Abstract
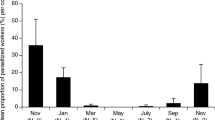
The parasite Xenos moutoni inactivates workers and castrates reproductives of the Japanese hornet Vespa analis. Using over 500 nests, we investigated the relationship between hornet nest size (number of cells) and the proportion of parasitized adults (i.e., prevalence) in central Japan. Over 3 years, 36–48% of nests had more than one parasitized adult, and approximately 3–5% of female adults (mostly workers) and 1–3% of male adults were parasitized within the population. The number of cells did not differ between nests with and without parasitized workers; therefore, the effects of parasite-caused losses within the worker force on nest size appear to be negligible. However, the prevalence of parasitized workers tended to decrease with an increase in the number of cells. Our analysis indicated that the number of parasitized workers was consistently low and did not increase with nest size, resulting in a relatively high prevalence in small nests.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beani L. 2006. Crazy wasps: when parasites manipulate the Polistes phenotype. Annal. Zool. Fennici 43: 564–574
Briano J., Patterson R. and Cordo H. 1995. Relationship between colony size of Solenopsis richteri (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and infection with Thelohania solenopsae (Microsporida: Thelohaniidae) in Argentina. J. Econ. Entomol. 88: 1233–1237
Crawley M.J. 2005. Statistics: An Introduction using R. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester. 342 pp
Hughes D.P., Beani L., Turillazzi S. and Kathirithamby J. 2003. Prevalence of the parasite Strepsiptera in Polistes as detected by dissection of immatures. Insect. Soc. 50: 62–68
Hughes D.P., Pierce N.E. and Boomsma J.J. 2008. Social insect symbionts: evolution in homeostatic fortresses. Trends Ecol. Evol. 23: 672–677
Kathirithamby J. 2009. Host–parasitoid associations in Strepsiptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 54: 227–249
Kifune T. 1992. Detailed localities in records of the Japanese strepsipterans. Trans. Essa Entomol. Soc. Niigata 74: 55–71
Kistner D.H. 1982. The social insects’ bestiary. In: Social Insects. Vol. III (Hermann H.R., Ed). Academic Press, New York. pp 1–244
MacFarlane R.P. and Pengelly D.H. 1974. Conopidae and Sarcophagidae (Diptera) as parasites of adult Bombinae (Hymenoptera) in Ontario. Proc. Entomol. Soc Ontario 105: 55–59
Makino S. 1989. Losses of workers and reproductives in colonies of the paper wasp Polistes riparius (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) due to the parasitic wasp Latibulus sp. Res. Popul. Ecol. 31: 1–10
Makino S. and Yamashita Y. 1998. Levels of parasitism by Xenos moutoni (Strepsiptera, Stylopidae) and their seasonal changes in hornets (Hymenoptera: Vespidae, Vespa) caught with bait traps. Entomol. Sci. 1: 537–543
Makino S. 2001. Seasonal changes in levels of parasitism and sex ratio of Xenos moutoni du Buysson (Strepsiptera, Stylopidae) in the Japanese hornet, Vespa analis insularis Dalla Torre (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) collected with attractant traps. Tijdschr. Entomol. 144: 217–222
Manfredini F., Giusti F., Beani L. and Dallai R. 2007. Developmental strategy of the endoparasite Xenos vesparum (Strepsiptera, Insecta): host invasion and elusion of its defense reactions. J. Morphol. 268: 588–601
Matsuura M. 1973. Colony development of Vespa crabro flavofasciata Cameron in early stage of nesting. Life Study 17: 1–12
Matsuura M. and Yamane S. 1990. Biology of the Vespine Wasps. Springer, Berlin. 323 pp
Matsuura M. 1995. Social Wasps of Japan in Color. Hokkaido University Press, Sapporo. 353 pp
Moore J. 2002. Parasites and the Behavior of Animals. Oxford University Press, New York. 315 pp
Müller C.B. and Schmid-Hempel P. 1992. Correlates of reproductive success among field colonies of Bombus lucorum: the importance of growth and parasites. Ecol. Entomol. 17: 343–353
Sammataro D., Gerson U. and Needham G. 2000. Parasitic mites of honeybees: life history, implications, and impact. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 45: 519–548
Schmid-Hempel P. 1998. Parasites in Social Insects. Princeton University Press, Princeton. 409 pp
Strassmann J.E. 1981. Parasitoids, predators, and group size in the paper wasp, Polistes exclamans. Ecology 62: 1225–1233
Tatsuta H. and Makino S. 2003. Rate of strepsipteran parasitization among overwintered females of the hornet Vespa analis (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Environ. Entomol. 32: 175–179
R Development Core Team 2008. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org
Yamane S. and Makino S. 1977. Bionomics of Vespa analis insularis and V. mandarinia latilineata in Hokkaido, northern Japan, with notes on vespine embryo nests (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Ins. matsum. N. S. 12: 1–33
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank two reviewers for improvement of the manuscript. This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid (No. 20380097) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makino, S., Yamaura, Y. & Yamauchi, H. Smaller nests of the hornet Vespa analis (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) are more severely affected by the strepsipteran parasite Xenos moutoni (Strepsiptera, Stylopidae) than are larger nests. Insect. Soc. 57, 83–90 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-009-0057-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-009-0057-6