Abstract
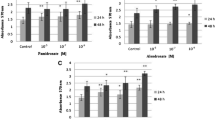
Ibuprofen is a nonselective nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug commonly prescribed for acute postsurgical and posttraumatic pain. However, little known is about the effect of this drug on osteoblasts. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of ibuprofen on cell proliferation, differentiation, antigenic profile, and phagocytic activity, in a human MG-63 osteosarcoma cell line, as a model of osteoblasts. Flow cytometry was used to study proliferation, antigenic profile, and phagocytic activity, and radioimmunoassay was used to determine osteocalcin synthesis as a cell differentiation marker. Our results showed that therapeutic doses of ibuprofen (5 and 25 μM) did not modify cell proliferation and osteocalcin synthesis in the MG-63 cellular line. However, treatment with a higher dose (25 μM) increased the expression of antigens CD21, CD44, CD80, CD86, and HLA-DR and decreased phagocytic activity. The results indicate that a therapeutic dose of ibuprofen has no adverse effects on growth of the osteoblast-like cells. Treatment with ibuprofen alone may produce some cell activation, which would explain the increase in expression of membrane markers and decrease in phagocytic capacity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith WL, Dewitt DL, Garavito RM (2000) Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem 69:145–182
Beck A, Krischak G, Sorg T, Augat P, Farker K, Merkel U, Kinzl L, Claes L (2003) Influence of diclofenac (group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) on fracture healing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 123:327–332
Gerstenfeld LC, Thiede M, Seibert K, Mielke C, Phippard D, Svagr B, Cullinane D, Einhorn TA (2003) Differential inhibition of fracture healing by non-selective and cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Orthop Res 21:70–75
Evans CE, Butcher C (2004) The influence on human osteoblasts in vitro of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs which act on different cyclooxygenase enzymes. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:444–449
Naruse T, Nishida Y, Hosono K, Ishiguro N (2006) Meloxicam inhibits osteosarcoma growth, invasiveness and metastasis by COX-2-dependent and independent routes. Carcinogenesis (Oxf) 27:584–592
Krischak GD, Augat P, Blakytny R, Claes L, Kinzl L, Beck A (2007) The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac reduces appearance of osteoblasts in bone defect healing in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127:453–458
Díaz-Rodríguez L, García-Martínez O, Arroyo-Morales M, Rodríguez-Pérez L, Rubio-Ruiz B, Ruiz C (2012) Effects of indomethacin, nimesulide, and diclofenac on human MG-63 osteosarcoma cell line. Biol Res Nurs 14:98–107
García-Martínez O, Díaz-Rodríguez L, De Luna-Bertos E, Reyes-Botella C, Ruiz C (2011) Effect of acetaminophen, ibuprofen and methylprednisolone on different parameters of human osteoblast-like cells. Arch Oral Biol 6:317–323
Chang JK, Wang GJ, Tsai ST, Ho ML (2005) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug effects on osteoblastic cell cycle, cytotoxicity and cell death. Connect Tissue Res 46:200–210
Chang JK, Li CJ, Liao HJ, Wang CK, Wang GJ, Ho ML (2009) Anti-inflammatory drugs suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis through altering expressions of cell cycle regulators and pro-apoptotic factors in cultured human osteoblasts. Toxicology 258:148–156
Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LS, Van de Puete LBA, Lipsky PE (1998) Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J 12:1063–1073
Reyes-Botella C, Montes MJ, Vallecillo-Capilla MF, Olivares EG, Ruiz C (2000) Expression of molecules involved in antigen presentation and T cell activation (HLA-DR, CD80, CD86, CD44 and CD54) by cultured human osteoblasts. J Periodontol 71:614–617
Reyes-Botella C, Montes MJ, Vallecillo-Capilla MF, Olivares EG, Ruiz C (2002) Antigenic phenotype of cultured human osteoblast-like cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:359–364
