Abstract
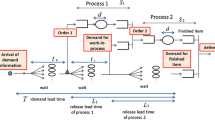
In inventory control and production planning one is tempted to use one of two strategies: produce all demand to stock or produce all demand to order. The disadvantages are well-known. In the ‘make everything to order’ case (MTO) the response times may become quite long if the load is high, in the ‘make everything to stock’ case (MTS) one gets an enormous inventory if the number of different products is large.
In this paper we study two simple models which combine MTO and MTS, and investigate the effect of combining MTO and MTS on the production lead times.
Zusammenfassung
In Lagerhaltung und Produktionsplanung werden überwiegend zwei alternative Strategien betrachtet: Produktion auf Bestellung oder auf Vorrat. Die Nachteile sind bekannt. Die erste Strategie kann zu sehr langen Durchlaufzeiten führen, die zweite zu hohen Beständen, insbesondere bei großer Produktanzahl. In dieser Arbeit werden zwei Modelle betrachtet, in denen die beiden Betrachtungsweisen kombiniert werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adan IJBF, van Doorn EA, Resing JAC, Scheinhardt, WRW (1996) A queueing system with two different service speeds. Memorandum COSOR 96-12, Department of Mathematics and Computing Science, Eindhoven University of Technology
Buzacott JA, Shanthikumar JG (1993) Stochastic models of manufacturing systems. Prentice Hall, New York
Carr AS, Güllü AR, Jackson PL, Muckstadt JA (1993) An exact analysis of a production-inventory strategy for industrial suppliers. Working paper, School of Operations Research and Industrial Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
Coddington EA, Levinson N (1955) Theory of ordinary differential equations. McGraw-Hill, London
Federgruen A, Katalan Z (1994) Make-to-stock or make-to-order: that is the question; novel answers to an ancient debate. Working paper, Graduate School of Business, Columbia University, New York
Kleinrock L (1975) Queueing systems, Vol. I. Theory. Wiley, New York
Neuts MF (1981) Matrix-geometric solutions in stochastic models. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Sox CR, Thomas LJ, McClain JO (1994) Jellybeans: Sorting capacity to improve service. Working paper, Department of Industrial Engineering, Auburn University, Alabama
Williams TM (1984) Special products and uncertainty in production/inventory systems. EJOR15: 46–54
Wolff RW (1982) Poisson arrivals see time averages. Opns. Res.30: 223–231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adan, I.J.B.F., van der Wal, J. Combining make to order and make to stock. OR Spektrum 20, 73–81 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01539854
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01539854