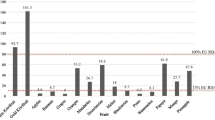
Abstract
A brief review is presented of the properties of nori relevant to health. The dried alga contains large amounts of protein, ash, vitamins and carbohydrate. The levels of taurine (/>- 1.2%) are notable as this compound aids enterohepatic circulation of bile acid, thus preventing gallstone through controlling blood-cholesterol levels. Relatively high levels of eicosapentanoic acid, choline, inositol and other B-group vitamins are regarded as beneficial to health. The occurrence of porphyosins and betaines that prevent respectively, gastric shay ulcers and lower blood-cholesterol levels are particular interest. A sulfated galactan, similar to agar, occurs in relatively large quantities; this is a water-soluble dietary fiber that has important functional activities such as an antiblood coagulant, antihypercholesterolemia and shows antitumor activity. Minerals which occur at relatively high levels in nori include Zn, Cu, Mn and Se.It is concluded that nori is a valuable health food in human diets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe S, Kaneda T (1973) Occurrence of γ-butyrobetaine in a red alga, Porphyra yezoensis. Bull. Jap. Soc. sci. Fish. 39: 239.
Anon. (1982) Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan, Fourth edition. Resources Council, Science and Technology Agency, Ishiyaku Publ., Inc., Tokyo, 262–263 (in Japanese).
Dyerberg J, Bang HO, Stoffersen E, Mancada S, Vane JR (1978) Eicosa-pentaenoic acid and prevention of thrombosis and atherosclerosis? Lancet 1978: 117–119.
Dyerberg J, Bang HO (1979) Hemostatic function and platelet polyunsaturated fatty acids in Eskimos. Lancet 1979: 433–435.
Horiguchi Y, Noda H, Naka M (1971) Biochemical studies on marine algae-VI. Concentration of selenium in marine algae and its importance as a trace metal for the growth of lavers. Bull. Jap. Soc. sci. Fish. 37: 996–1001.
Kagawa A (ed.) (1983) Amino acid composition in Japanese foods. Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan, Fourth edition Resources Council, Science and Technology Agency 253–259 (in Japanese).
Kanazawa A (1963) Vitamins in algae. Bull. Jap. Soc. sci. Fish. 29: 713–731.
Kayama M, Iijima N, Kuwahara M, Sado T, Araki S, Sakurai T (1985) Effect of water temperature on the fatty acid composition of Porphyra. Bull. Jap. Soc. sci. Fish. 51: 687.
Mindel, EL (1981) Vitamin Bible. Warner Communications Co., New York 69 pp.
Noda H (1971) Biochemical studies on marine algae — III. Relation between quality and inorganic constituents of hoshi-nori (dried Porphyra yezoensis). Bull. Jap. Soc. sci. Fish. 37: 35–39.
Noda H, Horiguchi Y, Araki S (1975) Studies on the flavor substances of ‘nori’, the dried laver Porphyra spp. — II. Free amino scids and 5′-nucleotides. Bull. Jap. Soc. sci. Fish. 41: 1299–1303.
Noda H, Amano H, Abo K, Horiguchi Y (1981) Sugars, organic acids, and minerals of nori, the dried laver Porphyra sp. Bull. Jap. Soc. sci. Fish. 47: 57–62.
Noda H, Amano H, Arashima K, Nishizawa K (1990) Antitumor activity of marine algae. In Lindstrom SC, Gabrielson PW (eds), Thirteenth International Seaweed Symposium. Developments in Hydrobiology 58. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 577–584. Reprinted from Hydrobiologia 204/205.
Sakagami Y (1983) Biochemistry and utilization of marine algae. In Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi (ed.), Antiulcer compounds. Koseisha-Koseikaku, Tokyo, 90–100.
Tujii K, Iwao T, Nakagawa Y, Seki T (1981) Effect of dietary taurine on bile acid metabolism in hypercholesterolemic rats. Sulfur Amino Acids 4: 111–119.
Tujii K, Ichikawa T, Nakagawa Y, Matsuura Y, Kawamura M (1983) Hypercholesterolemic effect of taurocyamine or taurine on the cholesterol metabolism in white rats. Sulfur Amino Acids 6: 239–248.
Yamamoto I, Maruyama H (1985) Effect of dietary seaweed preparation on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced intestinal carcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Lett. 26: 241–251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, H. Health benefits and nutritional properties of nori. J Appl Phycol 5, 255–258 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004027
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004027