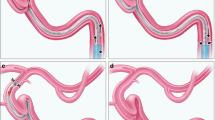
Abstract
Background
Endovascular techniques for treatment of large vessel occlusions (LVO) in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) have advanced in recent years. We report a multicenter experience using a combined aspiration and stent retriever technique for mechanical thrombectomy (MT).
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 32 consecutive MT patients using a novel, combined approach of Stent retriever Assisted Vacuum-locked Extraction (SAVE) by 3 operators at 3 stroke centers. Primary endpoint was successful first-pass reperfusion with a modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (mTICI) score of 3. Secondary endpoints were number of passes, time from groin puncture to reperfusion, embolization to new territories (ENT), postinterventional symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) and clinical outcome at discharge.
Results
First-pass mTICI 3 reperfusion was achieved in 23 out of 32 patients (72%) with a mean groin puncture to reperfusion time of 36.0 min ± 15.8 and mTICI 3 was accomplished in 25 out of 32 cases (78%) with a maximum of 3 attempts. Successful reperfusion (mTICI ≥ 2b) was achieved in all patients (100%) with a mean time from groin puncture to reperfusion of 44.5 min ± 25.8 and an average of 1.2 ± 0.7 attempts. The rate of ENT was 0% and 1 patient with sICH after MT died on postoperative day 4. At discharge, the median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score was 4 (range 0−17) and favorable neurological outcome by the modified Rankin score (mRS ≤ 2) was achieved in 19 out of 32 patients (59%).
Conclusion
SAVE is fast and appears to be very effective in terms of first-pass complete reperfusion in patients with LVO.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, Schonewille WJ, Vos JA, Nederkoorn PJ, Wermer MJ, van Walderveen MA, Staals J, Hofmeijer J, van Oostayen JA, Lycklama à Nijeholt GJ, Boiten J, Brouwer PA, Emmer BJ, de Bruijn SF, van Dijk LC, Kappelle LJ, Lo RH, van Dijk EJ, de Vries J, de Kort PL, van Rooij WJ, van den Berg JS, van Hasselt BA, Aerden LA, Dallinga RJ, Visser MC, Bot JC, Vroomen PC, Eshghi O, Schreuder TH, Heijboer RJ, Keizer K, Tielbeek AV, den Hertog HM, Gerrits DG, van den Berg-Vos RM, Karas GB, Steyerberg EW, Flach HZ, Marquering HA, Sprengers ME, Jenniskens SF, Beenen LF, van den Berg R, Koudstaal PJ, van Zwam WH, Roos YB, van der Lugt A, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Majoie CB, Dippel DW; MR CLEAN Investigators. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:11–20.
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL, Dowlatshahi D, Frei DF, Kamal NR, Montanera WJ, Poppe AY, Ryckborst KJ, Silver FL, Shuaib A, Tampieri D, Williams D, Bang OY, Baxter BW, Burns PA, Choe H, Heo JH, Holmstedt CA, Jankowitz B, Kelly M, Linares G, Mandzia JL, Shankar J, Sohn SI, Swartz RH, Barber PA, Coutts SB, Smith EE, Morrish WF, Weill A, Subramaniam S, Mitha AP, Wong JH, Lowerison MW, Sajobi TT, Hill MD; ESCAPE Trial Investigators. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1019–30.
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Albers GW, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W, Jansen O, Jovin TG, Mattle HP, Nogueira RG, Siddiqui AH, Yavagal DR, Baxter BW, Devlin TG, Lopes DK, Reddy VK, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Singer OC, Jahan R; SWIFT PRIME Investigators. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t‑PA vs. t‑PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2285–95.
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, Yan B, Dowling RJ, Parsons MW, Oxley TJ, Wu TY, Brooks M, Simpson MA, Miteff F, Levi CR, Krause M, Harrington TJ, Faulder KC, Steinfort BS, Priglinger M, Ang T, Scroop R, Barber PA, McGuinness B, Wijeratne T, Phan TG, Chong W, Chandra RV, Bladin CF, Badve M, Rice H, de Villiers L, Ma H, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM; EXTEND-IA Investigators. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1009–18.
