Abstract
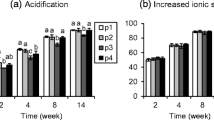
Elemental sulphur was added to three calcareous soils varying in texture, CaCO3 content, native phosphorus and micronutrient content at a rate of 0.5, 1.5 and 3.0% (w/w). The experiment was carried in soil columns which were intermittentantly leached and incubated at 30°C for 3,6,9, and 18 weeks. Sulphur applied at a rate of 0.5% significantly decreased the pH and increased the EC and the soluble sulphate content in all three soils and their leachates with slight differences among soils. Sulphur application generally increased 0.5M NaHCO3 extractable P and DTPA extractable Mn, slightly increased DTPA extractable Fe and Cu but had no significant effect on DTPA extractable Zn. The decrease in soil pH and the increase in DTPA extractable P,Mn,Fe, and Cu upon S-addition were higher with lower CaCO3 content, lower CaCO3/clay ratio and with higher extractable content of these nutrients. Most chemical changes occurred at rate of 0.5% sulphur within 9 weeks of incubation and were largely confined to the soil surface where sulphur was mixed with soil. DTPA extractable Fe and Cu, however, were affected only at higher rates of S-application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Elfattah A A and Hilal M H 1985 Effect of S-application on some properties of Egyptian desert soils.In Proc. Arab Reg. Conf. on Sulphur and Its Usages in the Arab Countries. Riyadh, 2–5, Saudi Arabia Vol. 1, 39–54.
Black C A 1965 Methods of Soil Analysis. Am. Soc. Argron. Madison, Wisc.
Bole J B 1986 Amelioration of calcareous solonetzic, soil by irrigation, deep ripping and acidification with elemental sulphur. Can. J. Soil Sci. 66, 347–356.
Dawood F, Al-Omari S M and Murtatha N 1985 High levels of sulphur affecting availability of some micronutrients in calcareous soils.In Proc. Sec. Reg. Conf. on Sulphur and Its Usage in Arab Countries. Riyadh, 2–5 March 1985, Saudi Arabia. vol. 1, 55–68.
Garcia M E and Carloni L 1977 The effect of sulphur on the solubility and forms of phosphorus in soil. Agrochemica 21, 163–169
Gary C L and Barber S A 1952 Evaluation of certain factors involved in increasing Mn availability with sulphur. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 16, 173–175.
Gupta V R and Mehla I S 1980 Influence of sulphur on the yield and concentration of Cu, Mn, Fe, and Mo in berseem (Trifolium alexandrium) grown in two different soils. Plant and Soil 56, 229–234.
Heter B 1985 Utilization of sulphur for amendment of calcareous soils of Jordan.In Proc. Sec. Reg. Conf. on Sulphur and its Usage in Arab Countries Riyadh 2–5 March, 1985. Saudi Arabia. Vol. 1, 85–100.
Hilal M H and Abd-Elfattah A A 1987 Effect of CaCO3 and clay content of alkali soils on their response to added sulphur. Sulphur Agric. 11, 15–17.
Hilal M H, Al-Badrawy E and Salem A 1985 Effect of sulphur on the properties and productivity of barley and corn in alkaline calcareious soils.In Proc. Sec. Reg. Conf. on Sulphur and Its Usage in Arab Countries. Riyadh 2–5 March, 1985, Saudi Arabia, Vol. 1, 101–118.
Hoeft R G and Sorensen R C 1969 Micronutrient availability in three soil materials as affected by application of zinc, lime and sulphur. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 30, 284–286.
Kashirad A and Bazargani J 1972 Effect of sulphur on pH and availability of phosphorus in calcareous soils. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. bodenkd. 131, 6–13.
Lindsay W L and Norvell W A 1978 Development of DTPA soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn, and Cu. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 321–328.
McCready R G and Krouse H R 1982 Sulphur isotop fractionation during the oxidation of elemental sulphur by Thiobacilli in solonetzic soil. Can. J. Soil Sci. 62, 105–110.
Morsey M Y 1985 Effect of sulphur on alluvial and calcareous soils.In Proc. Sec. Reg. Conf. on Sulphur and Its Usage in Arab Countries. Riyadh 2–5 March., 1985, Saudi Arabia. Vol. 1, 185–200.
Olson S R and Dean L A 1965 Phosphorus.In Methods of Soil Analysis, part 2. Ed. C A Black. Agron. 9, 1035–1048, Amer. Soc. Agron., Madison, Wisc.
Page A L 1982 Methods of Soil Analysis, part 2. Am. Soc. Agron. Madison Wisc.
Procopiou J, Wallace A and Alexander GV 1976 Micronutrient composition of plants grown with high to low levels of sulphur applied to calcareous soil in glasshouse. Plant and Soil 44, 359–365.
Rida M and Modaihsh A S 1988 Gypsum formation in sulphur treated calcareous soilf. Jrab Gulf J. Scient. Res.submitted
Shadfan H and Hussen A A 1985 Effect of sulphur application on the availability of P, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu in selected Saudi soils.In Proc. Sec. Reg. Conf. on Sulphur and its Usage in Arab Countries. Riyadh 2–5 March, 1985, Saudi Arabia. Vol. 1, 3–24.
Tisdale S L and Bertramson B R 1949 Elemental sulphur and its relationship to Mn availability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 14, 131–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Modaihsh, A.S., Al-Mustafa, W.A. & Metwally, A.I. Effect of elemental sulphur on chemical changes and nutrient availability in calcareous soils. Plant Soil 116, 95–101 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02327261
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02327261