Abstract
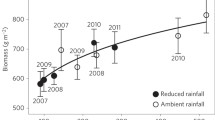
Field studies using open-top chambers were conducted at USDA-BARC involving the growth of soybeans ('89 & '90), wheat ('91 & '92), and corn ('91), under increased concentrations of atmospheric CO2 and O3. Treatment responses were compared in all cases to plants grown in charcoal-filtered (CF) air (seasonal 7-h mean = 25±3 n mol O3 mol−1) having 350 or 500 μ mol CO2 mol−1. Elevated seasonal O3 levels for the soybean, wheat, and corn studies averaged 72.2±4, 62.7±2, and 70.2 n mol O3 mol−1, respectively. Results presented were obtained for plants grown in silt loam soil under well-watered conditions. Grain yield increases in response to elevated CO2 in the absence of O3 stress averaged 9.0, 12.0, and 1.0% for soybean, wheat, and corn; respectively. Reductions in grain yields in response to the elevated O3 treatments at 350 μ mol CO, mol−1 averaged 20.0, 29.0 and 13.0% for soybean, wheat, and corn, respectively. Reductions in grain yields in response to elevated O3 at 500 μ mol CO2 mol−1 averaged 20.0, 8.0, and 7.0% for soybean, wheat, and corn, respectively. Dry biomass and harvest index in wheat were significantly reduced by O3 stress at 350 μ mol mol 1 CO2 but not at 500 u mol mol−1 CO2. Seed weight 1000−1 for scybeans and wheat was significantly increased by CO2 enrichment and decreased by O3 stress. Seed weight 1000−1 in corn was increased by O3 stress suggesting that O3 affected pollination resulting in fewer kernels per ear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R.M., Rosenzweig, C.,Pert, R.M., Ritchie, J.T., McCarl, B.A. Glyer, J.D., Curry, R.B., Jones, J.M., Boote, K.J. and Allen, Jr., L.H.: 1990. Global Climate Change and U.S. Agriculture, Nature. 345, 219–224.
Allen, Jr., L.H.: 1990, J. Environ. Qual. 19, 15–34.
Burke, L.M. and Lashof, D.A.: 1990, Greenhouse Gas Emissions Related to Agriculture and Land-Use Practices, Impact of Carbon Dioxide, Trace Gases, and Climate Change on Global Agriculture, ASA Special Publication Number 53, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI 27–44 pp.
Heagle, A.S., Body, D.E. and Heck, W.W.: 1973, J. of Environ. Qual. 2, 365–368Heck, W.W., Tingey,D.T. and Taylor, O.C. (Eds): 1988, Proc. Int. Conf. Assessment of Crop Loss From Air Pollutants, Elsevier Applied Science, London 552 pp.
Heggestad, H.E. and Bennett, J.H.: 1984, Impact of Atmospheric Pollution on Agriculture, Air Pollution and Plant Life, Treshow, M. (Ed.) John Wiley & Sons New York 357–395 pp.
Kimball, B.A.: 1986, Influence of Elevated CO2 on Crop Yield Carbon Dioxide Enrichment of Greenhouse Crops, Vol. II — Physiology Yield and Economics Enoch, H.2. and Kimball, B.A. (Eds.) CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 105–115 pp.
Kimball, B.A., Rosenberg, N.J. and Allen, Jr., L.H. (Eds.) 1990, Impact of Carbon Dioxide, Trace Gases, and Climate Change on Global Agriculture, ASA Special Publication No. 53. Amer. Soc. of Agronomy, Madison WI 133 pp.
Krupa, S.V. and Kickert, R.N.: 1989, The Greenhouse Effect: Impacts of Ultraviolet-B (UV-B) Radiation, Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Ozone (O3) on Vegetation, Env. Pollut. 61, 263–393.
Mulchi, C.L.: 1993, Estimating the Economic Impact of Air Pollution on Maryland Agriculture, Maryland Agriculture Experiment Station, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 22 pp.
Mulchi, C.L., Slaughter, L., Saleem, M., Lee, E.H., Pausch, R. and Rowland, R.: Agri. Ecosystems and Environ. 38, 107–118.
Pausch, R.: 1993, Use of 13 C and 15 N Isotopes to Study Effects of Ozone on Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism in Soybeans Grown in Open-Top Chambers, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 170pp.
Rudorff, B.F.T.: 1993, Interactive Effects of Enhanced Tropospheric Ozone and Carbon Dioxide on Wheat and Com, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 192 pp.
Stockle, C.O., Dyke, P.T., Williams, J.R., Jones, C.A., and Rosenberg, N.J.: 1992, Agricultural Systems 38, 239–256.
White, J.C., (Ed.): 1989, Global Climate Change Linkages, Acid Rain, Air Quality and Stratospheric Ozone, Elsevier Applied Science, New York 261 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Scientific Article No. A7784, Contribution No. 9105, Maryland Agric. Exp. Sta., Univ. of MD, College Park, MD 20472
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulchi, C., Rudorff, B., Lee, E. et al. Morphological responses among crop species to full-season exposures to enhanced concentrations of atmospheric CO2 and O3 . Water Air Soil Pollut 85, 1379–1386 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00477174
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00477174