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, San Román L, Serena J, Abilleira S, Ribó M, Millán M, Urra X, Cardona P, López-Cancio E, Tomasello A, Castaño C, Blasco J, Aja L, Dorado L, Quesada H, Rubiera M, Hernandez-Pérez M, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, von Kummer R, Gallofré M, Dávalos A; REVASCAT Trial Investigators. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2296–306.
Rha JH, Saver JL. The impact of recanalization on ischemic stroke outcome: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 2007;38:967–73.
Deshaies EM. Tri-axial system using the solitaire-FR and penumbra aspiration microcatheter for acute mechanical thrombectomy. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20:1303–5.
Humphries W, Hoit D, Doss VT, Elijovich L, Frei D, Loy D, Dooley G, Turk AS, Chaudry I, Turner R, Mocco J, Morone P, Fiorella D, Siddiqui A, Mokin M, Arthur AS. Distal aspiration with retrievable stent assisted thrombectomy for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7:90–4.
Turk AS, Spiotta A, Frei D, Mocco J, Baxter B, Fiorella D, Siddiqui A, Mokin M, Dewan M, Woo H, Turner R, Hawk H, Miranpuri A, Chaudry I. Initial clinical experience with the ADAPT technique: a direct aspiration first pass technique for stroke thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;6:231–7.
Kabbasch C, Möhlenbruch M, Stampfl S, Mpotsaris A, Behme D, Liebig T. First-line lesional aspiration in acute stroke thrombectomy using a novel intermediate catheter: Initial experiences with the SOFIA. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016;22:333–9.
Wiesmann M, Brockmann MA, Heringer S, Müller M, Reich A, Nikoubashman O. Active push deployment technique improves stent/vessel-wall interaction in endovascular treatment of acute stroke with stent retrievers. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Mar 14. [Epub ahead of print]
Nikoubashman O, Alt JP, Nikoubashman A, Büsen M, Heringer S, Brockmann C, Brockmann MA, Müller M, Reich A, Wiesmann M. Optimizing endovascular stroke treatment: removing the microcatheter before clot retrieval with stent-retrievers increases aspiration flow. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Apr 15. [Epub ahead of print]
Massari F, Henninger N, Lozano JD, Patel A, Kuhn AL, Howk M, Perras M, Brooks C, Gounis MJ, Kan P, Wakhloo AK, Puri AS. ARTS (Aspiration-Retriever Technique for Stroke): Initial clinical experience. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016;22:325–32.
Turk AS, Frei D, Fiorella D, Mocco J, Baxter B, Siddiqui A, Spiotta A, Mokin M, Dewan M, Quarfordt S, Battenhouse H, Turner R, Chaudry I. ADAPT FAST study: a direct aspiration first pass technique for acute stroke thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;6:260–4.
Kowoll A, Weber A, Mpotsaris A, Behme D, Weber W. Direct aspiration first pass technique for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: initial experience at a European stroke center. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016;8:230–4.
Nguyen TN, Malisch T, Castonguay AC, Gupta R, Sun CH, Martin CO, Holloway WE, Mueller-Kronast N, English JD, Linfante I, Dabus G, Marden FA, Bozorgchami H, Xavier A, Rai AT, Froehler MT, Badruddin A, Taqi M, Abraham MG, Janardhan V, Shaltoni H, Novakovic R, Yoo AJ, Abou-Chebl A, Chen PR, Britz GW, Kaushal R, Nanda A, Issa MA, Masoud H, Nogueira RG, Norbash AM, Zaidat OO. Balloon guide catheter improves revascularization and clinical outcomes with the Solitaire device: analysis of the North American Solitaire Acute Stroke Registry. Stroke. 2014;45:141–5.
Lee JS, Hong JM, Lee SJ, Joo IS, Lim YC, Kim SY. The combined use of mechanical thrombectomy devices is feasible for treating acute carotid terminus occlusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013;155:635–41.
