Abstract
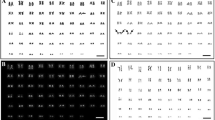
The shortnose sturgeon Acipenser brevirostrum was revealed to have a larger number of chromosomes than previously reported for other sturgeon species. Its chromosome number ranged from 362 to 372 (of ten specimens examined), showing intraindividual variation. The karyotype of metaphase with the highest chromosome number (372) consisted of 89 pairs of macrochromosomes and 97 pairs of microchromosomes (fundamental number; NF = 550). Although the microchromosomes were relatively shorter than the macrochromosomes, most of them had discernible arms and centromeres. Silver-stained nucleolar organizer regions (Ag-NORs) were localized on the telomeric regions of 5 pairs of chromosomes (Ag-NORs = 10): 4 were made up of small meta/submetacentrics and 1 of acrocentrics. Polyploidy of A. brevirostrum should be hexaploid based on the karyotype, numerous chromosomes, Ag-NORs, and previously reported large genome size (ca. 13 pg DNA/cell).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Electronic Supplementary Material

About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Nam, Y., Noh, J. et al. Karyotype of North American shortnose sturgeon Acipenser brevirostrum with the highest chromosome number in the Acipenseriformes. Ichthyol Res 52, 94–97 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-004-0257-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-004-0257-z