Abstract
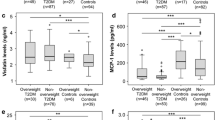
Background: Adiponectin has emerged over the last decade as a key adipokine linking obesity, insulin resistance, and Type 2 diabetes. However, the molecular mechanisms controlling adiponectin expression in adipose tissue are not fully elucidated. Furthermore, increasing evidence indicates that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) plays an important, and beneficial, role in modulating adiponectin expression. Aim: The aim of the present study was to assess the separate role of obesity and Type 2 diabetes in the relationship between endogenous PPAR-γ signaling and adiponectin expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue. Subjects and methods: Enzyme-linked immuno sor bent assay and real time quantitative PCR analysis were carried out in overweight, obese, and/or diabetic Tunisian patients who underwent an abdominal surgery. Results: These results collectively indicate that circulating levels of adiponectin were decreased in all over-weight, obese, and/or diabetic (p<0.001). However, the subcutaneous mRNA expression of adiponectin was reduced only in diabetics (p<0.01) but presents some discrepancies in obese individuals. Moreover, mRNA levels of adiponectin were positively correlated with levels of mRNA encoding PPARγ and its heterodimeric partner retinoid X receptor-α (RXR-α), in both obese and diabetic patients. Conclusion: Our study on Tunisian patients shows impaired regulation of circulating and mRNA adiponectin levels dependent of metabolic disorders in obesity and Type 2 diabetes. The data suggest that subcutaneous adipose tissue may play an important role in modulating adiponectin expression in diabetes and obesity. Moreover, adiponectin mRNA could be potentially regulated by endogenous PPARγ/RXRα-dependent pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attie AD, Scherer PE. Adipocyte metabolism and obesity. J Lipid Res 2008, 50 (Suppl): S395–9.
Ronti T, Lupattelli G, Mannarino E. The endocrine function of adipose tissue: an update. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2006, 64: 355–65.
Yu YH, Ginsberg HN. Adipocyte signaling and lipid homeostasis: sequelae of insulinresistant adipose tissue. Circ Res 2005, 96: 1042–52.
Guerre-Millo M. Adipose tissue and adipokines: for better or worse. Diabetes Metab 2004, 30: 13–9.
Garaulet M, Hernández-Morante JJ, de Heredia FP, Tébar FJ. Adiponectin, the controversial hormone. Public Health Nutr 2007, 10: 1145–50.
Matsuzawa Y. Adiponectin: Identification, physiology and clinical relevance in metabolic and vascular disease. Atheroscler Suppl 2005, 6: 7–14.
Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 1995, 270: 26746–9.
Gil-Campos M, Cañete RR, Gil A. Adiponectin, the missing link in insulin resistance and obesity. Clin Nutr 2004, 23: 963–74.
Iwaki M, Matsuda M, Maeda N, et al. Induction of adiponectin, a fat-derived antidiabetic and antiatherogenic factor, by nuclear receptors. Diabetes 2003, 52: 1655–63.
Geloneze B, Pereira JA, Pareja JC, et al. Overcoming metabolic syndrome in severe obesity: adiponectin as a marker of insulin sensitivity and HDL-cholesterol improvements after gastric bypass. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2009, 53: 293–300.
Nishida M, Funahashi T, Shimomura I. Pathophysiological significance of adiponectin. Med Mol Morphol 2007, 40: 55–67.
Okamoto Y, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Libby P. Adiponectin: a key adipocytokine in metabolic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 2006, 110: 267–78.
Hamdy O, Porramatikul S, Al-Ozairi E. Metabolic obesity: the paradox between visceral and subcutaneous fat. Curr Diabetes Rev 2006, 2: 367–73.
Drolet R, Bélanger C, Fortier M, et al. Fat depot-specific impact of visceral obesity on adipocyte adiponectin release in women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009, 17: 424–30.
Bonora E, Targher G, Alberiche M, et al. Homeostasis model assessment closely mirrors the glucose clamp technique in the assessment of insulin sensitivity: studies in subjects with various degrees of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2000, 23: 57–63.
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000, 20: 1595–9.
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001, 86: 1930–5.
Owecki M, Sowinski J. [Adiponectin and its role in the pathogenesis of obesity, diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance]. Pol Merkur Lekarski 2006, 20: 355–7.
Gavrila A, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, et al. Serum adiponectin levels are inversely associated with overall and central fat distribution but are not directly regulated by acute fasting or leptin administration in humans: cross-sectional and interventional studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 4823–31.
