Summary
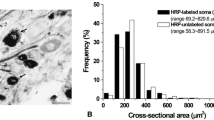
In the spinal trigeminal nucleus of the adult cat, the neuropil of the substantia gelatinosa (SG) layer is made up of axonal endings of V nerve axons, dendrites and axons of SG neurons and dendrites of marginal and magnocellular neurons. A typical SG glomerulus consists of a centrally located V nerve ending which contains large synaptic vesicles and forms asymmetrical axodendritic synapses on two kinds of dendritic spines and on dendritic shafts. The dendritic processes of the SG glomerulus are linked by two kinds of dendrodendritic synapses: type 2 dendritic spines, containing large synaptic vesicles, form slightly asymmetrical (intermediate) synapses on type I dendritic spines. Dendritic shafts, containing clusters of small synaptic vesicles, form symmetrical dendrodendritic synapses amongst themselves and on type I dendritic spines. Small axonal endings, containing small synaptic vesicles form intermediate axodendritic synapses on type I dendritic spines and on dendritic shafts. These small axons also form symmetrical axoaxonic synapses on the V nerve ending. The V nerve endings in the SG layer are dark and differ morphologically from the pale V nerve endings in other parts of the trigeminal nuclei.
The data are interpreted based on considerations that some marginal and magnocellular neurons are projection neurons and that some SG neurons are interneurons which form inhibitory synapses. The following circuits in the SG glomeruli are suggested: V nerve endings form excitatory synapses on the dendrites of projection neurons (marginal and magnocellular neurons) and on the dendrites of inhibitory interneurons (SG neurons). The interneurons inhibit transmission through the V nerve-projection neuron circuit by means of their axoaxonic synapses on the V nerve endings. Interneurons are linked together through inhibitory dendrodendritic synapses along their dendritic shafts. Two interpretations of dendrodendritic circuits between projection neurons and interneurons are considered. The morphologically distinct V nerve innervation of the SG layer and the internal circuitry of the SG glomeruli appear to be essential for the perception of thermal and painful stimuli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan-Palay, V. andPalay, S. L. (1971) The synapseen marron between Golgi II neurons and mossy fibres in the rat cerebellar cortex.Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 133, 274–87.
Colonnier, M. (1968) Synaptic patterns on different cell types in the different laminae of cat visual cortex. An electron microscope study.Brain Research 9, 268–87.
Conradi, S. (1969) Ultrastructure of dorsal root boutons on lumbosacral motoneurons of the adult cat, as revealed by dorsal root section.Acta Physiologica Scandinavica Supplementum322, 85–115.
Darian-Smith, I. (1965) Presynaptic component in the afferent inhibition observed within the trigeminal brain-stem nuclei of the cat.Journal of Neurophysiology 28, 695–709.
Darian-Smith, I. andYokota, T. (1966) Cortifugal effects on different neuron types within the cats brain stem activated by tactile stimulation of the face.Journal of Neurophysiology 29, 185–206.
Diamond, J., Gray, E. G. andYasargil, G. M. (1970) The function of the dendritic spine: An hypothesis. InExcitatory Synaptic Mechanisms (edited byAnderson, P. andJansen, J. K. S.), pp. 213–22. Oslo-Bergen-Tromso: Universtitetsforlaget.
Dowling, J. E. andWerblin, F. S. (1969) Organization of the retina of the mudpuppy,Necturus maculosus. I Synaptic structure.Journal of Neurophysiology 32, 315–38.
Dubner, R., Sumino, R. andStarkman, S. (1973) Responses of facial cutaneous thermosensitive and mechanosensitive afferent fibres in the monkey to noxious heat stimulation. InAdvances in Neurology, Vol. 4 International Symposium on Pain, (edited byBonica, J.) In press.
Eccles, J. C., Llinas, R. andSasaki, K. (1966) The mossy fibre-granule cell relay of the cerebellum and its inhibitory control by Golgi cells.Experimental Brain Research 1, 82–101.
Famiglietti, E. V. andPeters, A. (1972) The synaptic glomerulus and the intrinsic neuron in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 144, 285–334.
Gobel, S. (1971) Structural organization in the main sensory trigeminal nucleus. InOral-Facial Sensory and Motor Mechanisms (edited byDubner, R. andKawamura, Y.) pp. 183–204. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Gobel, S. andDubner, R. (1969) Fine structural studies of the main sensory trigeminal nucleus in the cat and rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 137, 459–94.
Gobel, S. andPurvis, M. B. (1972) Anatomical studies of the organization of the spinal V nucleus: The deep bundles and the spinal V tract.Brain Research 48, 27–44.
Gordon, G., Landgren, S. andSeed, W. A. (1961) The functional characteristics of single cells in the caudal part of the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve of the cat.Journal of Physiology (London) 158, 544–59.
Guillery, R. W. (1969) The organization of synaptic interconnections in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie 96, 1–38.
Hámori, J. andSzenthágothai, J. (1966) Participation of Golgi neuron processes in the cerebellar glomeruli: an electron microscope study.Experimental Brain Research 2, 35–48.
Jones, E. G. andPowell, T. P. S. (1970) An electron microscopic study of terminal degeneration in the neocortex of the cat.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B 257, 29–43.
Karnovsky, M. J. (1965) A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy.Journal of Cell Biology 27, 137A.
Kerr, F. W. L. (1970) The fine structure of the subnucleus caudalis of the trigeminal nerve.Brain Research 23, 129–45.
Kerr, F. W. L. (1970) The organization of primary afferents in the subnucleus caudalis of the trigeminal: A light and electron microscopic study of degeneration.Brain Research 23, 147–65.
