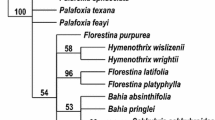
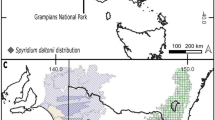
Abstract
A detailed analysis of chloroplast DNA restriction fragment length variation was undertaken to reconstruct the maternal phylogeny of 18 taxa from both sections of the papilionoid tropical forage legume genusStylosanthes. Data were analysed by means of the computer program PAUP, using an heuristic search with Wagner parsimony. The resulting cladogram dividedStylosanthes into four separate clades, which comprised: (i) theS. guianensis complex and related species (i.e.S. gracilis, S. grandifolia andS. montevidensis); (ii)S. hispida, tetraploidS. hamata s. l.,S. sympodialis, S. humilis, S. leiocarpa, S. angustifolia and certain accesions ofS. scabra; (iii)S. calcicola, S. viscosa, diploidS. hamata s. str., andS. fruticosa, plus accessions ofS. scabra, S. capitata and one accession ofS. grandifolia; and (iv)S. macrocephala and other accessions ofS. capitata not included within clade 3. Results are generally congruent with previously established interspecific relationships and, moreover, enabled identification of putative maternal progenitors for four tetraploid taxa:S. humilis was identified as a likely maternal parent of bothS. sympodialis andS. hamata s. l.,S. viscosa as a maternal parent ofS. scabra, andS. macrocephala as a maternal parent ofS. capitata.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum, B. R., 1992: Combining trees as a way of combining data sets for phylogenetic inference and the desirability of combining gene trees. — Taxon41: 3–10.
Bremer, K., 1988: The limits of amino acid sequence data in angiosperm phylogenetic reconstruction. — Evolution42: 795–803.
Bremer, B., 1991: Restriction data from chloroplast DNA for phylogenetic reconstruction: is there only one accurate way of scoring? — Pl. Syst. Evol.175: 39–54.
Burt, R. L., 1984: Natural variation inStylosanthes. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 103–124. — London, New York: Academic Press.
—, 1971: Numerical analysis of variation patterns in the genusStylosanthes, as an aid to plant introduction and assessment. — Austral. J. Agric. Res.25: 559–575.
—, —, —, 1974: Small sward testing ofStylosanthes in northern Australia. — Austral. J. Agric. Res.25: 559–575.
Caputo, P., Stevenson, D. W., Wurtzel, E. T., 1991: A phylogenetic analysis of AmericanZamiaceae (Cycadales) using chloroplast DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms. — Brittonia73: 135–145.
Clegg, M. T., Zurawski, G., 1992: Chloroplast DNA and the study of plant phylogeny: present status and future prospects. — InSoltis, P. S., Soltis, D. E., Doyle, J. J., (Eds): Molecular systematics of plants, pp. 1–13. — New York, London: Chapman & Hall.
Coates, D., Cullis, C. A., 1987: Chloroplast DNA variability amongLinum species. — Amer. J. Bot.74: 260–268.
Costa, N. M. S., Ferreira, M. B., 1984: Some Brazilian species ofStylosanthes. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 49–72. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Curtis, M. D., Cameron, D. F., Manners, J. M., 1995: Molecular evidence that diploidStylosanthes humilis and diploidStylosanthes hamata are progenitors of allotetraploidStylosanthes hamata cv. Verano. — Genome38: 344–348.
Dillon, M. O., 1980: Flora of Panama. 42.Stylosanthes. — Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard.67: 722–776.
Doebley, J., 1989: Molecular evidence for a missing wild relative of maize and the introgression of its chloroplast genome intoZea perennis. — Evolution43: 1555–1559.
—, 1992: Chloroplast DNA variation and the phylogeny ofHordeum (Poaceae). — Amer. J. Bot.79: 576–584.
Doyle, J. J., Doyle, J. L., Brown, A. H. D., 1990: Multiple origins of polyploids in the B genome ofGlycine subgenusGlycine (Leguminosae). — Amer. J. Bot.77: 772–782.
Dorado, O., Rieseberg, L. H., Arias, D. M., 1991: Chloroplast DNA introgression in Southern California sunflowers. — Evolution46: 566–572.
Edye, L. A., 1987: Potential ofStylosanthes for improving tropical grasslands. — Outlook Agric.16: 124–130.
Feinberg, A. P., Vogelstein, B., 1983: A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. — Analytical Biochem.132: 6–13.
