Abstract
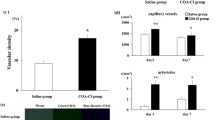
BPC 157, a pentadecapeptide with extensive healing effects, has recently been suggested to contribute to angiogenesis. However, the underlying mechanism is not yet clear. The present study aimed to explore the potential therapeutic effect and pro-angiogenic mechanism of BPC 157. As demonstrated by the chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay and endothelial tube formation assay, BPC 157 could increase the vessel density both in vivo and in vitro, respectively. BPC 157 could also accelerate the recovery of blood flow in the ischemic muscle of the rat hind limb as detected by laser Doppler scanning, indicating the promotion of angiogenesis. Histological analysis of the hind limb muscle confirmed the increased number of vessels and the enhanced vascular expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) in rat with BPC 157 treatment. In vitro study using human vascular endothelial cells further confirmed the increased mRNA and protein expressions of VEGFR2 but not VEGF-A by BPC 157. In addition, BPC 157 could promote VEGFR2 internalization in vascular endothelial cells which was blocked in the presence of dynasore, an inhibitor of endocytosis. BPC 157 time dependently activated the VEGFR2-Akt-eNOS signaling pathway which could also be suppressed by dynasore. The increase of endothelial tube formation induced by BPC 157 was also inhibited by dynasore. This study demonstrates the pro-angiogenic effects of BPC 157 that is associated with the increased expression, internalization of VEGFR2, and the activation of VEGFR2-Akt-eNOS signaling pathway. BPC 157 promotes angiogenesis in CAM assay and tube formation assay. BPC 157 accelerates the blood flow recovery and vessel number in rats with hind limb ischemia. BPC 157 up-regulates VEGFR2 expression in rats with hind limb ischemia and endothelial cell culture. BPC 157 promotes VEGFR2 internalization in association with VEGFR2-Akt-eNOS activation.
Key message
-
BPC 157 promotes angiogenesis in CAM assay and tube formation assay.
-
BPC 157 accelerates the blood flow recovery and vessel number in rats with hind limb ischemia.
-
BPC 157 up-regulates VEGFR2 expression in rats with hind limb ischemia and endothelial cell culture.
-
BPC 157 promotes VEGFR2 internalization in association with VEGFR2-Akt-eNOS activation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seiwerth S, Sikiric P, Grabarevic Z, Zoricic I, Hanzevacki M, Ljubanovic D, Coric V, Konjevoda P, Petek M, Rucman R et al (1997) BPC 157’s effect on healing. J Physiol Paris 91:173–178
Sikiric P, Petek M, Rucman R, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z, Rotkvic I, Turkovic B, Jagic V, Mildner B, Duvnjak M et al (1993) A new gastric juice peptide, BPC. An overview of the stomach-stress-organoprotection hypothesis and beneficial effects of BPC. J Physiol Paris 87:313–327
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Brcic L, Sever M, Klicek R, Radic B, Drmic D, Ilic S, Kolenc D (2010) Revised Robert’s cytoprotection and adaptive cytoprotection and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Possible significance and implications for novel mediator. Curr Pharm Des 16:1224–1234
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R, Turkovic B, Rokotov DS, Brcic L, Sever M, Klicek R, Radic B, Drmic D et al (2014) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157-NO-system relation. Curr Pharm Des 20:1126–1135
Seiwerth S, Brcic L, Vuletic LB, Kolenc D, Aralica G, Misic M, Zenko A, Drmic D, Rucman R, Sikiric P (2014) BPC 157 and blood vessels. Curr Pharm Des 20:1121–1125
Shibuya M (2011) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) signaling in angiogenesis: a crucial target for anti- and pro-angiogenic therapies. Genes Cancer 2:1097–1105
Zhang X, Lanahan AA, Simons M (2013) VEGFR2 trafficking: speed doesn’t kill. Cell Cycle 12:2163–2164
Jopling HM, Odell AF, Pellet-Many C, Latham AM, Frankel P, Sivaprasadarao A, Walker JH, Zachary IC, Ponnambalam S (2014) Endosome-to-plasma membrane recycling of VEGFR2 receptor tyrosine kinase regulates endothelial function and blood vessel formation. Cells 3:363–385
Ji Y, Chen S, Li K, Xiao X, Xu T, Zheng S (2014) Upregulated autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor-2 loop prevents apoptosis in haemangioma-derived endothelial cells. Br J Dermatol 170:78–86
Ruan L, Wang B, ZhuGe Q, Jin K (2015) Coupling of neurogenesis and angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Brain Res 1623:166–173
Holfeld J, Tepekoylu C, Blunder S, Lobenwein D, Kirchmair E, Dietl M, Kozaryn R, Lener D, Theurl M, Paulus P et al (2014) Low energy shock wave therapy induces angiogenesis in acute hind-limb ischemia via VEGF receptor 2 phosphorylation. PLoS One 9:e103982. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103982