Kerr, F. W. L. (1971) Electron microscopic observations on primary deafferentation of subnucleus caudalis of the trigeminal nerve. InOral-Facial Sensory and Motor Mechanisms (edited byDubner, R. andKawamura, Y.) pp. 159–82. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Larramendi, L. M. H., Fickenscher, L. andLemkey-Johnston, N. (1967) Synaptic vesicles of inhibitory and excitatory terminals in the cerebellum.Science 156, 967–9.
Lenn, N. J. andReese, T. S. (1966) The fine structure of nerve endings in the nucleus of the trapezoid body and the ventral cochlear nucleus.American Journal of Anatomy 118, 375–90.
Lieberman, A. R. (1973) Neurons with presynaptic perikarya and presynaptic dendrites in the rat lateral geniculate nucleus.Brain Research 59, 35–59.
Lund, R. D. (1969) Synaptic patterns of the superficial layers of the superior colliculus of the rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 135, 179–208.
Melzack, R. andWall, P. D. (1965) Pain mechanisms: A new theory.Science 150, 971–9.
Morest, D. K. (1971) Dendrodendritic synapses of cells that have axons: The fine structure of the Golgi type II cell in the medial geniculate body of the cat.Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 133, 216–46.
Mosso, J. A. andKruger, L. (1973) Receptor categories represented in spinal trigeminal nucleus caudalis.Journal of Neurophysiology 36, 472–88.
Olszewski, J. (1950) On the anatomical and functional organization of the trigeminal nucleus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 92, 401–13.
O'neal, J. T. andWestrum, L. E. (1973) The fine structural synaptic organization of the cat lateral cuneate nucleus. A study of sequential alterations in degeneration.Brain Research 51, 97–124.
Peach, R. (1972) Fine structural features of light and dark cells in the trigeminal ganglion of the rat.Journal of Neurocytology 1, 151–60.
Pinching, A. J. andPowell, T. P. S. (1971) The neuropil of the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb.Journal of Cell Science 9, 347–78.
Poulos, D. A. (1971) Trigeminal temperature mechanisms. InOro-facial Sensory and Motor Mechanisms (edited byDubner, R. andKawamura, Y.), pp. 47–72. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Ralston, H. J., III (1969) The synaptic organization of lemniscal projections to the ventrobasal thalamus of the cat.Brain Research 14, 99–115.
Ralston, H. J., III. (1971) The synaptic organization in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and in the ventrobasal thalamus in the cat. InOral-Facial Sensory and Motor Mechanisms (edited byDubner, R. andKawamura, Y.) pp. 229–50. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Ralston, H. J., III andHerman, M. M. (1969) The fine structure of neurons and synapses in the ventrobasal thalamus of the cat.Brain Research 14, 77–97.
Ramón Y Cajal, S. (1909)Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés. Vol. 1. pp. 393–429; 859–88. Madrid: Instituto Ramón y Cajal. (1952 Reprint).
Rustioni, A., Sanyal, S. andKuypers, H. G. J. M. (1971) A histochemical study of the distribution of the trigeminal divisions in the substantia gelatinosa of the rat.Brain Research 32, 45–52.
Scheibel, M. E. andScheibel, A. B. (1968) Terminal axonal patterns in cat spinal cord. II. The dorsal horn.Brain Research 9, 32–58.
Sjöqvist, O. (1938) Studies of pain conduction in the trigeminal nerve. A contribution to the surgical treatment of facial pain.Acta Psychiatrica et Neurologica Scandinavica Supplementum17, 1–139.
Stensaas, L. J. andStensaas, S. S. (1968) Astrocytic neuroglial cells, oligodendrocytes and microgliacytes in the spinal cord of the toad. I. Light microscopy.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 84, 473–89.
Stewart, Jr., D. H., Scibetta, C. J. andKing, R. B. (1967) Presynaptic inhibition in the trigeminal relay nuclei.Journal of Neurophysiology 30, 135–53.
Sumino, R., Dubner, R. andStarkman, S. (1973) Responses of small myelinated ‘warm’ fibres to noxious heat stimuli applied to the monkey's face.Brain Research 62, 260–3.
Trevino, D. L., Coulter, J. D. andWillis, W. D. (1973) Location of cells or origin of spinothalamic tract in lumbar enlargement of the monkey.Journal of Neurophysiology 36, 750–61.
Uchizono, K. (1965) Characteristics of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central nervous system of the cat.Nature 207, 642–3.
Vaughn, J. E. andPeters, A. (1966) Aldehyde fixation of nerve fibres.Journal of Anatomy (London) 100, 687.
Wall, P. D. (1964) Presynaptic control of impulses at the first central synapse in the cutaneous pathway.Progress in Brain Research 12, 92–118.
Westrum, L. E. andBlack, R. G. (1971) Fine structural aspects of the synaptic organization of the spinal trigeminal nucleus (Pars interpolaris) of the cat.Brain Research 25, 265–88.
White, E. L. (1972) Synaptic organization in the olfactory glomerulus of the mouse.Brain Research 37, 69–80.
Witkovsky, P. andDowling, J. E. (1969) Synaptic relationships in the plexiform layers of carp retina.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 100, 60–82.
Wong-Riley, M. T. T. (1972) Changes in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the squirrel monkey after unilateral ablation of visual cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 146, 519–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gobel, S. Synaptic organization of the substantia gelatinosa glomeruli in the spinal trigeminal nucleus of the adult cat. J Neurocytol 3, 219–243 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01098390
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01098390