Dippel DW, Majoie CB, Roos YB, van der Lugt A, van Oostenbrugge RJ, van Zwam WH, Lingsma HF, Koudstaal PJ, Treurniet KM, van den Berg LA, Beumer D, Fransen PS, Berkhemer OA; MR CLEAN Investigators. Influence of device choice on the effect of intra-arterial treatment for acute Ischemic stroke in MR CLEAN (Multicenter randomized clinical trial of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke in the Netherlands). Stroke. 2016;47:2574–81.
Zaidat OO, Castonguay AC, Gupta R, Sun CH, Martin C, Holloway WE, Mueller-Kronast N, English JD, Linfante I, Dabus G, Malisch TW, Marden FA, Bozorgchami H, Xavier A, Rai AT, Froehler MT, Badruddin A, Nguyen TN, Taqi MA, Abraham MG, Janardhan V, Shaltoni H, Novakovic R, Yoo AJ, Abou-Chebl A, Chen PR, Britz GW, Kaushal R, Nanda A, Issa MA, Nogueira RG. North American Solitaire Stent Retriever Acute Stroke registry: post-marketing revascularization and clinical outcome results. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;6:584–8.
Delgado Almandoz JE, Kayan Y, Young ML, Fease JL, Scholz JM, Milner AM, Hehr TH, Roohani P, Mulder M, Tarrel RM. Comparison of clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischemic strokes treated with mechanical thrombectomy using either Solumbra or ADAPT techniques. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;8:1123–8.
Turk AS, Turner R, Spiotta A, Vargas J, Holmstedt C, Ozark S, Chalela J, Turan T, Adams R, Jauch EC, Battenhouse H, Whitsitt B, Wain M, Chaudry MI. Comparison of endovascular treatment approaches for acute ischemic stroke: cost effectiveness, technical success, and clinical outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7:666–70.
Vargas J, Spiotta A, Fargen K, Turner R, Chaudry I, Turk A. Long term experience using the ADAPT technique for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Apr 18. [Epub ahead of print]
Möhlenbruch MA, Kabbasch C, Kowoll A, Broussalis E, Sonnberger M, Müller M, Wiesmann M, Trenkler J, Killer-Oberpfalzer M, Weber W, Mpotsaris A, Bendszus M, Stampfl S. Multicenter experience with the new SOFIA Plus catheter as a primary local aspiration catheter for acute stroke thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Dec 20. [Epub ahead of print]
Velasco A, Buerke B, Stracke CP, Berkemeyer S, Mosimann PJ, Schwindt W, Alcázar P, Cnyrim C, Niederstadt T, Chapot R, Heindel W. Comparison of a balloon guide catheter and a non-balloon guide catheter for mechanical thrombectomy. Radiology. 2016;280:169–76.
Mocco J, Zaidat OO, von Kummer R, Yoo AJ, Gupta R, Lopes D, Frei D, Shownkeen H, Budzik R, Ajani ZA, Grossman A, Altschul D, McDougall C, Blake L, Fitzsimmons BF, Yavagal D, Terry J, Farkas J, Lee SK, Baxter B, Wiesmann M, Knauth M, Heck D, Hussain S, Chiu D, Alexander MJ, Malisch T, Kirmani J, Miskolczi L, Khatri P; THERAPY Trial Investigators*. Aspiration thrombectomy after intravenous alteplase versus intravenous alteplase alone. Stroke. 2016;47:2331–8.
Haussen DC, Rebello LC, Nogueira RG. Optimizating clot retrieval in acute stroke: the push and fluff technique for closed-cell stentrievers. Stroke. 2015;46:2838–42.
Nogueira RG, Lutsep HL, Gupta R, Jovin TG, Albers GW, Walker GA, Liebeskind DS, Smith WS; TREVO 2 Trialists. Trevo versus Merci retrievers for thrombectomy revascularisation of large vessel occlusions in acute ischaemic stroke (TREVO 2): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2012;380:1231–40.