Ruiz C, Pérez E, Vallecillo-Capilla MF, Reyes-Botella C (2003) Phagocytosis and allogeneic T cell stimulation by cultured human osteoblastic-like cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:309–314
Schrum LW, Bost KL, Hudson MC, Marriott I (2003) Bacterial infection induces expression of functional MHC class II molecules in murine and human osteoblasts. Bone (NY) 33:812–821
Pérez E, García-Martínez O, Arroyo-Morales M, Reyes-Botella C, Ruiz C (2006) Modulation of antigenic phenotype in cultured human osteoblast-like cells by FGFb, TGFβ1, PDGF-BB, IL-2, IL-1β, LPS and IFNγ. Biosci Rep 26:281–289
Stanley KT, Vandort C, Motyl C, Endres J, Fox DA (2006) Immunocompetent properties of human osteoblasts: interactions with T lymphocytes. J Bone Miner Res 21:29–36
García-Martínez O, Reyes-Botella C, Aguilera-Castillo O, Vallecillo-Capilla MF, Ruiz C (2006) Antigenic profile of osteoblasts present in human bone tissue sections. Biosci Rep 26:39–43
Díaz-Rodríguez L, García-Martínez O, Arroyo-Morales M, Reyes-Botella C, Ruiz C (2009) Antigenic phenotype and phagocytic capacity of MG63 osteosarcoma line. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1173(suppl 1):E46–E54
Prouillet C, Mazičre JC, Mazičre C, Wattel A, Brazier M, Kamel S (2004) Stimulatory effect of naturally occurring flavonols quercetin and kaempferol on alkaline phosphatase activity in MG-63 human osteoblasts through ERK and estrogen receptor pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 67:1307–1313
Nayab SN, Jones FH, Olsen I (2005) Effects of calcium ion implantation on human bone cell interaction with titanium. Biomaterials 26:4717–4727
García-Martínez O, Reyes-Botella C, Díaz-Rodríguez L, De Luna-Bertos E, Ramos-Torrecillas J, Vallecillo-Capilla MF, Ruiz C (2011) Effect of platelet-rich plasma on growth and antigenic profile of human osteoblasts and its clinical impact. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2011.06.199
Vuolteenaho K, Moilanen T, Moilanen E (2008) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, cyclooxygenase-2 and the bone healing process. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 102:10–14
Akman S, Gögüs A, Sener N, Bilgiç B, Aksov B, Seckin F (2002) Effect of diclofenac sodium on union of tibial fractures in rat. Adv Ther 19:119–125
Mullis BH, Copland ST, Weinhold PS, Miclau T, Lester GE, Bos DG (2006) Effect of COX-2 inhibitors and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on a mouse fracture model. Injury 37:827–837
Salari P, Abdollahi M (2009) Controversial effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on bone: a review. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 8:169–175
Abukawa H, Phelps M, Jackson P, Smith M, Vacanti JP, Kaban LB, Troulis MJ (2009) Effect of ibuprofen on osteoblast differentiation of porcine bone marrow-derived progenitor cells. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:2412–2417
Raisz LG, Pilbeam CC, Fall PM (1993) Prostaglandins: mechanisms of action and regulation in bone. Osteoporos Int 3(suppl 1):136–140
Ruiz C, Pérez E, García-Martínez O, Díaz-Rodríguez L, Arroyo-Morales M, Reyes-Botella C (2007) Expression of cytokines IL-4, IL-12, IL-15, IL-18, and IFNγ and modulation by different growth factors in cultured human osteoblast-like cells. J Bone Miner Metab 25:286–292
Andreae S, Piras F, Burdin N, Triebel F (2002) Maturation and activation of dendritic cells induced by lymphocyte activation gene-3 (CD223). J Immunol 168:3874–3880
Díaz-Rodríguez L, García-Martínez O, Arroyo-Morales M, Rubio-Ruiz B, Ruiz C (2010) Effect of paracetamol on human MG63 osteosarcoma cellular line. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:1495–1499
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research group BIO277 (Junta de Andalucía) and by the Department of Nursing of the Faculty of Health Sciences of the University of Granada.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-Rodríguez, L., García-Martínez, O., De Luna-Bertos, E. et al. Effect of ibuprofen on proliferation, differentiation, antigenic expression, and phagocytic capacity of osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Metab 30, 554–560 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0356-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0356-2