Abstract
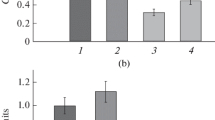
Experiments were conducted to elucidate the effects of chronic low power-level microwave radiation on the immunological systems of rabbits. Fourteen male Belgian white rabbits were exposed to microwave radiation at 5 mW/cm2, 2.1 GHz, 3 h daily, 6 days/week for 3 months in two batches of 7 each in specially designed miniature anechoicchambers. Seven rabbits were subjected to sham exposure for identical duration. The microwave energy was provided through S band standard gain horns connected to a 4K3SJ2 Klystron power amplifier. The first batch of animals were assessed for T lymphocyte-mediated cellular immune response mechanisms and the second batch of animals for B lymphocyte-mediated humoral immune response mechanisms. The peripheral blood samples collected monthly during microwave/sham exposure and during follow-up (5/14 days after termination of exposures, in the second batch animals only) were analysed for T lymphocyte numbers and their mitogen responsiveness to ConA and PHA. Significant suppression of T lymphocyte numbers was noted in the microwave group at 2 months (P<0.01, Δ% 21.5%) and during follow-up (P<0.01, Δ% 30.2%). The first batch animals were initially sensitised with BCG and challenged with tuberculin (0.03 ml) at the termination of microwave irradiation/sham exposure and the increase in foot pad thickness (Δ mm), which is a measure of T cell-mediated immunity (delayed type hypersensitivity response, DTH) was noted in both the groups. The microwave group revealed a better response than the control group (Δ%+12.4 vs.+7.54). The animals were sacrified and the tissue T lymphocyte counts (spleen and lymph node) were analysed. No significant variation was observed in the tissue T lymphocyte counts of microwave-irradiated rabbits. From these results it is speculated that the T lymphocytes are sequestered to various lymphoid organs under the influence of microwaves. A sub-population of T cells known as T helper cells (mediating DTH response) are probably not affected by microwave radiation. It is clear from our experiments that although chronic microwave radiation at 5 mW/cm2 leads to suppression of peripheral T lymphocyte numbers, there is no concomitant functional impairment of these cells as evidenced by functional assays.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American National Standards Institute Committee (1982) Safety levels with respect to human exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields, 300 KHz to 100 GHz. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, New York, NY 10017. ANSI Committee C 95.1
Baranska W (1967) Lymphoblastoid transformation of lymphocytes in vitro after microwave irradiation. Nature 214:102
Baranski S (1971) Effect of chronic microwave irradiation on the blood forming system of guinea pigs and rabbits. Aerosp Med 42:1196
Baranski S (1972) Effect of microwaves on the reactions of the white blood cell system. Acta Physiol Pol 23:685–695
Chou CK, Guy AW, Bornemen LE, Kunz LL, Kramer P (1983) Chronic exposure of rabbits to 0.5 and 5 mW/cm2 2450 MHz CW microwave radiation. Bioelectromagnetics 4:63–77
Czerski P (1975) Microwave effects on the blood forming system with particular reference to the lymphocyte. Ann NY Acad Sci 247:232–241
Durney CH, Johnson CC, Barber PW, Iskander MF, Lords JL, Ryser DK, Allen SJ, Mitchell JC (1978) Radiofrequency radiation dosimetry handbook, 2nd edn. Report SAM-TR-78-22 Brooks AFB, USAF Texas
Guy AW (1979) Miniature anechoic chamber for chronic exposure of small animals to plane wave microwave fields. J Microw Power 14:327–338
Huang AT, Engle ME, Elder JA, Kinn JB, Ward TR (1977) The effect of microwave radiation (2450 MHz) on the morphology and chromosomes of lymphocytes. Radio Sci (Suppl) 12:173
McRee DI, Faith R, Mc Cornell EE, Guy AW (1980) Long term 2450 MHz CW microwave irradiation of rabbits: Evaluation of haematological and immunological effects. J Microw Power 15:45
Nageswari KS, Tandon HC, Varma S, Bhatnagar VM (1982) Effects of prolonged low power microwave radiation on peripheral leucocyte counts in rabbits. Indian J Med Res 75:453–459
Roszkowski W, Rosykowski K, Wrembel JK, Szmigielski S, Pulverer G, Jeljaszewicz J (1981) Effect of whole body hyperthermia on delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity to oxalazone in mice. J Clin Lab Immunol 6:257–261
Shandala MG, Rudnex MI, Vinogradov GK, Belonozhko NG, Gonchar NM (1977) Immunological and haematological effects of microwaves at low power densities. In: Proceedings of International Union of Radio Science Symposium on Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Waves. Airlie VA, p 84
Smialowicz RJ, Kinn JB, Elder JA (1979a) Perinatal exposure of rats to 2450 MHz (CW) microwave radiation: effects on lymphocytes. Radio Science 14(65):147
Smialowicz RJ, Riddle MM, Brugnolotti PL, Sperazza JM, Kinn JB (1979b) Evaluation of lymphocyte function in mice exposed to 2450 MHz (CW) microwaves. In: Stuchly SS (ed) Proceedings of the Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Biosystems. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, p 122
Smialowicz RJ, Compton KL, Riddle MM, Rogers RR, Brugnolotti PL (1980) Microwave radiation (2450 MHz) alters the endotoxin induced hypothermic response of rats. Bioelectromagnetics 1:353
Szmigielski S, Szudzinski A, Piestraszek A, Bielec M, Janiak M, Wrembel JK (1982) Accelerated development of spontaneous and benzopyrene induced skin cancer in mice exposed to 2450 MHz microwave radiation. Bioelectromagnetics 3:179
Wiktor-Jedrzejczak W, Ahmed A, Czerski P, Leach WM, Sell KW (1977) Immune response of mice to 2450 MHz microwave radiation: overview of immunology and empirical studies of lymphoid splenic cells. Radio Science (Suppl) 12:209
Wilson AB, Gurner BW, Coombs RRA (1975) Observations on rabbit thymocytes and peripheral T Cells. Int Arch Allergy 48:383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nageswari, K.S., Sarma, K.R., Rajvanshi, V.S. et al. Effect of chronic microwave radiation on T cell-mediated immunity in the rabbit. Int J Biometeorol 35, 92–97 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01087483
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01087483