Abstract
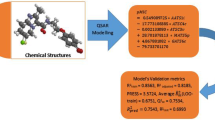
Designing compounds having good anti-tubercular activity is gaining much importance in the area of tuberculosis research due to the reemergence of antibiotic resistance strains. In this study, quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) of a group of 55 anti-tubercular agents with varying structures and potencies, CoMFA, Topomer CoMFA, and HQSAR studies have been performed on a series of antimycobacterial pyrroles. A training set containing 46 compounds served to establish the model and CoMFA was assessed by r 2 value of 0.852 and cross-validated the q 2 value of 0.614. In the Topomer CoMFA, r 2 was 0.805, whole cross-validated q 2 was 0.535. The predictive ability of CoMFA and Topomer CoMFA models was determined using a test set of 9 compounds, which gave the predictive correlation coefficients (r 2pred ) of 0.623 and 0.458, respectively. HQSAR was also carried out as a complementary study, and the best HQSAR model was generated using atoms, bond, connectivity, and hydrogen atoms as fragment distinction, 7–10 as fragment size and three components showing the cross-validated q 2 value of 0.710 and conventional r 2 value of 0.795. CoMFA, Topomer CoMFA steric, electrostatic, and HQSAR atomic contribution maps were generated to analyze the structural features of the datasets on that govern their inhibitory potency.
Graphical Abstract
3D and 2D-QSAR studies (CoMFA, Topomer CoMFA, HQSAR) of antimycobacterial pyrroles are described.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Taylor EW (1993) 3-D QSAR for intrinsic activity of 5-HT1 A receptor ligands by the method of comparative molecular field analysis. J Comput Chem 14(2):237–245
Bakkestuen AK, Gundersen LL, Langli G, Liu F, Nolsøe JM (2000) 9-Benzylpurines with inhibitory activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:1207–1210
Baurin N, Vangrevelinghe E, Morin-Allory L, Mérour JY, Renard P, Payard M, Guillaumet G, Marot C (2000) 3D-QSAR CoMFA study on imidazolinergic I2 ligands: a significant model through a combined exploration of structural diversity and methodology. J Med Chem 43:1109–1122
Biava M, Fioravanti R, Porretta GC, Deidda D, Maullu C, Pompei R (1999) New pyrrole derivatives as antimycobacterial agents analogs of BM212. Biorg Med Chem Lett 9:2983–2988
Biava M, Cesare Porretta G, Deidda D, Pompei R, Tafi A, Manetti F (2003) Importance of the thiomorpholine introduction in new pyrrole derivatives as antimycobacterial agents analogues of BM 212 Biorg Med Chem 11:515–520
Bush BL, Nachbar RB Jr (1993) Sample-distance partial least squares: PLS optimized for many variables, with application to CoMFA. J Comput Aided Mol Des 7:587–619
Clark M, Cramer RD III, Jones DM, Patterson DE, Simeroth PE (1990) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 2. Toward its use with 3D-structural databases. Tetrahedron Comput Methodol 3(1):47–59
Coats EA (1998) The CoMFA steroids as a benchmark dataset for development of 3D QSAR methods. Perspect Drug Discov Des 12(13/14):199–213
Cramer RD III (2011) Rethinking 3D-QSAR. J Comput Aided Mol Des 25:197–201
Cramer RD III, Reld G, Berkoff CE (1974) Substructural analysis. A novel approach to the problem of drug design. J Med Chem 17:533–535
Cramer RD III, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988a) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Cramer RD III, Bunce JD, Patterson DE, Frank IE (1988b) Crossvalidation, bootstrapping, and partial least squares compared with multiple regression in conventional QSAR studies. Quant Struct Act Relat 7:18–25 (erratum 1988, 7:91)
Cramer RD III, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1989) Recent advances in comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). Prog Clin Biol Res 291:161–165
Cramer RD III, Clark RD, Patterson DE, Ferguson AM (1996) Bioisosterism as a molecular diversity descriptor: steric fields of single “topomeric” conformers. J Med Chem 39(16):3060–3069
Dabak K, Sezer O, Akar A, Anac O (2003) Synthesis and investigation of tuberculosis inhibition activities of some 1,2,3-triazole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 38:215–218
Daffe M, Draper P (1998) The envelope layers of mycobacteria with reference to their pathogenicity. Adv Microb Physiol 39:131–203. doi:10.1016/S0065-2911(08)60016-8
Dean PM (1993) Molecular similarity. In: Kubunyi H (ed) 3D QSAR in drug design: theory, methods and applications. ESCOM Science Publishers, Leiden, pp 150–172
Dolin PJ, Raviglione MC, Kochi A (1994) Global tuberculosis incidence and mortality during 1990–2000. Bull World Health Organ 72:213–220
Dye C, Scheele S, Dolin P, Pathania V, Raviglione MC (1999) Consensus statement. Global burden of tuberculosis: estimated incidence, prevalence, and mortality by country. WHO Global Surveillance and Monitoring Project. JAMA 282:677–686. doi:10.1001/jama.282.7.677
Hansch C, Leo A (1995) Exploring QSAR. Fundamentals and applications in chemistry and biology. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
