Abstract
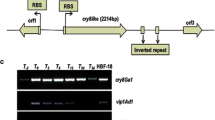
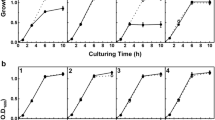
The genome of the insect pathogenPhotorhabdus luminescens TT01 strain contains multiple genes predicted to encode toxins. One of these,plu0840, has 55% sequence identity with an enterotoxin fromAeromonas hydrophila. In order to further investigate this gene, we successfully cloned the completeplu0840 fromPhotorhabdus sp. HB78 and expressed it as a GST-Plu0840 fusion protein inEscherichia coli BL21 (DE3) using pGEX-4T-1 as a vector. Most of GST-Plu0840 was insoluble and sequestered into inclusion bodies. The inclusion bodies were harvested and dissolved. The resultant protein was cleaved and purified from the GST-tag. Oral bioassay showed that Plu0840 inhibited growth ofSpodoptera litura andSpodoptera exigua larvae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackburn M., Golubeva E., Bowen D., Ffrench-Constant R.H. (1998). A novel insecticidal toxin fromPhotorhabdus luminescens, toxin complex a (tca), and its histopathological effects on the Midgut of Manduca Sexta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64: 3036–3041.
Bowen D.J., Ensign J.C. (1998). Purification and characterization of a high-molecular-weight insecticidal protein complex produced by the entomopathogenic bacteriumphotorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64: 3029–3035.
Brillard J., Duchaud E., Boemare N., Kunst F., Givaudan A. (2002). The PhIA hemolysin from the entomopathogenic bacteriumPhotorhabdus luminescens belongs to the two-partner secretion family of hemolysins. J. Bacteriol., 184: 3871–3878.
Brown S.E., Cao A.T., Hines E.R., Akhurst R.J., East P.D. (2004). A novel secreted protein toxin from the insect pathogenic bacteriumXenorhabdus nematophila. J. Biol. Chem., 15: 14595–14601.
Cowles K.N., Goodrich-Blair H. (2005). Expression and activity of aXenorhabdus nematophila haemolysin required for full virulence towardsManduca sexta insects. Cell Microbiol., 7: 209–219.
Daborn P.J., Waterfield N., Silva C.P., Au C.P.Y., Sharma S., Ffrench-Constant R.H. (2002). A singlePhotorhabdus gene, makes caterpillars floppy (mcf), allowsEscherichia coli to persist within and kill insects. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 99: 10742–10747.
Duchaud E., Rusniok C., Frangeul L.,et al. (2003). The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacteriumPhotorhabdus lumnnescens. Nature Biotechnol., 21: 1307–1313.
Dunphy G.B., Webster J.M. (1988). Virulence mechanisms ofHeterorhabditis heliothidis and its bacterial associate,Xenorhabdus luminescens, in the non-immune larvae of the greater wax moth,Galleria mellonella. Int. J. Parasitol., 18: 729–737.
Ffrench-Constant R.H., Bowen D.J. (2000). Novel insecticidal toxins from nematode symbiotic bacteria. Cell Mol. Life Sci., 57: 828–833.
Ffrench-Constant R.H., Waterfield N., Burland V., Perna N.T., Daborn P.J., Bowen D., Blattner F.R. (2000). A genomic sample sequence of the entomopathogenic bacteriumPhotorhabdus luminescens W14: potential implications for virulence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66: 3310–3329.
Ffrench-Constant R., Waterfield N., Daborn P., Joyce S., Bennett H., Au C., Dowling A, Boundy S., Reynolds S., Clarke D. (2003).Photorhabdus: towards a functional genomic analysis of a symbiont and pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 26: 433–456.
Forst S., Dowds B., Boemare N., Stackebrandt E. (1997).Xenorhabdus andphotorhabdus spp.: bugs that kill bugs. Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 51: 47–72.
Fridjonsson O., Watzlawick H., Gehweiler A., Rohrhirsch T., Mattes R. (1999). Cloning of the gene encoding a novel thermostable α-galactosidase fromThermus brockianus ITI360. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65: 3955–3963.
Khandelwal P., Choudhury D., Birah A., Reddy M.K., Gupta G.P., Banerjee N. (2004). Insecticidal pilin subunit from the insect pathogenXenorhabdus nematophila. J. Bacteriol., 19: 6465–6476.
Luonteri E., Tenkanen M., Viikari L. (1998). Substrate specificities ofPenicillium simplicissimum α-galactosidases. Enzyme Microb. Technol., 22: 192–198.
Morgan J.A.W., Sergeant M., Ellis D., Ousley M., Jarrett P. (2001). Sequence analysis of insecticidal genes fromXenorhabdus nematophilus PMF1296. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 67: 2062–2069.
Obendorf D., Peel B., Akhurst R.,et al. (1983). Non-susceptibility of mammals to the entomopathogenic bacteriumXenorhabdus nematophilus. Environ. Entomol., 12: 368–370.
Poinar G.O., Thomas G.M., Hess R.et al. (1977). Characteristics of the specific bacterium associated withHeterorhabditis bacteriophora (Heterorhabditidae: Rhabditida). Nematologica, 23: 97–102.
Poinar G., Thomas G.M., Presser S.,et al. (1982). Inoculation of entomogenouse nematodes,Neoaplectana andHeterorhabditis, and their associated bacteria,Xenorhabdus spp., into chicks and mice. Environ. Entomol., 11: 137–138.
Sergeant M., Jarrett P., Ousley M., Morgan J.A.W. (2003). Interactions of insecticidal toxin gene products fromXenorhabdus nematophilus PMF1296. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69: 3344–3349.
Sha J., Kozlova E.V., Chopra A.K. (2002). Role of various enterotoxins inAeromonas hydrophila-induced gastroenteritis: generation of enterotoxin gene-deficient mutants and evaluation of their enterotoxic activity. Infect. Immun., 70: 1924–1935.
Waterfield N., Hares M., Yang G., Dowling A., Ffrench-Constant R. (2005a). Potentiation and cellular phenotypes of the insecticidal toxin complexes ofPhotorhabdus bacteria. Cell Microbiol., 7: 373–382.
Waterfield N., Kamita S.G., Hammock B.D., Ffrench-Constant R. (2005b). ThePhotorhabdus Pir toxins are similar to a developmentally regulated insect protein but show no juvenile hormone esterase activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 245: 47–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Qiu, L. & Pang, Y. Cloning and expression analysis of a predicted toxin gene fromPhotorhabdus sp. HB78. Ann. Microbiol. 57, 313–319 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175066
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175066