Summary
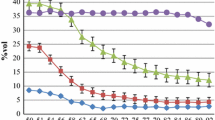
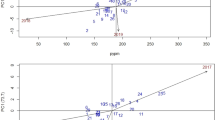
Comparison of genotypes in line source based drought screening has a number of statistical problems because of the systematic nature of irrigation treatments. A method of applying the joint regression approach has been developed and applied to evaluate sensitivity of 22 groundnut genotypes grown under 11 patterns of drought which were simulated in the field using a line-source sprinkler technique. The experimental errors in neighbouring environments are assumed correlated to account for the systematic nature of the environments. The estimation of parameters of the model and comparison of genotypes for their sensitivity to drought are presented for the pod yield. Stability in performance across the line-source environment was estimated for 22 genotypes. None of the genotypes tested was insensitive to drought across all patterns. Genotypes with stability and high mean yield could be identified in early and mid-season drought patterns but not in other patterns where genotypic sensitivity was strongly correlated with yield performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, H.C., 1981. Correlations among some statistical measures of phenotypic stability. Euphytica 30: 835–840.
Besag, J. & R., Kempton, 1986. Statistical analysis of field experiments using neighbouring plots. Biometrics 42: 231–251.
Digby, P.G.N., 1979. Modified joint regression analysis for incomplete variety x environment data. J. Agric. Sc., Cambridge 93: 81–86.
Eberhart, S.A. & W.A., Russell, 1966. Stability parameters for comparing varieties. Crop Sc. 6: 36–40.
Finlay, K.W. & G.N., Wilkinson, 1963. The analysis of adaptation in a plant breeding programme. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 14: 742–754.
Hanks, R.J., J., Keller, V.P., Rasmussen & G.D., Wilson, 1976. Line-source sprinkler for continuous variable irrigation-crop production studies. Proceedings of Soil Science Society of America 40: 426–429.
Johnston, J., 1972. Econometric Methods, Second Edition. McGraw-Hill Kogakusha, Ltd. Tokyo.
Lin, C.S., M.R., Binns & L.P., Lefkovitch, 1986. Stability analysis: where do we stand? Crop Sc. 26: 894–900.
Morgan, D.D.V. & M.K.V., Carr, 1988. Analysis of experiments involving line source sprinkler irrigation. Exp. Agric. 24: 169–176.
Rao, R.C.N., J.H., Williams & M., Singh, 1989. Genotypic sensitivity to drought and yield potential of peanut. Agron. J. 81: 887–893.
Perkins, J.M. & J.L., Jinks, 1968. Environmental and genotype-environmental components of variability. III. Multiple lines and crosses. Heredity 23: 339–356.
Wilkinson, G.N., S.R., Eckert, T.W., Hancock & O., Mayo, 1983. Nearest Neighbour (NN) analysis of field experiments (with discussion). J. Roy. Statist. Soc., Series B 45: 151–211.
Yates, F. & W.G., Cochran, 1938. The analysis of groups of experiments. J. Agric. Sc., Cambridge 28: 556–580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Rao, R.C.N. & Williams, J.H. A statistical assessment of genotypic sensitivity of groundnut (Arachis hypogae L.) to drought in line source sprinkler experiments. Euphytica 57, 19–25 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040474
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040474