Chiang KC, Sun CC, Chen MH, Huang CY, Hsu JT, Yeh TS, Chen LW, Kuo SF, Juang HH, Takano M et al (2016) MART-10, the new brand of 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 analog, is a potent anti-angiogenic agent in vivo and in vitro. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 155:26–34
Gourlaouen M, Welti JC, Vasudev NS, Reynolds AR (2013) Essential role for endocytosis in the growth factor-stimulated activation of ERK1/2 in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 288:7467–7480
Sikiric P (1999) The pharmacological properties of the novel peptide BPC 157 (PL-10). Inflammopharmacology 7:1–14
Lovric-Bencic M, Sikiric P, Hanzevacki JS, Seiwerth S, Rogic D, Kusec V, Aralica G, Konjevoda P, Batelja L, Blagaic AB (2004) Doxorubicine-congestive heart failure-increased big endothelin-1 plasma concentration: reversal by amlodipine, losartan, and gastric pentadecapeptide BPC157 in rat and mouse. J Pharmacol Sci 95:19–26
Prkacin I, Separovic J, Aralicia G, Perovic D, Gjurasin M, Lovric-Bencic M, Stancic-Rokotov D, Staresinic M, Anic T, Mikus D et al (2001) Portal hypertension and liver lesions in chronically alcohol drinking rats prevented and reversed by stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 (PL-10, PLD-116), and propranolol, but not ranitidine. J Physiol Paris 95:315–324
Chang CH, Tsai WC, Hsu YH, Pang JH (2014) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 enhances the growth hormone receptor expression in tendon fibroblasts. Molecules 19:19066–19077
Sikiric P, Separovic J, Anic T, Buljat G, Mikus D, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z, Stancic-Rokotov D, Pigac B, Hanzevacki M et al (1999) The effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157, H2-blockers, omeprazole and sucralfate on new vessels and new granulation tissue formation. J Physiol Paris 93:479–485
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Brcic L, Blagaic AB, Zoricic I, Sever M, Klicek R, Radic B, Keller N, Sipos K et al (2006) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in trials for inflammatory bowel disease (PL-10, PLD-116, PL 14736, Pliva, Croatia). Full and distended stomach, and vascular response. Inflammopharmacology 14:214–221
Brcic L, Brcic I, Staresinic M, Novinscak T, Sikiric P, Seiwerth S (2009) Modulatory effect of gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on angiogenesis in muscle and tendon healing. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(Suppl 7):191–196
Huang T, Zhang K, Sun L, Xue X, Zhang C, Shu Z, Mu N, Gu J, Zhang W, Wang Y et al (2015) Body protective compound-157 enhances alkali-burn wound healing in vivo and promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro. Drug design, development and therapy 9:2485–2499
Cooke JP, Losordo DW (2015) Modulating the vascular response to limb ischemia: angiogenic and cell therapies. Circ Res 116:1561–1578
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z, Rucman R, Petek M, Jagic V, Turkovic B, Rotkvic I, Mise S, Zoricic I et al (1997) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 positively affects both non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent-induced gastrointestinal lesions and adjuvant arthritis in rats. J Physiol Paris 91:113–122
Keremi B, Lohinai Z, Komora P, Duhaj S, Borsi K, Jobbagy-Ovari G, Kallo K, Szekely AD, Fazekas A, Dobo-Nagy C et al (2009) Antiinflammatory effect of BPC 157 on experimental periodontitis in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(Suppl 7):115–122
Tkalcevic VI, Cuzic S, Brajsa K, Mildner B, Bokulic A, Situm K, Perovic D, Glojnaric I, Parnham MJ (2007) Enhancement by PL 14736 of granulation and collagen organization in healing wounds and the potential role of egr-1 expression. Eur J Pharmacol 570:212–221
Malavaud B, Tack I, Jonca F, Praddaude F, Moro F, Ader JL, Plouet J (1997) Activation of Flk-1/KDR mediates angiogenesis but not hypotension. Cardiovasc Res 36:276–281
Masaki I, Yonemitsu Y, Yamashita A, Sata S, Tanii M, Komori K, Nakagawa K, Hou X, Nagai Y, Hasegawa M et al (2002) Angiogenic gene therapy for experimental critical limb ischemia: acceleration of limb loss by overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 but not of fibroblast growth factor-2. Circ Res 90:966–973
Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, Fahrig M, Vandenhoeck A, Harpal K, Eberhardt C et al (1996) Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature 380:435–439
Henry TD, Annex BH, McKendall GR, Azrin MA, Lopez JJ, Giordano FJ, Shah PK, Willerson JT, Benza RL, Berman DS et al (2003) The VIVA trial: vascular endothelial growth factor in ischemia for vascular angiogenesis. Circulation 107:1359–1365