Ferreira, M. B., Costa, N. M. S., 1979: O generoStylosanthes Sw. no Brasil. — EPAMIG Belo Horizonte.
Gardener, C. J., 1984: The dynamics ofStylosanthes pastures. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 333–358. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Gillard, P., Winter, W. H., 1984: Animal production fromStylosanthes based pastures in Australia. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 405–432. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Gillies, A. C. M., 1994: Molecular analysis of genetic diversity and evolutionary relationships in the tropical legume genusStylosanthes (Aubl.)Sw. — Ph.D. Thesis, University of St. Andrews.
Glover, B. J., Gillies, A. C. M., Abbott, R. J., 1994: Use of the polymerase chain reaction to investigate the delimitation of two agronomically important species ofStylosanthes (Aubl.)Sw. — Bot. J. Scotland47: 83–96.
Harris, S. A., Ingram, R., 1991: Chloroplast DNA and biosystematics: the effect of intraspecific diversity and plastid transmission. — Taxon40: 393–412.
—, —, 1992: Molecular systematics of the genusSenecio L. II. The origin ofS. vulgaris L. — Heredity69: 112–121.
—, 1994: A phylogenetic analysis ofLeucaena (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae). — Pl. Syst. Evol.19: 1–26.
Kazan, K., Manners, J. M., Cameron, D. F., 1993a: Genetic variation in agronomically important species ofStylosanthes determined using random amplified polymorphic markers. — Theor. Appl. Genet.85: 882–888.
—, —, —, 1993b: Inheritance of random amplified polymorphic markers in an inter-specific cross in the genusStylosanthes. — Genome36: 50–56.
—, —, —, 1993c: Genetic relationships and variation in theStylosanthes guianensis (Aubl.)Sw. species complex assessed by random amplified polymorphic DNA. — Genome36: 43–49.
Kirkbride, J. H., Kirkbride, C. G., 1987: Typification ofStylosanthes (Leguminosae) and its sections. — Taxon36: 455–458.
Lazier, J. R., 1984: Global adventures inStylosanthes IV: West Africa. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 503–528. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Lewis, G., 1987: Legumes from Bahia. — Kew: Royal Botanic Gardens.
Mannetje, L. 'T, 1969:Rhizobium affinities and phenetic relationships within the genusStylosanthes. — Austral. J. Bot.17: 553–564.
—, 1977: A revision of varieties ofStylosanthes guianensis (Aubl.)Sw. — Austral. J. Bot.25: 347–362.
—, 1984: Considerations on the taxonomy of the genusStylosanthes. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 1–23. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Mohlenbrock, R. H., 1957: A revision of the genusStylosanthes. — Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard.44: 299–355.
Moretti, A., Caputo, P., Cozzolino, S., de Luca, P., Gaudio, L., Siniscalco Gigliano, G., Stevenson, D. W., 1993: A phylogenetic analysis ofDioon (Zamiaceae). — Amer. J. Bot.80: 2204–2214.
Olmstead, R. G., Palmer, J. D., 1994: Chloroplast DNA systematics—a review of methods and data analysis. — Amer. J. Bot.81: 1205–1224.
Palmer, J. D., 1986: Isolation and structural analysis of chloroplast DNA. — Meth. Enzymol.118: 167–186.
—, 1987: Chloroplast DNA evolution and biosystematic uses of chloroplast DNA variation. — Amer. Naturalist.130: 456–529.
—, 1988: Chloroplast DNA variation and plant phylogeny. — Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard.75: 1180–1206.
—, 1983: Chloroplast DNA and the origin of amphidiploidBrassica species. — Theor. Appl. Genet.65: 181–189.
—, 1982: Chloroplast DNA evolution and phylogenetic relationships inLycopersicon. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA79: 55006–5010.
Potter, D., Doyle, J. J., 1994: Phylogeny and systematics ofSphenostylis andNesphostylis (Leguminosae: Phaseoleae) based on morphological and chloroplast DNA data. — Syst. Bot.19: 389–406.
Rieseberg, L. H., Brunsfeld, S. J., 1992: Molecular evidence and plant introgression. — InSoltis, P. S., Soltis, D. E., Doyle, J. J., (Eds): Molecular systematics of plants, pp. 151–176. — London, New York: Chapman & Hall.
—, 1991: Phylogenetic consequences of cytoplasmic gene flow in plants. — Evol. Trends Pl.5: 65–84.