Head RD, Smythe ML, Oprea TI, Waller CL, Green SM, Marshall GR (1996) VALIDATE: a new method for the receptor-based prediction of binding affinities of novel ligands. J Am Chem Soc 118:3959–3969
Jackson CJ, Lamb DC, Kelly DE, Kelly SL (2000) Bactericidal and inhibitory effects of azole antifungal compounds on Mycobacterium smegmatis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 192:159–162
Jilek RJ, Cramer RD III (2004) Topomers: a validated protocol for their self-consistent generation. J Chem Inf Comp Sci 44:1221–1227
Joshi SD, Vagdevi HM, Vaidya VP, Gadaginamath GS (2008) Synthesis of new 4-pyrrol-1-yl benzoic acid hydrazide analogs and some derived oxadiazole, triazole and pyrrole ring systems, a novel class of potential antibacterial and antitubercular agents. Eur J Med Chem 43:1989–1996
Joshi SD, More Y, Vagdevi HM, Vaidya VP, Gadaginamath GS, Kulkarni VH (2013) Synthesis of new 4-(2,5-dimethylpyrrol-1-yl)/4-pyrrol-1-yl benzoic acid hydrazide analogs and some derived oxadiazole, triazole and pyrrole ring systems a novel class of potential antibacterial, antifungal and antitubercular agents. Med Chem Res 22:1073–1089
Klimesova V, Zahajska L, Waisser K, Kaustova J, Mollmann U (2004) Synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of 1,2,4-triazole 3-benzylsulfanyl derivatives II. Farmaco 59:279–288
Kucukguzel SG, Oruc EE, Rollas S, Sahin F, Ozbek A (2002) Synthesis, characterisation and biological activity of novel 4-thiazolidinones, 1,3,4-oxadiazoles and some related compounds. Eur J Med Chem 37:197–206
Kuçukguzel I, Kuçukguzel SG, Rollas S, Kiraz M (2001) Some 3-thioxo/alkylthio-1,2,4-triazoles with a substituted thiourea moiety as possible antimycobacterials. Biorg Med Chem Lett 11:1703–1707
Lemmen C, Lengauer T (2000) Computational methods for the structural alignment of molecules. J Comput Aided Mol Des 14:215–232
Lowis DR (1998) HQSAR a new, highly predictive QSAR technique. www.tripos.com/AppNotes/HQSAR/hqsar.html
Mamolo MG, Zampieri D, Falagiani V, Vio L, Banfi E (2003) Synthesis and antifungal activity of (±)-1-(5-aryl-3-pyridin-2-yl-4,5-dihydro-pyrazol-1-yl)-2-imidazol-1-yl-ethanone derivatives. II Farmaco 58:315–322
Na YM, Le Borgne M, Pagniez F, Le Baut G, Le Pape P (2003) Synthesis and antifungal activity of new 1-halogenobenzyl-3-imidazolylmethylindole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 38:75–87
Sanna P, Carta A, Nikookar ME (2000) Synthesis and antitubercular activity of 3-aryl substituted-2-[1H(2H)benzotriazol-1(2)-yl]acrylonitriles. Eur J Med Chem 35:535–543
Sbardella G, Mai A, Artico M, Loddo R, Setzu MG, La Colla P (2004) Synthesis and in vitro antimycobacterial activity of novel 3-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)-2-oxazolidinone analogues of PNU-100480. Biorg Med Chem Lett 14:1537–1541
Somu RV, Boshoff H, Qiao C, Bennett EM, Barry CE 3rd, Aldrich CC (2006) Antitubercular nucleosides that inhibit siderophore biosynthesis: SAR of the glycosyl domain. J Med Chem 49:31–34
Testa B, Carrupt PA, Gaillard P, Tasai RS (1997) Intra molecular interactions encoded in lipophilicity. In: Pliska V, Testa B, Van der Waterbeemd H (eds) Lipophilicity in drug action and toxicology. Wiley, Weinheim, p 49
Tirado-Rives J, Jorgensen W (2006) Contribution of conformer focusing on the uncertainty in predicting free energies for protein-ligand binding. J Med Chem 49:5880–5884
Tong W, Lowis DR, Perkins R, Chen Y, Welsh WJ, Goddette DW, Hetitage TW, Sheehan DM (1998) Evaluation of quantitative structure–activity relationship methods for large-scale prediction of chemicals binding to the estrogen descriptor. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 38:669–677
Tripos International (2012) Sybyl-X 2.0, Tripos International, St. Louis, MO
Ulusoy N, Gursoy A, Otuk G (2001) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some 1,2,4-triazole-3-mercaptoacetic acid derivatives. II Farmaco 56:947–952
Warren GL, Andrews CW, Capelli A-M, Clarke B, Lalonde B, Lambert MH, Lindvall M, Nevins N, Semus SF, Senger S, Tedesco G, Wall ID, Woolven JM, Peishoff CE, Head MS (2006) A critical assessment of docking programs and scoring functions. J Med Chem 49:5912–5931
Zhang Y, Wade MM, Scorpio A, Zhang H, Sun Z (2003) Mode of action of pyrazinamide: disruption of Mycobacterium tuberculosis membrane transport and energetics by pyrazinoic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother 52:790–795
Acknowledgments
We thank research support from the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi (File No. 64/4/2011-BMS, IRIS Cell No. 2010-08710). We also thank Dr. V. H. Kulkarni, Principal, Shri. H. V. Dambal, President, S.E.T’s College of Pharmacy, Dharwad, Karnataka, India, for providing the facilities. The authors are grateful to Mr. S. A. Tiwari for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, S.D., More, U.A., Aminabhavi, T.M. et al. Two- and three-dimensional QSAR studies on a set of antimycobacterial pyrroles: CoMFA, Topomer CoMFA, and HQSAR. Med Chem Res 23, 107–126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0607-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0607-3