Summary
-
1.
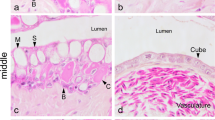
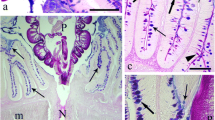
Scanning electron microscopy of the intestinal epithelium in the cel showed an important mucus layer over the middle intestine.
-
2.
Ion-selective microelectrodes (Na+, Cl−, K+) demonstrated several standing gradients of ion activities in the mucus layer.
-
3.
The Na+ and Cl− gradients were identical and related to transepithelial NaCl absorption. They were cancelled by ouabain application on the serosal side.
-
4.
Symmetrical substitution of Na+ or Cl− in the luminal and serosal Ringer solution gave results in agreement with the presence of an apical Na+−K+−2Cl− cotransport system, and of K+ channels.
-
5.
The intestinal mucus appeared, at least in the middle part of the intestine, to act as a diffusion barrier essential to K+ recycling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SW :
-
seawater
- SEM :
-
scanning electron microscope
- TEM :
-
transmission electron microscope
- ISM :
-
ion-selective microelectrode
- PD sm :
-
transepithelial potential difference relative to the muscosal side
References
Allen A, Pain RH, Robsen TR (1976) Model for the structure of the gastric mucous gel. Nature 264:88–89
Ando M (1980) Chloride-dependent sodium and water transport in the seawater eel intestine. J Comp Physiol 138:87–91
Armstrong WM, Garcia-Diaz JF (1980) Ion-selective microelectrodes: theory and techniques. Fed Proc 39:2851–2859
Bandurko LN, Brodskii RA, Gal-Perin YM, Lazarev PI (1984) Enzymes of the small intestinal mucus. Byull Eksp Biol Med 97:160–163
Bell AE, Sellers LA, Allen A, Cunliffe WJ, Morris ER, Ross-Murphy SB (1985) Properties of gastric and duodenal mucus. Effect of proteolysis, disulfite reduction, bile, acid, ethanol and hypertonicity on mucus gel structure. Gastroentrology 88:269–280
Bogomoletz WV, Puchelle E, Durand MC, Petit A (1984) Histochemistry of mucosubstances in the frog respiratory epithelium. Acta Histochem 74:189–194
Crowther RS, Hughes DRL, Marriott C (1984) Mucus glycoprotein gels: a scanning electron microscopy study of the effect of cations. Micron Microscp Acta 15:37–45
Denny M (1983) Molecular biomechanics of Molluscan mucous secretions. In: The Mollusca, vol 1: Metabolic Chemistry and Molecular Biomechanics. Academic Press, London New York, pp 431–465
Field M, Karnaky KJ, Smith PL, Bolton JE, Kinter WB (1978) Ion transport across isolated intestinal mucosa of the winter founder,Pseudopleuronectes americanus. I. Functional and structural properties of cellular and paracellular pathways for Na and Cl. J Memb Biol 41:265–293
Frase LL, Strickland AD, Kachel GW, Krejs GJ (1985) Enhanced glucose absorption in the jejunum of patients with cystic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 88:478–484
Frizzell RA, Halm DR, Musch MW, Stewart CP, Field M (1984) Potassium transport by flounder intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol 246:F946-F951
Garner A, Flemström G, Allen A (1983) Gastroduodenal alkaline and mucus secretions. Scand J Gastroenterol 18:25–41
Gilles-Baillien M (1981) Na, Cytoleucine and insulin compartments in tortoise intestinal mucus. Possible role of the mucus in intestinal absorption processes. Mol Physiol 1:265–272
Greger R, Schlatter S (1981) Presence of luminal K+, a prerequisite for active NaCl transport in cortical thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 392:92–94
House CR, Green K (1965) Ion and water transport in isolated intestine of the marine teleost,Cottus scorpius. J Exp Biol 42:117–189
Humbert W, Kirsch R, Meister MF (1984) Scanning electron microscopic study of the oesophageal mucous layer in the celAnguilla anguilla L. J Fish Biol 25:117–122
Humbert W, Kirsch R, Simonneaux V (1986) Is mucus involved in biocrystallisation? Study of the intestinal mucus of the seawater eelAnguilla anguilla L. Cell Tissue Res 245:599–604
Kirsch R, Meister MF (1982) Progressive processing of ingested water in the gut of sea-water teleosts. J Exp Biol 98:67–81
Kirsch R, Humbert W, Rodeau JL (1984) Control of the blood osmolality in fishes with references to the functional anatomy of the gut. In: Pequeux A, Gilles R and Bolis L (eds) Osmoregulation in Estuarine and Marine Animals. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 67–92
Kirsch R, Humbert W, Simonneaux V (1985) The gut as an osmoregulatory organ: Comparative aspects and special references to fishes. In: Gilles R, Gilles-Baillien (eds) Transport Processes, Iono- and Osmoregulation. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 265–277
Kirschner LB (1978) External charged layer and Na+ regulation. In: Osmotic and Volume Regulation. Alfred Benzon symposium. XI. Munskgaard, Academic Press, New York, pp 310–322
Lee CO (1981) Determination of selectivity coefficients of ionselective microelectrodes. In: Sykova E, Hnik P, Vyklicky L (eds) Ion-selective microelectrodes and their use in excitable tissues. Plenum Press, New York, pp 47–52
Lemoine AM, Olivereau M (1973) Variations de la teneur en acide N acetyl neuraminique de la branchie de l'anguille au cours des changements de salinité. C R Soc Biol 167:411–416
