Abstract
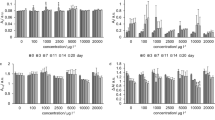
A culture of anaerobic sludge was bioaugmented withDesulfovibrio desulfuricans for the color removal of authentic textile wastewater containing a substantial amount of sulfate, in order to improve the decolorization process. The sulfide produced by sulfate respiration ofD. desulfuricans can chemically reduce azo bonds to produce a colorless metabolite in the form of aromatic amines. In the case where the culture of anaerobic sludge was bioaugmented withD. desulfuricans, the decolorization of C.I. Reactive Black 5 showed an increase of more than 14% after 48 h in comparison with that in the culture of anaerobic sludge alone. In the decolorization of authentic textile wastewater, the color removal (about 69.0%) was improved by the mixed culture of anaerobic sludge andD. desulfuricans, compared with results obtained with only anaerobic sludge as reported in our previous work, suggesting that bioaugmentation byD. desulfuricans can be useful for the decolorization of wastewater that contains complex dye compounds and sulfate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, J. S., C. Chou, Y. C. Lin, J. Y. Ho, and T. L. Hu (2001) Kinetic characteristics of bacterial azodye decolorization byPseudomonas luteola.Water Res. 35: 2841–2850.
Chen, K. C., J. Y. Wu, D. J. Liou, and S. C. J. Hwang (2003) Decolorization of the textile dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains.J. Biotechnol. 101: 57–68.
Swamy, J. and J. A. Ramsay (1999) The evaluation of white rot fungi in the decoloration of textile dyes.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 24: 130–137.
Van der Zee, F. P. and S. Villaverde (2005) Combined anaerobic-aerobic treatment of azo dyes: A short review of bioreactor studies.Water Res. 39: 1425–1440.
Bras, R., M. I. A. Ferra, H. M. Pinheiro, and I. Cabral Goncalves (2001) Batch tests for assessing decolourisation of azo dyes by methanogenic and mixed cultures.J. Biotechnol. 89: 155–162.
Bras, R., A. Gomes, M. I. A. Ferra, H. M. Pinheiro, and I. C. Goncalves (2005) Monoazo and diazo dye decolourisation studies in a methanogenic UASB reactor.J. Biotechnol. 115: 57–66.
Vallero, M. V. G., R. H. M. Trevino, P. L. Paulo, G. Lettinga, and P. N. L. Lens (2003) Effect of sulfate on methanol degradation in thermophilic (55°C) methanogenic UASB reactors.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 32: 676–687.
Chung, K. T. and S. E. Stevens, Jr. (1993) Degradation of azo dyes by environmental microorganisms and helminthes.Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12: 2121–2132.
Yoo, E. S., J. Libra, and U. Wiesmann (2000) Reduction of azo dyes by desulfovibrio desulfuricans.Water Sci. Technol. 41: 15–22.
Yoo, E. S., J. Libra, and L. Adrian (2001) Mechanism of decolorization of azo dyes in anaerobic mixed culture.J. Environ. Eng. 127: 844–849.
Kim, S. Y., J. Y. An, and B. W. Kim (2007) Effect of chemical reductant and carbon source on the microbial decolorization of azo dyes in an anaerobic sludge process.Dyes and Pigments, In press.
Moon, S. H., J. M. Park, H. Y. Chun, and S. J. Kim (2006) Comparisons of physical properties of bacterial celluloses produced in different culture conditions using saccharified food wastes.Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 11: 26–31.
Jang, S. J., M. S. Kim, and B. W. Kim (2004) Photodegradation of Reactive Black 5 in photoreactors using TiO2 immobilized on a glass tube.J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 10: 544–550.
Van der Zee, F. R., G. Lettinga, and J. A. Field (2001) Azo dye decolourisation by anaerobic granular sludge.Chemosphere 44: 1169–1176.
Kapdan, I. K. and S. Alparslan (2005) Application of anaerobic-aerobic sequential treatment system to real textile wastewater for color and COD removal.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 36: 273–279.
Wee, Y. J., J. N. Kim, J. S. Yun, and H. W. Ryu (2005) Optimum conditions for the biological production of lactic acid by a newly isolated lactic acid bacterium.Lactobacillus sp. RKY2.Biotechonol. Bioprocess Eng. 10: 23–28.
Liu, L. M., G. C. Du, Y. Li, H. Z. Li, and J. Chen (2005) Enhancement of pyruvate production byTorulopsis glabrata through supplement of oxaloacetate as carbon source.Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 10: 136–141.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1992)Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 19th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington DC, USA.
Kosinska, K. and T. Miskiewicz (1999) Upgrading the efficiency of dissimilatory sulfate reduction byDesulfovibrio desulfuricans via adjustment of the COD/SO4 ratio.Biotechnol. Lett. 21: 299–302.
Yamaguchi, T., H. Harada, T. Hisano, S. Yamazaki, and I. C. Tseng (1999) Process behavior of UASB reactor treating a wastewater containing high strength sulfate.Water Res. 33: 3182–3190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SY., An, JY. & Kim, BW. Improvement of the decolorization of azo dye by anaerobic sludge bioaugmented withDesulfovibrio desulfuricans . Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 12, 222–227 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931096
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931096