Abstract
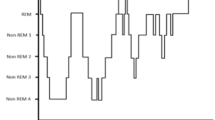
Sleep apnoea is a common disorder that is usually diagnosed through expensive studies conducted in sleep laboratories. Sleep apnoea is accompanied by a characteristic cyclic variation in heart rate or other changes in the waveform of the electrocardiogram (ECG). If sleep apnoea could be diagnosed using only the ECG, it could be possible to diagnose sleep apnoea automatically and inexpensively from ECG recordings acquired in the patient's home. This study had two parts. The first was to assess the ability of an overnight ECG recording to distinguish between patients with and without apnoea. The second was to assess whether the ECG could detect apnoea during each minute of the recording. An expert, who used additional physiological signals, assessed each of the recordings for apnoea. Research groups were invited to access data via the world-wide web and submit algorithm results to an international challenge linked to a conference. A training set of 35 recordings was made available for algorithm development, and results from a test set of 35 different recordings were made available for independent scoring. Thirteen algorithms were compared. The best algorithms made use of frequency-domain features to estimate changes in heart rate and the effect of respiration on the ECG waveform. Four of these algorithms achieved perfect scores of 100% in the first part of the study, and two achieved an accuracy of over 90% in the second part of the study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force (1999): ‘Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research’,Sleep,22, pp. 667–689
Ballora, M., Pennycook, B., Ivanov, P. C., Goldberger, A., andGlass, L. (2000): ‘Detection of obstructive sleep apnea through auditory display of heart rate variability’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 739–740
De Chazal, P., Heneghan, C., Sheridan, E., Reilly, R., Nolan, P., andO'Malley, M. (2000): ‘Automatic classification of sleep apnea epochs using the electrocardiogram’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 745–748
Dimsdale, J. E., Loredo, J. S., andProfant, J. (2000): ‘Effect of continous airway pressure on blood pressure’,Hypertension,35, pp. 144–147
Drinnan, M. J., Murray, A., Griffiths, C. J., andGibson, G. J. (1998): ‘Interobserver variability in recognizing arousal in respiratory sleep disorders’,Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.,158, pp. 358–362
Drinnan, M. J., Allen, J., Langley, P., andMurray, A. (2000): ‘Detection of sleep apnoea from frequency analysis of heart rate variability’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 259–262
Goldberger, A. L., Amaral, A. N., Glass, L., Hausdorff, J. M., Ivanov, P. C., Mark, R. G., Mietus, I. E., Moody, G. B., Peng, C. K., andStanley, H. E. (2000): ‘Physiobank, Physiotoolkit, and Physionet’,Circulation,101, pp. e215-e220
Guilleminault, C., Connolly, S. J., Winkle, R., Melvin, K., andTilkian, A. (1984): ‘Cyclical variation of the heart rate in sleep apnoea syndrome. Mechanisms and usefulness of 24h electrocardiography as a screening technique’,The Lancet,I, pp. 126–131
Hilton, M. F., Bates, R. A., Godfrey, K. R., Chappell, M. J., andCayton, R. M. (1999): ‘Evaluation of frequency and timefrequency spectral analysis of heart rate variability as a diagnostic marker or the sleep apnoea syndrome’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,37, pp. 760–769
Jarvis, M. R.,andMitra, P. P. (2000): ‘Apnea patients characterized by 0.02 Hz peak in the multitaper spectrogram of electrocardiogram signals’,Comput. Cardiol. 27, pp. 769–772
Maier, C., Bauch, M., andDickhaus, H. (2000): ‘Recognition and quantification of sleep apnea by analysis of heart rate variability parameters’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 741–744
Marchesi, C., Paoletti, M., andDi Gaetano, S. (2000): ‘Global waveform delineation for RR series estimation: detecting the sleep apnea pattern’Comput. Cardiol.-Abstracts, p. 71
