Abstract
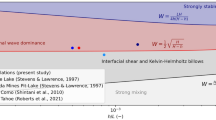
Analyses of observations from four lakes in British Columbia, Canada, compare estimates of the amplitude of thermocline deflections to predictions of wind-driven internal seiche amplitudes made using the Wedderburn number,W. The study sites range from the 750 m diameter Brenda Mines pit-lake to the 107 km long Kootenay Lake. Causal filtering of the wind data with a frequency cut-off based on the fundamental baroclinic time-scale is critical for correct calculation ofW. With the filtering incorporated, good comparison betweenW, its integral equivalent the Lake numberL N and the observations can be made. In all but the mine pit-lake, upwelling or near-upwelling conditions (W≈1) were encountered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmack, E. C., R. C. Wiegand, R. J. Daley, C. B. Gray, S. Jasper and C. H. Pharo, 1986. Mechanisms influencing the circulation and distribution of water mass in a medium residence-time lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31 (2): 249–265.
Chen, C.-T., 1979. One-dimensional digital signal processing. Dekker, 448 pp.
Christensen, B., 1995. Too good to be true: ALCAN’s Kemano Completion Project. Talonbooks, Vancouver, 352 pp.
Donelan, M. A., 1990. Air-sea Interaction, In: The Sea, B. LeMéhauté and D. Hanes, (eds.). Vol. 9A, Wiley, 239–292.
Heaps, N. S. and A. E. Ramsbottom, 1966. Wind effects on water in a narrow two-layered lake. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 259: 391–430.
Houston, A. H., 1982. Thermal effects upon fishes. National Research Council of Canada, Rep. No. 18566, 200 pp.
Hutter, K., 1984. Hydrodynamics of Lakes. CISMA course and lectores no. 286, Springer-Verlag, 341 pp.
Imberger, J., 1985. The diurnal mixed layer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30(4): 737–770.
Imberger, J. and J. C. Patterson, 1990. Physical Limnology. Advances in Applied Mechanics 27: 303–473.
Imboden, D. M. and R. P. Schwarzenbach, 1985. Spatial and temporal distribution of chemical substances in takes: modelling concepts. In: Chemical Processes in Lakes, W. Stumm (ed.), 1–30.
Ishikawa, T. and M. Tanaka, 1993. Diurnal stratification and its effects on wind induced currents and water qualities in Lake Kasumigaura. J. Hyd. Res. Vol. 31 (3): 307–322.
Macdonald, R. H., 1995. Hypolimnetic withdrawal from a shallow, eutrophic lake. MSc. Thesis, University of British Columbia, 185 pp.
MacIntyre, S., 1993. Vertical mixing in a shallow, eutrophic lake: Possible consequences for the light climate of phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 38(4): 798–817.
Maas, L. R. M. and F.-P. A. Lam, 1995. Geometric focusing of internal waves. J. Fluid Mech. 300: 1–42.
Monismith, S. G., 1985. Wind-forced motions in stratified lakes and their effect on mixed layer shear. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30(4): 771–783.
Monismith, S. G. 1986. An experimental study of the upwelling response of stratified reservoirs to surface shear stress. J. Fluid Mech. 171: 407–439.
Münnich, M., A. Wüest and D. M. Imboden, 1992. Observations of the second vertical mode of the internal seiche in an alpine lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37 (8): 1705–1719.
Roget, E., G. Salvadé, F. Zamboni and J. E. Llebot, 1993. Internal waves in a small lake with a thick metalimnion. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. Vol. 25: 91–99.
Spigel, R. H. and J. Imberger, 1980. The classification of mixed-layer dynamics in lakes of small to medium size. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 10: 1104–1121.
Stevens, C. and G. A. Lawrence, 1996. Physical transport processes in a water-filled mine pit. Submitted to Limnol. Oceanogr.
Stevens, C. L., G. A. Lawrence, P. F. Hamblin and E. C. Carmack, 1996. Wind forcing of internal waves in a long narrow stratified lake. Dynamics of Atmos. Oceans, 24(1–4): 41–50.
Stevens, C. and J. Imberger, 1996. The initial response of a stratified lake to a surface shear stress. J. Fluid Mech 312: 39–66.
Stumm, W., 1985. Chemical Processes in Lakes. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 435 pp.
Thorpe, S. A., 1977. Turbulence and mixing in a Scottish loch. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London, A 286: 125–181.
Wiegand, R. C. and V. Chamberlain, 1987. Internal waves of the second vertical mode in a stratified lake. Limnol. and Oceanogr. 32(1): 29–42.
Wüest, A., D. C. Van Senden, J. Imberger, G. Piepke and M. Gloor, 1996. Comparison of diapycnal diffusivity measured by tracer and microstructure techniques. Dynamics of Atmos. Oceans 24(1–4): 27–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, C.L., Lawrence, G.A. Estimation of wind-forced internal seiche amplitudes in lakes and reservoirs, with data from British Columbia, Canada. Aquatic Science 59, 115–134 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523176
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523176