Abstract
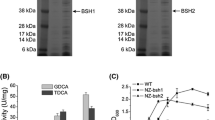
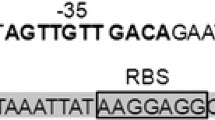
Bile salt hydrolase (BSH) is one of the genes relevant to bile tolerance. Biochemical assay showed thatLactobacillus casei Zhang was able to deconjugate sodium taurocholate during growth. To explore the possible relationship between BSH activity and bile tolerant ability, we cloned and determined full-length DNA sequence of the BSH gene inL. casei Zhang, and monitored its expression pattern under the stress of bile salts. The DNA sequence consists of 1181 nucleotides; the putative protein includes 338 amino acids. The sequences alignment and homology studies illustrated a great diversity between species. Further real-time PCR analysis revealed that expression of the BSH gene was up-regulated when there presented bile salts in the growth medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Altschul S.F., Madden T.L., Schaffer A.A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., Lipman D.J. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res., 25: 3389–3402.
Brashears M.M., Gilliland S.E., Buck L.M. (1998). Bile salt deconjugation and cholesterol removal from media byLactobacillus casei. J. Dairy Sci., 81: 2103–2110.
Begley M., Gahan CG., Hill C. (2005a). The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 29: 625–651.
Begley M., Sleator R.D., Gahan CG., Hill C. (2005b). Contribution of three bile-associated loci,bsh, pva, andbtlB, to gastrointestinal persistence and bile tolerance ofListeria monocytogenes. Infect. Immun., 73: 894–904.
Begley M., Hill C, Gahan C.G. (2006). Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72: 1729–1738.
Bran P.A., Molenaar D., De Vos W.M., Kleerebezem M. (2006). DNA micro-array-based identification of bile-responsive genes inLactobacillus plantarum. J. Appl. Microbiol., 100: 728–738.
Christiaens H., Leer R.J., Pouwels P.H., Verstraete W. (1992). Cloning and expression of a conjugated bile acid hydrolase gene fromLactobacillus plantarum by using a direct plate assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 58: 3792–3798.
De Boever P., Wouters R., Verschaeve L., Berckmans P., Schoeters G., Verstraete W. (2000). Protective effect of the bile salt hydrolase-activeLactobacillus reuteri against bile salt cytotoxicity. Appl. Microbiol., 53: 709–714.
Elkins CA., Moser S.A., Savage D.C. (2001). Genes encoding bile salt hydrolases and conjugated bile salt transporters inLactobacillus johnsonii 100-100 and otherLactobacillus species. Microbiology, 147: 3403–3412.
Grill J., Schneider F., Crociani J., Ballongue J. (1995). Purification and characterization of conjugated bile salt hydrolase fromBifidobacterium longum BB536. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61: 2577–2582.
Gueimonde M., Salminen S. (2006). New methods for selecting and evaluating probiotics. Dig. Liver Dis., 38 Suppl. 2: S242-S247.
Jones B.V., Begley M., Hill C, Gahan CG., Marchesi J.R. (2008). Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105: 13580–13585.
Kim G.B., Miyamoto CM., Meighen E.A., Lee B.H. (2004). Cloning and characterization of the bile salt hydrolase genes (bsh) fromBifidobacterium bifidum strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 70: 5603–5612.
Kim G.B., Brochet M., Lee B.H. (2005). Cloning and characterization of a bile salt hydrolase (bsh) fromBifidobacterium adolescents. Biotechnol. Lett., 27: 817–822.
Livak K.J., Schmittgen TD. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-AACT method. Methods (San Diego, Calif.), 25: 402–408.
Mcauliffe O., Cano R.J., Klaenhammer T.R. (2005). Genetic analysis of two bile salt hydrolase activities inLactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 71: 4925–4929.
Mulder N.J., Apweiler R., Attwood T.K., Bairoch A., Bateman A., Binns D., Bradley P., Bork P., Bucher P., Cerutti L, Copley R., Courcelle E., Das U., Durbin R., Fleischmann W., Gough J., Haft D., Harte N., Hulo N., Kahn D., Kanapin A., Krestyaninova M., Lonsdale D., Lopez R., Letunic I., Madera M., Maslen J., McDowall J., Mitchell A., Nikolskaya A.N., Orchard S., Pagni M., Ponting C.P., Quevillon E., Selengut J., Sigrist C.J., Silventoinen V, Studholme D.J., Vaughan R., Wu CH. (2005). InterPro, progress and status in 2005. Nucleic Acids Res., 33: D201–205.
Oh H.K., Lee J.Y., Lim SJ., Kim M.J., Kim G.B., Kim J.H., Hong S.K., Kang D.K. (2008). Molecular doning and characterization of a bile salt hydrolase fromLactobacillus acidophilus PFOl. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 18: 449–456.
Pineiro M., Stanton C. (2007). Probiotic bacteria: legislative framework-requirements to evidence basis. J. Nutr., 137: 850S-853S.
Ridlon J.M., Kang D.J., Hylemon P.B. (2006). Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria. J. Lipid Res., 47: 241–259.
Suresh CG., Pundle A.V., Sivaraman H., Rao K.N., Brannigan J.A., McVey CE., Verma CS., Dauter Z., Dodson E.J., Dodson G.G. (1999). Penicillin V acylase crystal structure reveals new Ntn-hydrolase family members. Nat. Struct. Biol., 6: 414–416.
Succi M., Tremonte P., Reale A., Sorrentino E., Grazia L., Pacifico S., Coppola R. (2005). Bile salt and acid tolerance of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains isolated from Parmigiano Reggiano cheese. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 244: 129–137.
Thompson J.D., Higgins D.G., Gibson T.J. (1994). CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res., 22: 4673–4680.
Tanaka H., Doesburg K., Iwasaki T., Mierau I. (1999). Screening of lactic acid bacteria for bile salt hydrolase activity. J. Dairy Sci., 82: 2530–2535.
Van De Guchte M., Serror P., Chervaux C, Smokvina T., Ehrlich S.D., Maguin E. (2002). Stress responses in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 82: 187–216.
Walker D.K., Gilliland S.E. (1993). Relationship among bile tolerance, bile salt deconjugation, and assimilation of cholesterol byLactobacillus acidophilus. J. Dairy Sci., 76: 956–961.
Wu R., Wang L, Wang J., Li H., Menghe B., Wu J., Guo M., Zhang H. (2009). Isolation and preliminary probiotic selection of lactobacilli from koumiss in Inner Mongolia. J. Basic Microbiol., 49: 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W.Y., Wu, R.N., Sun, Z.H. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of bile salt hydrolase inLactobacillus casei Zhang. Ann. Microbiol. 59, 721–726 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179214
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179214