Abstract
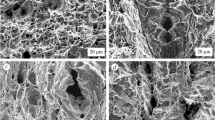
Fracture of materials caused by hydrogen embrittlement is a very serious problem in the operation of pipelines subjected to the effect of hydrogen charging (hydrosulfide-bearing media, external corrosion cracking under stress, contact with active sulfate-reducing bacteria, etc.). As a rule, this damage occurs in the final stage of the process of crack propagation initiated by hydrogen. In order to predict the transition from a subcritical stage to a critical stage of unstable fracture and to calculate the strength characteristics of pipes with cracks of a metallurgical or operational origin we must know the permissible margin of safety with allowance for hydrogen absorption in the operating period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. A. Ezhov, L. P. Gerasimov, and N. F. Kasatkina, “Effect of hydrogen on the properties and fracture of steels with various structures,”Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 2, 23–25 (1978).
V. V. Panasyuk, S. E. Kovchik, and G. I. Smoroda, “Methods for evaluating hydrogen embrittlement of structural materials,”Fiz.-Khim. Mechan. Mater., No. 3, 5–17 (1979).
T. Tough and W. Bolduin, “Effect of different hydrogen concentrations on the ductility of steel,” in:Corrosion Cracking and Brittleness, Coll. Works [in Russian], Mashgiz, Moscow (1961), pp. 166–173.
B. A. Kolachev, “Reversible hydrogen embrittlement of metals,”Fiz.-Khim. Mechan. Mater., No. 3, 17–23 (1979).
M. V. Romaniv, G. N. Nkiforchin, and A. V. Student, “Threshold of corrosion-static crack resistance as a characteristic of competitiveness of various structural alloys,”Fiz.-Khim. Mechan. Mater., No. 2, 20–31 (1985).
A. Ikada, H. Ioshida, and M. Katsuta, “Hydrogen cracking of steel pipes after a long-term hold in a medium of humid hydrogen sulfide (translated by Chetmetinformatsiya, No. 11415),”Tetsu to Hagane,65(3), 433–442 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 14–17, May, 1997.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volgina, N.I., Nasibov, A.G., Ilyukhina, M.V. et al. Evaluation of crack resistance of carbon and low-alloy structural steels under conditions of hydrogen charging. Met Sci Heat Treat 39, 194–197 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02467283
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02467283