Summary
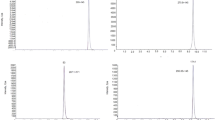
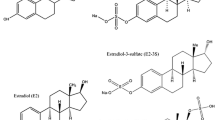
‘Free’ steroidal estrogens have been identified as compounds possibly responsible for endocrine-disruption of aquatic fauna populating rivers in which municipal sewage-treatment plants (STP) discharge their effluents. Natural and synthetic estrogens are excreted, as glucuronides and sulfates, by man, in the urine but these are bioconverted back to the unconjugated forms in wastewater discharges. For this reason we have developed a sensitive analytical procedure, without derivatization, for identification and quantitation of conjugated and free estrogens in surface and waste waters. The hormones were extracted and fractionated, by use of Carbograph cartridges, into neutral and acid fractions which were then analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Recoveries were between 66 and 100% and limits of detection (LOD) between 15.0 and 0.003 ng L−1, depending on the compound and the water matrix. When this methodology was applied to real sewage and river water we could measure the main free estrogens at ng L−1 levels. Among the conjugates we always observed the presence of estrone 3-sulfate (at levels between 8.0 and 0.5 ng L−1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodge, J.A.Pure Appl. Chem. 1998,70, 1725–1733.
Jimenez, B.Anal. Chem. 1997,16, 596–605.
Liehr, J.G.; Somasunderam, A.; Roy, D.Pure Appl. Chem. 1998,70, 1747–1758; Andreolini, F.; Borra, C.; Caccamo, F.; Di Corcia, A.; Samperi, R.Anal. Chem. 1987,59, 1720–1725.
Preziosi, P.Pure Appl. Chem. 1998,70, 1617–1631.
Tyler, C.R.; Routledge, E.J.Pure Appl. Chem. 1998,70, 1795–1804.
Sharpe, R.M.Pure Appl Chem. 1998,70, 1685–1701.
Routledge, E.J.; Sheahan, D.; Desbrow, C.; Brighty, G.C.; Sumpter, P.Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998,32, 1559–1565.
Desbrow, C.; Routledge, E.J.; Brighty, G.C.; Sumpter, J.P.; Waldock, M.Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998,32, 1549–1557.
Snyder, S.A.; Keith, T.L.; Verbrugge, D.A.; Snyder, E.M.; Gross, T.S.; Kannan, K.; Giesy, J.P.A.Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999,33, 2814–2820.
Routledge, E.J.; Sumpter, J.P.J. Biol. Chem. 1997,272, 3280–3288.
Shackleton, C.H.L.J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl. 1986,379, 91–156.
Oosterkamp, A.J.; Hock, B.; Seifert, M.; Irth, H.Trends Anal. Chem. 1997,16, 544–553.
Lee, H.; Peart, T.J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. Int. 1998,81, 1209–1216.
Ternes, T.A.; Stumpf, J.; Mueller, J.; Habere, K.; Wilken, R-D.; Servos, M.Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999,225, 81–90.
Belfroid, A.C.; Van der Horst, A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Schäfer, A.J.; Rijs, G.B.J.; Wegener, J.; Cofino, W.P.The Science of the Total Environment 1999,225, 101–108.
Andreolini, F.; Borra, C.; Caccamo, F.; Di Corcia, A.Anal. Chem. 1987,59, 1720–1725.
Crescenzi, C.; Di Corcia, A.; Passariello, G.; Samperi, R.; Turnes Carou, M.I.J. Chromatogr. 1996,733, 41–55.
Zhang, H.; Henion, J.Anal. Chem. 1999,71, 3955–3964.
Parker, G.A.J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1991,74, 868–873.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gentili, A., Perret, D., Marchese, S. et al. Analysis of free estrogens and their conjugates in sewage and river waters by solid-phase extraction then liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry. Chromatographia 56, 25–32 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02490242
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02490242