Yasumura EG, Stilhano RS, Samoto VY, Matsumoto PK, de Carvalho LP, Valero Lapchik VB, Han SW (2012) Treatment of mouse limb ischemia with an integrative hypoxia-responsive vector expressing the vascular endothelial growth factor gene. PLoS One 7:e33944. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033944
Lederman RJ, Mendelsohn FO, Anderson RD, Saucedo JF, Tenaglia AN, Hermiller JB, Hillegass WB, Rocha-Singh K, Moon TE, Whitehouse MJ et al (2002) Therapeutic angiogenesis with recombinant fibroblast growth factor-2 for intermittent claudication (the TRAFFIC study): a randomised trial. Lancet 359:2053–2058
Belch J, Hiatt WR, Baumgartner I, Driver IV, Nikol S, Norgren L, Van Belle E, Committees T, Investigators (2011) Effect of fibroblast growth factor NV1FGF on amputation and death: a randomised placebo-controlled trial of gene therapy in critical limb ischaemia. Lancet 377:1929–1937
Creager MA, Olin JW, Belch JJ, Moneta GL, Henry TD, Rajagopalan S, Annex BH, Hiatt WR (2011) Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha gene therapy on walking performance in patients with intermittent claudication. Circulation 124:1765–1773
Willmann JK, Chen K, Wang H, Paulmurugan R, Rollins M, Cai W, Wang DS, Chen IY, Gheysens O, Rodriguez-Porcel M et al (2008) Monitoring of the biological response to murine hindlimb ischemia with 64Cu-labeled vascular endothelial growth factor-121 positron emission tomography. Circulation 117:915–922
Dokun AO, Chen L, Lanjewar SS, Lye RJ, Annex BH (2014) Glycaemic control improves perfusion recovery and VEGFR2 protein expression in diabetic mice following experimental PAD. Cardiovasc Res 101:364–372
Imoukhuede PI, Dokun AO, Annex BH, Popel AS (2013) Endothelial cell-by-cell profiling reveals the temporal dynamics of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 membrane localization after murine hindlimb ischemia. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 304:H1085–H1093
Wu FT, Stefanini MO, Mac Gabhann F, Kontos CD, Annex BH, Popel AS (2010) VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor-1 (sFlt-1) distributions in peripheral arterial disease: an in silico model. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 298:H2174–H2191
Wieczor R, Gadomska G, Ruszkowska-Ciastek B, Stankowska K, Budzynski J, Fabisiak J, Suppan K, Pulkowski G, Rosc D (2015) Impact of type 2 diabetes on the plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and its soluble receptors type 1 and type 2 in patients with peripheral arterial disease. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 16:948–956
Jin ZG, Ueba H, Tanimoto T, Lungu AO, Frame MD, Berk BC (2003) Ligand-independent activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by fluid shear stress regulates activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circ Res 93:354–363
Shi F, Wang YC, Zhao TZ, Zhang S, Du TY, Yang CB, Li YH, Sun XQ (2012) Effects of simulated microgravity on human umbilical vein endothelial cell angiogenesis and role of the PI3K-Akt-eNOS signal pathway. PLoS One 7:e40365. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040365
Philippova M, Joshi MB, Pfaff D, Kyriakakis E, Maslova K, Erne P, Resink TJ (2012) T-cadherin attenuates insulin-dependent signalling, eNOS activation, and angiogenesis in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 93:498–507
Jeltsch M, Leppanen VM, Saharinen P, Alitalo K (2013) Receptor tyrosine kinase-mediated angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009183
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital [Grants CMRPD1A0531, CMRPD1C0231, CMRPG391311, CMRPG3A1131] and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan [Grant NMRPD181001-3].
Author contributions
Authors responsible for concept and design were MJH, HTL, HYH, YL, and JHSP. Experimental performance: MJH, HTL, HYH, and YL. Technical supports: CNW, YSK, VHSC, and JSW. MJH, HTL, and JHSP were responsible in the analysis and interpretation of data. MJH and JHSP drafted the manuscript. MJH and HTL contribute to this work equally.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures complied with the standards for care and use of animal subjects as stated in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Institute of Laboratory Resources, National Academy of Sciences, Bethesda, MD). The protocols in our animal studies were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Chang Gung University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, MJ., Liu, HT., Wang, CN. et al. Therapeutic potential of pro-angiogenic BPC157 is associated with VEGFR2 activation and up-regulation. J Mol Med 95, 323–333 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1488-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1488-y