McNames, J. N., andFraser, A. M. (2000) ‘Obstructive sleep apnea classification based on spectrogram patterns in the electrocardiogram’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 749–752
Mietus, J. E., Peng, C. K., Ivanov, P. C., andGoldberger, A. L. (2000): ‘Detection of obstructive sleep apnea from cardiac interbeat interval time series’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 753–756
Moody, G. B., Mark, R. G., Zoccola, A., andMantero, S. (1985): ‘Derivation of respiratory signals from multi-lead ECGs’,Comput. Cardiol.,12, pp. 113–116
Moody, G. B., Mark R. G., Goldberger, A. L., andPenzel, T. (2000): ‘Stimulating rapid research advances via focused competition: the computers in cardiology challenge 2000’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 207–210
Moody, G. B., Mark, R. G., andGoldberger, A. L. (2001): ‘PhysioNet: a web-based resource for the study of physiologic signals’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol.,20, pp. 70–75
Ng, F., Garcia, I., Gomis, P., La Cruz, A., Passariello, G., andMora, F. (2000): ‘Bayesian hierarchical model with wavelet transform coefficients of the ECG in obstructive sleep apnea screening’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 275–278
Nieto, F. J., Young, T. B., Lind, B. K., Shahar, E., Samet, J. M., Redline, S., D'Agostino, R. B., Newman, A. B., Lebowitz, M. D., andPickering, T. G. (2000): ‘Association of sleepdisordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study’,J. Am. Med. Assoc.,283, pp. 1829–1836
Penzel, T., Amend, G., Meinzer, K., Peter, J. H., andVon Wichert, P. (1990): ‘Mesam: a heart rate and snoring recorder for detection of obstructive sleep apnea’,Sleep,13, pp. 175–182
Penzel, T., Moody, G. B., Mark, R. G., Goldberger, A. L., andPeter, J. H. (2000): ‘The Apnea-ECG database’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 255–258
Raymond, B., Cayton, R. M., Bates, R. A., andChappell, M. J. (2000): ‘Screening for obstructive sleep apnoea based on the electrocardiogram — the Computers in Cardiology Challenge’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 267–270
Roche, F., Gaspoz, J. M., Court-Fortune, I., Minini, P., Pichot, V., Duverney, D., Costes, F., Lacour, J. R., andBarthélémy, J. C. (1999): ‘Screening of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome by heart rate variability analysis’,Circulation,100, pp. 1411–1415
Schrader, M., Zywietz, C., von Einem V., Widiger, B., andJoseph, G. (2000): ‘Detection of sleep apnea in single channel ECGs from the PhysioNet data base’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 263–266
Shinar, Z., Baharav, A., andAkselrod, S. (2000): ‘Obstructive sleep apnea detection based on electrocardiogram analysis’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 757–760
Stein, P. K., andDomitrovich, P. P. (2000): ‘Detecting OSAHS from patterns seen on heart-rate tachograms’,Comput. Cardiol.,27, pp. 271–274
Whitney, C. W., Gottlieb, D. J., Redline, S., Norman, R. G., Dodge, R. R., Shahar, E., Surovec, S.,andNieto, F. J. (1998): ‘Reliability of scoring respiratory disturbance indices and sleep staging’,Sleep,21, pp. 749–757
Young, T., Palta, M., Dempsey, J., Skatrud, J., Weber, S., andBadr, S. (1993): ‘The occurence of sleep-disorderd breathing among middle-aged adults’,New Engl. J. Med.,328, pp. 1230–1235
Young, T., Peppard, P., Palta, M., Hla, K. M., Finn, L., Morgan, B., andSkatrud, J. (1997): ‘Population-based study of sleep-disordered breathing as a risk factor for hypertension’,Arch. Intern. Med.,157, pp. 1746–1752
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penzel, T., McNames, J., de Chazal, P. et al. Systematic comparison of different algorithms for apnoea detection based on electrocardiogram recordings. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 40, 402–407 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345072
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345072