Shand BI, Scott RS, Elder PA, George PM. Plasma adiponectin in overweight, nondiabetic individuals with or without insulin resistance. Diabetes Obes Metab 2003, 5: 349–53.
Mojiminiyi OA, Abdella NA, Al Arouj M, Ben Nakhi A. Adiponectin, insulin resistance and clinical expression of the metabolic syndrome in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007, 31: 213–20.
Tabak AG, Brunner EJ, Miller MA, et al. Low serum adiponectin predicts 10-year risk of type 2 diabetes and hba1c independently of obesity, lipids, and inflammation: Whitehall II study. Horm Metab Res 2009, 41: 626–9.
Daimon M, Oizumi T, Saitoh T, et al. Decreased serum levels of adiponectin are a risk factor for the progression to type 2 diabetes in the Japanese Population: the Funagata study. Diabetes Care 2003, 26: 2015–20.
Snijder MB, Heine RJ, Seidell JC, et al. Associations of adiponectin levels with incident impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes in older men and women: the hoorn study. Diabetes Care 2006, 29: 2498–503.
Hivert MF, Sullivan LM, Fox CS, et al. Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008, 93: 3165–72.
Lihn AS, Østergard T, Nyholm B, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B, Schmitz O. Adiponectin expression in adipose tissue is reduced in first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003, 284: E443-8.
Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Verdich C, et al. Regulation of adiponectin by adipose tissue-derived cytokines: in vivo and in vitro investigations in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003, 285: E527–33.
Lihn AS, Richelsen B, Pedersen SB, et al. Increased expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-8 in HALS: implications for reduced adiponectin expression and plasma levels. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003, 285: E1072–80.
Lihn AS, Bruun JM, He G, Pedersen SB, Jensen PF, Richelsen B. Lower expression of adiponectin mRNA in visceral adipose tissue in lean and obese subjects. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2004, 219: 9–15.
Ryo M, Nakamura T, Kihara S, et al. Adiponectin as a biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. Circ J 2004, 68: 975–81.
Ohashi N, Ito C, Fujikawa R, Yamamoto H, Kihara Y, Kohno N. The impact of visceral adipose tissue and high-molecular weight adiponectin on cardio-ankle vascular index in asymptomatic Japanese subjects. Metabolism 2009, 58: 1023–9.
Berg AH, Combs TP, Scherer PE. ACRP30/adiponectin: an adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2002, 13: 84–9.
Savu MK, Phillips SA, Oh DK, et al. Response of adiponectin and its receptors to changes in metabolic state after gastric bypass surgery: dissociation between adipose tissue expression and circulating levels. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2009, 5: 172–80.
Yang WS, Chen MH, Lee WJ, et al. Adiponectin mRNA levels in the abdominal adipose depots of nondiabetic women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003, 27: 896–900.
Ribot J, Rodriguez AM, Rodriguez E, Palou A. Adiponectin and resistin response in the onset of obesity in male and female rats. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008, 16: 723–30.
Liu YM, Lacorte JM, Viguerie N, et al. Adiponectin gene expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women in response to short-term very low calorie diet and refeeding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 5881–6.
Horenburg S, Fischer-Posovszky P, Debatin KM, Wabitsch M. Influence of sex hormones on adiponectin expression in human adipocytes. Horm Metab Res 2008, 40: 779–86.
Plaisance EP, Grandjean PW, Judd RL, Jones KW, Taylor JK. The influence of sex, body composition, and nonesterified fatty acids on serum adipokine concentrations. Metabolism 2009, 58: 1557–63.
Kern PA, Di Gregorio GB, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G. Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes 2003, 52: 1779–85.
Xie L, O’Reilly CP, Chapes SK, Mora S. Adiponectin and leptin are secreted through distinct trafficking pathways in adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008, 1782: 99–108.
Després JP, Lemieux I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006, 444: 881–7.
Barth N, Langmann T, Schölmerich J, Schmitz G, Schäffler A. Identification of regulatory elements in the human adipose most abundant gene transcript-1 (apM-1) promoter: role of SP1/SP3 and TNF-alpha as regulatory pathways. Diabetologia 2002, 45: 1425–33.
Maeda N, Shimomura I, Kishida K, et al. Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30. Nat Med 2002, 8: 731–7.
Phillips SA, Ciaraldi TP, Oh DK, Savu MK, Henry RR. Adiponectin secretion and response to pioglitazone is depot dependent in cultured human adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2008, 295: E842–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Co-second authors
Co-last authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kouidhi, S., Jarboui, S., Marrakchi, R. et al. Adiponectin expression and metabolic markers in obesity and Type 2 diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest 34, e16–e23 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347056
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347056