Lukie BE (1986) Serum protein content of rat small intestinal mucus. Dig Dis Sci 31:73–78
Marshall WS (1978) On the involvement of mucous secretion in teleost osmoregulation. Can J Zool 56:1088–1091
Meister MF, Humbert W, Kirsch R, Vivien-Roëls B (1983) Structure and ultrastructure of the oesophagus in seawater and freshwater teleosts (Pisces). Zoomorphology 102:33–51
Mello ML (1984) Extracellular organization of an insect mucus elaborated by Malpighian tubules. Cell Mol Biol 30:353–356
Musch MW, Orellana SA, Kimberg LS, Field M, Halm DR, Krasny EJ, Frizzell RA (1982) Na+−K+−Cl− cotransport in the intestine of a marine teleost. Nature 300:351–353
Nonnotte G (1983) Fonctions de la peau des téléostéens: Etude expérimentale des échanges respiratoires et des échanges ioniques. Thèse, Strasbourg
Pang PKT, Griffith RW, Maetz J, Pic P (1980) Calcium uptake in fishes. In: Epithelial Transport in the Lower Vertebrates. Cambridge University Press, pp 121–132
Parmelee JT, Renfro JL (1983) Esophageal desalination of seawater in flounder: role of active sodium transport. Am J Physiol 245:R888-R893
Pärt P, Lock RA (1983) Diffusion of calcium, cadmium and mercury in a mucous solution from rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol 76C:259–263
Pearson JP, Kaura R, Taylor W, Allen A (1982) The composition and polymeric structure of mucus glycoprotein from human gallbladder bile. Biochim Biophys Acta 706:221–228
Peppas NA, Hansen PF, Buri PA (1984) A theory of molecular diffusion in the intestinal mucus. Int J Pharmaceutics 20:107–118
Portier P, Duval M (1922) Variation de la pression osmotique du sang de l'anguille en fonction des modifications de salinité du milieu extérieur. C R Acad Sc Paris 175:1105–1106
Rechkemmer G, Wahl M, Kuschinsky W, Engelhardt W v (1979) pH-microclimate at the surface of the intestine in guinea pig and rat. Pflügers Arch 382:R31
Rikihisa Y, Lin YC (1984)Taenia taeniaeformis: Increased cell growth and neutral mucus production in the gastric mucosa of the rat with a larval infection. Exp Parasitol 58:147–155
Saglio P, Fauconneau B (1985) Free amino-acid content in the skin mucus of goldfishCarassius auratus: influence of feeding. Comp Biochem Physiol 82A:67–70
Sakata T, Engelhardt W v (1981) Luminal mucin in the large intestine of mice, rats and guinea pigs. Cell Tissue Res 219:629–635
Sarosiek J, Slomiany A, Slomiany BL (1983) Retardation of hydrogen ion diffusion by gastric mucus constituents: effect of proteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Communications 115:1053–1060
Schlichter LC (1982) Unstirred mucus layers: ion exchange properties and effect on ion regulation inLymnaea stagnalis. J Exp Biol 98:363–372
Sharratt BM, Bellamy D, Chester-Jones I (1964) Adaptation of the silver eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) to seawater and to artificial media together with observations on the role of the gut. Comp Biochem Physiol 14:19–30
Shelhamer JH, Marom Z, Logun C, Kaliner M (1984) Human respiratory mucous glycoproteins. Exp Lung Res 7:149–162
Shephard KL (1981) The influence of mucus on the diffusion of water across fish epidermis. Physiol Zool 54:224–229
Shephard KL (1982) The influence of mucus on the diffusion of ions across the esophagus of fish. Physiol Zool 55:23–34
Shephard KL (1984a) Diffusion of chloride ions in the mucus of the oesophagus ofEnophrys bison, a marine teleost fish. Pflügers Arch 402:207–210
Shephard KL (1984b) The influence of mucus on the diffusion of chloride ions across the oesophagus of the minnow (Phoxinus phoxinus). J Physiol 346:449–460
Simonneaux V, Barra JA, Humbert W, Kirsch R (1987) The role of mucus in ion absorption by the oesophagus of the sea-water eel (Anguilla anguilla L.): Electrophysiological, structural and cytochemical investigations. J Comp Physiol B157: 187–199
Singh W, Singh HR (1984) Functional morphology and histology of the olfactory organs of the hill stream carpCrossocheilus latius latius. Folia Morphologica 32:269–274
Singh B, Thakur R (1975) A histochemical study on the respiratory epithelia of an eel fish,Amphipnous cuchia. Acta Hist 54:161–167
Skadhauge E (1969) The mechanism of salt and water absorption in the intestine of the eel (Anguilla anguilla) adapted to waters of various salinities. J Physiol 204:135–158
Skadhauge E (1974) Coupling of transmural flows of NaCl and water in the intestine of the eel (Anguilla anguilla). J Exp Biol 60:535–546
Smith HW (1930) The absorption and excretion of water and salts by marine teleosts. Am J Physiol 93:480–505
Stith BJ (1984) Biochemical examination ofRana pipiens epithelial mucus. J Comp Physiol B 155:89–96
Whitear M, Mittal AK (1984) Surface secretions of the skin ofBlennius (Lipophrys) pholis L. J Fish Biol 25:317–331
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonneaux, V., Humbert, W. & Kirsch, R. Mucus and intestinal ion exchanges in the sea-water adapted eel,Anguilla anguilla L.. J Comp Physiol B 157, 295–306 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693356
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693356