Robinson, P. J., Megarrity, R. G., 1975: Characterisation ofStylosanthes introductions by using seed protein patterns. — Austral. J. Agric. Res.26: 467–479.
Schultze-Kraft, R., Costa, N. M. S., Flores, A., 1984:Stylosanthes macrocephala M. B. Ferr etS. Costa—collection and preliminary agronomic evaluation of a new tropical pasture legume. — Trop. Agric. (Trinidad)61: 230–240.
Smith, R. L., Sytsma, K. J., 1990: Evolution ofPopulus nigra (Sect.Aigeiros) introgressive hybridisation and the chloroplast contribution ofPopulus alba (Sect.Populus). — Amer. J. Bot.77: 1176–1187.
Soltis, P. S., Doyle, J. J., Soltis, D. E., 1992: Molecular data and polyploid evolution in plants. — InSoltis, P. S., Soltis, D. E., Doyle, J. J., (Eds): Molecular systematics of plants, pp. 177–201. — London, New York: Chapman & Hall.
Soltis, D. E., Soltis, P. S., 1989: Allopolyploid speciation inTragopogon: insights from chloroplast DNA. — Amer. J. Bot.76: 1119–1124.
Southern, E. M., 1975: Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. — J. Molec. Biol.98: 503–517.
Stace, H. M., 1981: Breeding systems and species relationships inStylosanthes. — In: CSIRO Division of Tropical Crops and Pastures, Annual Report, p. 36.
—, 1982: Breeding systems inStylosanthes I. Observations of outcrossing inS. scabra at an alcohol dehydrogenase locus. — Austral. J. Agric. Res.33: 87–96.
—, 1984: Cytogenetics and the evolution ofStylosanthes. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 50–72. — London, New York: Academic Press.
—, —, 1987: Cytogenetic reviews of taxa inStylosanthes hamata sensu lato. — Trop. Grasslands21: 182–188.
Sutherst, R. W., Jones, R. J., Schnitzerling, H. J., 1982: Tropical legumes of the genusStylosanthes immobilize and kill cattle ticks. — Nature295: 320–321.
—, 1988: A survey of the ability of tropical legumes in the genusStylosanthes to trap larvae of the cattle tick,Boophilus microplus. — Austral. J. Exp. Agric.28: 473–479.
Swartz, O., 1788: Prod. Veg. Ind. Occ. 108.
Swofford, D. L., 1993: PAUP—Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, version 3.1. Computer program distributed by the Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign USA.
—, 1990: Phylogeny construction. — InHillis, D. M., Moritz, C., (Eds): Molecular systematics, pp. 411–501. — Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer.
Sytsma, K. J., Schaal, B. A., 1985: Phylogenetics of theLisianthus skinneri (Gentianaceae) species complex in Panama utilising DNA restriction fragment analysis. — Evolution39: 594–608.
Thomas, D., 1984: Global adventures inStylosanthes I: South America. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 451–466. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Vogel, J. R. T., 1838: de Hedysareis Brasiliae. — Linnaea12: 63–71.
Waugh, R., van de Ven, G. T. W., Phillips, M. S., Powell, W., 1990: Chloroplast DNA diversity in the genusRubus (Rosaceae) revealed by Southern hybridisation. — Pl. Syst. Evol.37: 221–244.
Wendel, J. F., Stewart, J. McD., Rettig, J. H., 1991: Molecular evidence for homoploid reticulate evolution among Australian species ofGossypium. — Evolution45: 694–711.
Whittemore, A. T., Schaal, B. A., 1991: Interspecific gene flow in sympatric oaks. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA88: 2540–2544.
Williams, R. J., Reid, R., Schultze-Kraft, R., Sousa Costa, N. M., Thomas, B. D., 1984: Natural distribution ofStylosanthes. — InStace, H. M., Edye, L. A., (Eds): The biology and agronomy ofStylosanthes, pp. 73–102. — London, New York: Academic Press.
Wolfe, P. G., Soltis, D. E., Soltis, P. S., 1990: Chloroplast DNA and allozyme variation in diploid and autotetraploidHeuchera grossulariifolia (Saxifragaceae). — Amer. J. Bot.77: 232–244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillies, A.C.M., Abbott, R.J. Phylogenetic relationships in the genusStylosanthes (Leguminosae) based upon chloroplast DNA variation. Pl Syst Evol 200, 193–211 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984935
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984935