Abstract
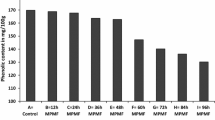
The changes in proximate composition, phytate phosphorus, thiamine and ascorbic acid content of finger millet, pearl millet and foxtail millet during progressive germination were studied. Germination resulted in a slight decrease in total protein and minerals, a marked fall in phytate-phosphorus and a significant increase in the ascorbic acid content of the millets. An increase in lysine and tryptophan but no appreciable changes in threonine and sulfur amino acid content of the millets were observed as a result of germination. However, the protein efficiency ratio values of ungerminated control seeds, 48 h germinated green malt and kilned malt were not significantly different.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (1969) Approved methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists. St. Paul, Minnisota, USA
Barton-Wright EC (1952) The microbiological assay of vitamin B-complex and amino acids. Sir Issac Pitman & Sons Ltd., London
Dalby A, Tsai CY (1979) Lysine and tryptophan increases during germination of cereal grains. Cereal Chem 53:222–226
Fordham JR, Wells CE, Chen LH (1975) Sprouting of seeds and nutrient composition of seeds and sprouts. J Food Sci 40:552–556
Gopaldas T, Inamdar F, Patel J (1982) Malted versus toasted young child mixes: viscosity, storage and acceptability trials. Indian J Nutr Dietet 19:327–336
Goldberg L, Thorp JM (1945) A survey of vitamins in African foodstuffs. VI. Thiamine, riboflavin and nicotinic acid in sprouted and fermented cereal foods. S Afr J Med Sci 10:177–185
Hamad AM, Fields ML (1979) Evaluation of protein quality and available lysine of germinated and fermented cereals. J Food Sci 44:456–459
Hemanalini G, Umapathy KP, Rao JR, Saraswathi G (1980) Nutritive evaluation of sprouted ragi. Nutr Rep Int 22:271–277
ISI Guidelines No. 7481 (1974) Method for determination of protein efficiency ratio. Indian Standards Institution, New Delhi
Indira R, Naik MS (1971) Nutrient composition and protein quality of some minor millets. Indian J Agric Sci 41:795–797
Lorenz K (1980) Cereal sprouts: composition, nutritive value, food applications. CRC Cri Revs Food Sci Nutr 13:353–385
Malleshi NG, Desikachar HSR (1982) Formulation of a weaning food with low hot paste viscosity based on malted ragi and green gram. J Food Sci Technol 19:193–197
Malleshi NG (1984) Studies on malting of millet grains. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Mysore, Mysore, India
Malleshi NG, Desikachar HSR (1986) The influence of malting conditions on the quality of finger millet malt. J Inst Brew 92:81–83
Narayana Rao M, Kurien PP, Swaminathan M, Subrahmanyan V (1961) Nutritive value of certain cereals and cereal diets consumed in India. Food Sci (Mysore) 10:163–175
Pokhriyal TG, Chatterjee SR, Abrol YP (1977) Protein content and amino acid composition of pearl millet. J Food Sci Technol 14:231–233
Ram PC, Lodha ML, Srivastava KN, Tyagi RS, Joginder Singh, Mehta SL (1979) Improving nutritive value of maize by germination. J Food Sci Technol 16:258–260
Robinson WB, Stotz E (1945) The Indophenol-xylene extraction method for ascorbic acid and modification for interfering substances. J Biol Chem 160:217–225
Swaminathan M (1942) An improved method for the estimation of vitamin B in foods by thiochrome reaction. Indian J Med Res 30:263–272
Virupaksha TK, Ramachandra G, Nagaraju D (1975) Seed proteins of finger millet and their amino acid composition. J Sci Food Agric 26:1237–1246
Wheeler EL, Farrel RE (1971) A method for phytic acid determination in wheat and wheat fractions. Cereal Chem 48:312–320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malleshi, N.G., Desikachar, H.S.R. Nutritive value of malted millet flours. Plant Food Hum Nutr 36, 191–196 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01092036
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01092036