Pereira VM, Gralla J, Davalos A, Bonafé A, Castaño C, Chapot R, Liebeskind DS, Nogueira RG, Arnold M, Sztajzel R, Liebig T, Goyal M, Besselmann M, Moreno A, Schroth G. Prospective, multicenter, single-arm study of mechanical thrombectomy using solitaire flow restoration in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2013;44:2802–7.
Almekhlafi MA, Menon BK, Freiheit EA, Demchuk AM, Goyal M. A meta-analysis of observational intra-arterial stroke therapy studies using the Merci device, Penumbra system, and retrievable stents. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:140–5.
Bracard S, Ducrocq X, Mas JL et al. Mechanical thrombectomy after intravenous alteplase versus alteplase alone after stroke (THRACE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2016;15:1138–47.
Broderick JP, Palesch YY, Demchuk AM et al. Endovascular therapy after intravenous t-PA versus t-PA alone for stroke. N Engl J Med 2013;368:893–903.
Saver JL, Jahan R, Levy EI, Jovin TG, Baxter B, Nogueira RG, Clark W, Budzik R, Zaidat OO; SWIFT Trialists. Solitaire flow restoration device versus the Merci retriever in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (SWIFT): a randomised, parallel-group, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2012;380:1241–9.
Singer OC, Berkefeld J, Nolte CH et al. Mechanical recanalization in basilar artery occlusion: the ENDOSTROKE study. ANN NEUROL 2015;77:415–424.
McTaggart RA, Tung EL, Yaghi S, Cutting SM, Hemendinger M, Gale HI, Baird GL, Haas RA, Jayaraman MV. Continuous aspiration prior to intracranial vascular embolectomy (CAPTIVE): a technique which improves outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Dec 16. [Epub ahead of print]
Brinjikji W, Rabinstein AA, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ. Patient outcomes with endovascular embolectomy therapy for acute ischemic stroke: a study of the national inpatient sample: 2006 to 2008. Stroke. 2011;42:1648–52.
Zhu W, Xiao L, Lin M, Liu X, Yan B. Large-vessel occlusion is associated with poor outcome in stroke patients aged 80 years or older who underwent intravenous thrombolysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25:2712–6.
Sauer EM, Sauer R, Kallmunzer B, Blinzler C, Breuer L, Huttner HB, Schwab S, Köhrmann M. Impaired renal function in stroke patients with atrial fibrillation. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23:1225–8.
Chueh JY, Puri AS, Wakhloo AK, Gounis MJ. Risk of distal embolization with stent retriever thrombectomy and ADAPT. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016;8:197–202.
Chueh JY, Kühn AL, Puri AS, Wilson SD, Wakhloo AK, Gounis MJ. Reduction in distal emboli with proximal flow control during mechanical thrombectomy: a quantitative in vitro study. Stroke. 2013;44:1396–401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
V. Maus reports minor travel grants from Stryker Neurovascular. D. Behme reports minor travel grants from Stryker Neurovascular. C. Kabbasch reports minor travel grants from Stryker Neurovascular. J. Borggrefe has nothing to disclose. I. Tsogkas has nothing to disclose. O. Nikoubashman has nothing to disclose. M. Wiesmann reports grants and personal fees from Stryker Neurovascular, non-financial support from Covidien, non-financial support from Penumbra, non-financial support from Microvention/Terumo. M. Knauth has nothing to disclose. A. Mpotsaris reports personal fees for consultancy from Neuravi and Penumbra. M.N. Psychogios has nothing to disclose.
Ethical standards
According to the guidelines of the respective local ethics committees, no approval was necessary for this anonymous study, which was conducted in accordance to the Declaration of Helsinki (in its current revised form). Due to the retrospective nature of the study informed consent from participants was deemed unnecessary. Consent was obtained from any patients identifiable from images or other information in the manuscript.
Additional information
A. Mpotsaris and M.N. Psychogios contributed equally.
Caption Electronic Supplementary Material
Illustrative video case of SAVE technique
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maus, V., Behme, D., Kabbasch, C. et al. Maximizing First-Pass Complete Reperfusion with SAVE. Clin Neuroradiol 28, 327–338 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0566-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0566-z