Abstract
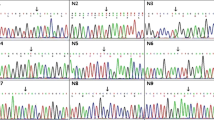
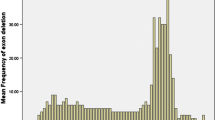
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common X-linked disorder in children affecting 1 in 3500 males. Since, as of now, we have no treatment for DMD, carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis is the most important preventive strategy. Multiplex PCR helps in rapid detection of hot spot exonal deletions (positive in 65% of cases) as many exons can be identified in a single run. 10 children with characterstic clinical features of DMD and chorionic villus samples of 10 antenatal patients with positive family history were studied. We identified a deletion mutation in exon 49 of the dystrophin gene in a 4 yr old boy referred with signs and symptoms suggestive of DMD using primers for exons 45, 48, 49, 43, 44, 19, 3, 8, 13 and muscle promoter, subjected to multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and agarose/Nu-Sieve gel electrophoresis. These genetic methods aid in prenatal diagnosis of DMD as well as confirmation of diagnosis in children with signs and symptoms suggestive of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maheshwari, M., Vijaya, R., Kabra, M., Arora, S., Shastri, S.S., Deka, D., Kriplani, A. and Menon, P. (2000). Prenatal diagnosis of duchenne muscular dystrophy. Natl. Med. J. India. 13 (3), 129–131.
Emery, A.E.H. (1991). Population frequencies of inherited neuromuscular diseases—a world survey. Neuromuscular disorders 1, 19–29.
Kawamura, J. (1997). Detection of mutation in dystrophin gene in Duchenne muscular dystrophy —multiplex PCR and Southern blot analysis. Nippon Rinsho. 55 (12), 3126–3130.
Evans, M.I., Greb, A., Kunkel, L.M., Sacks, A.J., Johnson, M.P., Boehm, C., Kazazian, H.H. Jr. and Hoffman, E.P. (1991). In utero fetal muscle biopsy for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 165, 728.
Den Dunnen, J.T., GrootScholten, P.M., Bakker, E., Blonden, L.A.J., Ginjaar, H.B., Wapenaar, M.C., Paassen, H.M.B., Broeckhoven, C., Pearson, P.L. and Ommen, G.B.J. (1989). Topography of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene: FIGE and eDNA analysis of 194 cases reveals 115 deletions and 13 duplications. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 45, 835–847.
Bakker, E., Hofker, M.H., Goor, N., Mendel, J.L., Wrogemann, K., Davies, K.E., Kunkel, L.M., Willard, H.F., Fenton, W.A., Sandkeyl, L. and Krakouer, M. (1985). Prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of Duchenne Muscular dystrophy with closely linked RFLPs. Lancet. 1 (8430), 655–658.
Champerlain, J.S., Gibbs, R.A., Ranier, J.E., Nguyen, P.N. and Caskey, C.T. (1988). Deletion Screening of Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus via multiplex DNA amplification. Nucleic acid Res. 16, 11141–11156.
Chamberlain, J.S., Chamberlain, J.R., Fenwick, R.G., Ward, P.A., Caskey, C.T., Dimnik, L.S., BechHansen, N.D., Hoar, D.I., Tantravahi, V., Richards, S., Covane, A.E., Romeo, G., Abbs, S., Bentley, D.R., Bobrow, M., Rysiecki, G., Ray, P.N., Boileac, C., Junien, C., Boehm, C., Venne, V.L., Fujimura, F.K., Spiga, I., Ferrari, M., Tedeschi, S., Bakker, E., Kneppers, L.J., VanOmen, G.J.B., Jain, K., Spector, E., Crandall, B., Kiuru, A. and Savonisus, M.L. (1992). Diagnosis of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies by polymerase chain reaction—A multicenter study. JAMA. 267, 2609–2615.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor. N.Y.
Beggs, A.L.L., Koenig, M., Boycee, F.M. and Kunkel, L.M. (1990). Detection of 98% of DMD/BMD gene deletions by polymerase Chain reaction. Hum. Genet. 86, 45–48.
Emery, A.E. and Burt, D. (1980). Intracellular Calcium, pathogenesis and antenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Brit. Med. J. 280, 355–357.
Edwards, R.R., Watts, D.C., Watts, R.L. and Rodeck, C.H. (1984). Creatinine Kinase estimation in pure fetal blood samples for prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Pre. Diag. 4, 267–277.
Darras, B.T., Harper, J.F. and Francke, U. (1988). Direct method of prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy using the entire dystrophin cDNA. Am. J. Med. Genet. 29, 713–726.
Werneck, L.C., Scola, R.H., Maegawa, G.H. and Werneck, M.C. (2001). Comparative analysis of PCR deletion detection and immunochemistry in Brazilian Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. 103 (2), 115–120.
Banerjee, M. and Verma, I.C. (1997). Are there Ethnic Differences in Deletions in the Dystrophin Gene? Am. J. Med. Genet. 68, 152–157.
Xu, X., Burghes, A.H.M., Ray, P.N., Thompson, M.W., Murphy, E.G. and Worton, R.G. (1988). Partial gene duplication in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. J. Med. Genet. 25, 369–376.
Forrest, S.M., Cross, G.S., Flint, T., Speer, A., Robson, K.J.H. and Davies, K.E. (1988). Further studies of gene deletions that cause Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Genomics. 2, 109–114.
Clemens, P.R., Fenwick, R.G., Chamberlain, J.S., Gibbs, R.A., de Andrade, M., Chakraborty, R. and Caskey, C.T. (1991). Carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy families using dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49, 951–960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Work done as WHO fellow in Deptt. of Genetics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Vijjaya & Kabra, M. Multiplex PCR for rapid detection of exonal deletions in patients of duchenne muscular dystrophy. Indian J Clin Biochem 21, 147–151 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913084
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913084