang Y, Wang S, Fu R, Guo C, Wang H, Zhao J, Gaskin F, Chen J, Yang N, Fu SM (2015) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells contribute to bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis by differentiating to osteoclasts. J Autoimmun 65:82–89
Yang XH, Ren LS, Wang GP, Zhao LL, Zhang H, Mi ZG, Bai X (2012) A new method of establishing orthotopic bladder transplantable tumor in mice. Cancer Biol Med 9:261–265
Camps M, Ruckle T, Ji H, Ardissone V, Rintelen F, Shaw J, Ferrandi C, Chabert C, Gillieron C, Francon B, Martin T, Gretener D, Perrin D, Leroy D, Vitte PA, Hirsch E, Wymann MP, Cirillo R, Schwarz MK, Rommel C (2005) Blockade of PI3Kgamma suppresses joint inflammation and damage in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med 11:936–943
Wang H, Zhao J, Zhang H, Huang Y, Wang S, Tu Q, Yang N (2014) CARD11 blockade suppresses murine collagen-induced arthritis via inhibiting CARD11/Bcl10 assembly and T helper type 17 response. Clin Exp Immunol 176:238–245
Zhou R, Zhu F, Wu X, Song S, Chen Y, Zhu C, Dai B, Qian X, Wang K, Hu W, Chen F (2019) Effects of autophagy on apoptosis of articular chondrocytes in adjuvant arthritis rats. J Cell Mol Med 23:7879–7884
Larson-Casey JL, Deshane JS, Ryan AJ, Thannickal VJ, Carter AB (2016) Macrophage Akt1 kinase-mediated mitophagy modulates apoptosis resistance and pulmonary fibrosis. Immunity 44:582–596
Pandya JM, Lundell AC, Andersson K, Nordstrom I, Theander E, Rudin A (2017) Blood chemokine profile in untreated early rheumatoid arthritis: CXCL10 as a disease activity marker. Arthritis Res Ther 19:20
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858
Filkova M, Jungel A, Gay RE, Gay S (2012) MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: potential role in diagnosis and therapy. BioDrugs 26:131–141
Song YJ, Li G, He JH, Guo Y, Yang L (2015) Bioinformatics-based identification of microRNA-regulated and rheumatoid arthritis-associated genes. PLoS One 10:e0137551
Garcia-Carbonell R, Divakaruni AS, Lodi A, Vicente-Suarez I, Saha A, Cheroutre H, Boss GR, Tiziani S, Murphy AN, Guma M (2016) Critical role of glucose metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:1614–1626
Attia RR, Connnaughton S, Boone LR, Wang F, Elam MB, Ness GC, Cook GA, Park EA (2010) Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) by thyroid hormone: role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator (PGC-1 alpha). J Biol Chem 285:2375–2385
Kwon HS, Harris RA (2004) Mechanisms responsible for regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 gene expression. Adv Enzym Regul 44:109–121
Ferland A, Eckel RH (2011) Does sustained weight loss reverse the metabolic syndrome? Curr Hypertens Rep 13:456–464
Wang Y, Liu W, Masuyama R, Fukuyama R, Ito M, Zhang Q, Komori H, Murakami T, Moriishi T, Miyazaki T, Kitazawa R, Yoshida CA, Kawai Y, Izumi S, Komori T (2012) Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 induces bone loss at unloading by promoting osteoclastogenesis. Bone 50:409–419
Chen Z, Wang H, Xia Y, Yan F, Lu Y (2018) Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cell-derived miRNA-150-5p-expressing exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis mediated by the modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol 201:2472–2482
Cosenza S, Ruiz M, Maumus M, Jorgensen C, Noel D (2017) Pathogenic or Therapeutic Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatic Diseases: Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci:18
Chan SH, Wang LH (2015) Regulation of cancer metastasis by microRNAs. J Biomed Sci 22:9
Xia Y, Darling EM, Herzog W (2018) Functional properties of chondrocytes and articular cartilage using optical imaging to scanning probe microscopy. J Orthop Res 36:620–631
Zhou Y, Li S, Chen P, Yang B, Yang J, Liu R, Li J, Xia D (2019) MicroRNA-27b-3p inhibits apoptosis of chondrocyte in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting HIPK2. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:1766–1771
Jiang L, Cao S (2020) Role of microRNA-26a in cartilage injury and chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis rats by regulating expression of CTGF. J Cell Physiol 235:979–992
Zhang J, Ren J, Chen H, Geng Q (2014) Inflammation induced-endothelial cells release angiogenesis associated-microRNAs into circulation by microparticles. Chin Med J 127:2212–2217
Fernandes JG, Borrego A, Jensen JR et al (2018) miRNA expression and interaction with genes involved in susceptibility to pristane-induced arthritis. J Immunol Res 2018:1928405
Feng X, Lv C, Wang F, Gan K, Zhang M, Tan W (2013) Modulatory effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 on IL1 beta -induced RANKL, OPG, TNF alpha , and IL-6 expression in human rheumatoid synoviocyte MH7A. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:160123
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge and appreciate our colleagues for their valuable efforts and comments on this paper.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81302576 and No. 81402936), Six Talent Peak Research Project in Jiangsu Province (No. 2015-WSN-105), the 333 Project of Jiangsu Province, Jiangsu Province Youth Medical Talent Project (No. QNRC2016348), Key Talents of Science and Education in Yangzhou City in 13th Five-Year (No. ZDRC201881), and Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. BK20131234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DL, YXF, YJR, WT, WZ, and XW designed the study. DL, YXF, CWZ, YZ, YQL, and MS collated the data, carried out data analyses, and produced the initial draft of the manuscript. YJR, TH, and GQL contributed in drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was conducted with the approval of the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University. All participating patients signed written informed consent documentation prior to enrollment into the study. The animal experiment protocol was approved by the medical ethics committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University and strictly adhered to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institutes of Health to minimize the usage, suffering, and discomfort to experimental animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PNG 385 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Fang, Y., Rao, Y. et al. Synovial fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-106b suppresses chondrocyte proliferation and migration in rheumatoid arthritis via down-regulation of PDK4. J Mol Med 98, 409–423 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01882-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01882-2