Abstract
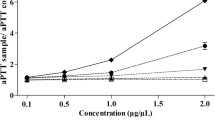
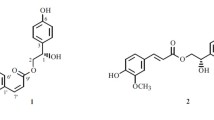
Tissue factor (TF, tissue thromboplastin or coagulation factor III) accelerates the blood clotting, activating both the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathways to serve as a cofactor. In order to isolate TF inhibitors from the fruits ofChaenomeles sinensis, an activity-guided purification utilizing a bio-assay method of prothrombin time prolongation, was carried out to yield five active flavoniods such as hovetrichoside C (1) (IC50 = 14.0 μg), luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide (3) (IC50 = 31.9 μg), hyperin (4) (IC50 = 20.8 μg), avicularin (6) (IC50 = 54.8 μg) and quercitrin (10) (IC50 = 135.7 μg), along with other inactive compounds such as (±)-(2E,4E)-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-4′-hydroxy-β-ionylideneacetic acid ester (2), genistein-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (5), luteolin-3′-methoxy-4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (7), luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide methyl ester (8), tricetin-3′-methoxy-4′-O-p-D-glucopyranoside (selagin-4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside) (9), (-)-epicatechin (11), luteolin-4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (12) and apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide methyl ester (13). The structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated through spectral analysis. Among them, compounds1 to9,12 and13 were isolated for the first time from the fruits of this plant and the compound9 is a new flavonoid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allais, D. P., Simon, A., Bennini, B., Chulia, A. J., Kaouadji, M. and Delage, C., Flavone and flavonol glycosides fro.Calluna Vulgaris. Phytochem., 30, 3099–3101 (1991).
Bennini, B., Chulia, A. J., Kaouadji, M. and Thomasson, F., Flavonoid glycosides fro.Erica cinerea.Phytochem., 31, 2483–2486 (1992).
Han, Y. N. and Rhee, Y. K., Changes of tissue factor activity on inflammatory stimulus and aging in rat.Arch. Pharm. Res., 21, 549–554 (1998).
Harker, L. A., Hanson, S. R. and Kelly, A. B., Antithrombotic benefits and hemorrhagic risks of direct thrombin antagonists.Thromb. Haemost., 74, 464–472 (1995).
Im, K. S. and Roh, S. B., Structures of chaenoside A and B isolated from the fruits o.Chaenomeles sinensis Koehne.Pusan. Bull. Pharm. Sci., 28, 35–41 (1994).
Im, K. S. and Roh, S. B., Two major triterpene acids from the fruits o.Chaenomeles sinensis Koehne.Pusan. Bull. Pharm. Sci., 25, 1 (1991).
Kim, H. K., Jeon, W. K. and Ko, B. S., Flavanone glycoside from the fruits o.Chaenomeles sinensis.Nat. Prod. Sci., 6, 79–81 (2000).
Lee, S. J., Korean folk medicine. Publishing Center of Seoul National University, Seoul, pp. 67–68 (1966).
Lu, Y. and Yeap, Foo, L., Identification and quantification of major polyphenols in apple pomace.Food Chem., 59, 187–194 (1997).
Markham, K. R. and Geiger, H.,1H Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of flavonoids and their glycosides in hexadeuterodimethyl-sulfoxide, In Harborne, J. B. (Ed). The Flavonoids, Advances in research. Chapman & Hall, London, pp. 441–497 (1994).
Matsuo, T. and Ito, S., A simple and rapid purification method of condensed tannins from several young fruits.Agric. Biol. Chem., 45, 1884 (1981).
Mattice, W. L. and Porter, L. J., Molecular weight averages and13C NMR intensities provide evidence for branching in pro-anthocyanidin polymers.Phytochem., 23, 1309–1311 (1984).
Mazurek, A. P., Dobrowolski, J. Cz., Sadlej, J., Bednarek, E. and Kozerski, L., Genistein complexes with amines. Part II: ab initio study of the complexes with piperazine and trithy-lamine.J. Mol. Struc., 520, 45–52 (2000).
Namba, T., The Encyclopedia of Wakan-Yaku (Traditional Sino-Japanese Medicines) with color pictures. Vol. I. Hoikusha, Osaka, pp. 193–194 (1992).
Nemerson, Y., Tissue factor and hemostasis.Blood, 71, 1–8 (1988).
NØrbæk, R., Nielsen, J. K. and Kondo, T., Flavonoids from flowers of tw.Crocus chrysanthus-biflorus cultivars: “Eye-catcher” and “Spring Pearl” (Iridaceae).Phytochem., 51, 1139–1146 (1999).
Oritani, T. and Yamashita, K., Studies on abscisic acid. Part VI. Syntheses of hydroxy-ionylideneacetic acids.Agric. Biol. Chem., 36 (3), 362–369 (1972).
Oritani, T. and Yamashita, K., Synthesis and metabolism of (±)-(2-14C)-4-hydroxy--ionylideneacetic acid.Agric. Biol. Chem., 43, 1613–1614 (1979).
Osawa, K., Arakawa, T., Shimura, S. and Takeya, K., New quinic acid derivatives from the fruits o.Chaenomeles sinensis (Chinese quince).Nat. Med., 55, 255–257 (2001).
Osterud, B. and Rapaport, S. I., Activition of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: Additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation.Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 74, 5260–5364 (1977).
Ricardo, D. R. and Alicia, B. P., 5,7,3′-Trihydroxy-4′,5′-dimeth-oxyflavone and other phenolics fromPoa Huecu.Phyto-chem., 24, 2131–2132 (1985).
Roh, S. B., Chang, E. H. and Im, K. S., Isolation and characterization of acidic triterpenes from the fruits o.Chaenomeles sinensis.Yakhak Hoeji, 39, 610–615 (1995).
Schulz, M., Strack, D., Weissenböck, G., Markham, K. R., Dellamonica, G. and Chopin, J., Two luteolin O-glucuronides from Primary Leaves o.Secale cereale.Phytochem., 24, 343–345 (1985).
Sharaf, M., El-Ansari, M. A. and Saleh, N. A. M., Flavone glycosides fro.Mentha longifolia.Fitoterapia, 70, 478–483 (1999).
Sun, L. N. and Hong, Y. F., Chemical constituents o.Chae-nomeles sinensis (Thouin.) Koehne.J. Chin. Pharm. Sci., 9, 6–9 (2000).
TradiMed, Traditional oriental medicines database, Seoul National University Natural Products Research Institute, in Seoul Systems Co., LTD., Seoul (1996).
Winterhalter, P., Harmsen, S. and Trani, F., A C13-norisoprenoid gentiobioside fro.quince fruits.Phytochem., 30, 3021–3025 (1991).
Yoshikawa, K., Eiko, K., Mimura, N., Kondo, Y. and Arihara, S., Hovetrichosides C-G, five new glycosides of two auronols, two neolignans, and a phenylpropanoid from the Bark ofHovenia trichocarea.J. Nat. Prod., 61, 786–790 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.H., Son, Y.K. & Han, Y.N. Tissue factor inhibitory flavonoids from the fruits ofChaenomeles sinensis . Arch Pharm Res 25, 842–850 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977002
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977002