Abstract
Synoptivity and the exemplified fracture systems exhibited by the space borne imagery data has helped in solving many of the geological enigma in various parts of the world. The study conducted, using such remotly sensed data, in Jhalawar anticline, part of Proterozoic Cratonic Vindhyan Basin, Rajasthan, India, led to infer the history of tectonic evolution of peribasinal deformation which has been a matter of controversy for a century and more.
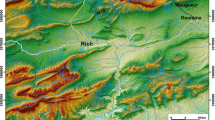
In Landsat MSS data the Jhalawar region displays a panorama of lineaments and their analysis through azimuthal frequency diagrams, isofracture, lineament incidence and lineament intersection incidence density maps shows that the mean orientation of the lineaments fall in NW-SE and NE-SW and the shape of the various lineament density contours also show NE-SW and NW-SE orientations. In aerial photographs the area exhibits four sets of lineaments in NE-SW, NW-SE, N-S and E-W directions. Amongst these the former two sets are expressed as wide open master fracture systems with prolific vegetation fills along them and the latter two sets are characteristically observed as thin vegetation linears with frequent strike slip faulting along them. The further analysis of these fracture/lineament systems derived from multi-level remote sensing data shows that the Jhalawar anticline, which followed the pattern of flexural slip fold mechanism, was evolved by horizontally disposed σ1 (greatest principal stress) and 3σ (least principal stress) with the former oriented in NE-SW and the latter aligned in NW-SE directions with vertically disposed 2σ. The inference of such palaeostress environment of the Jhalawar region lead in the identification of a buried rigid basement high southwest of Jhalawar anticline, beneath the Deccan pile and loci of ground water, silica sand and probable igneous plug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, E.M., 1951, The dynamics of faulting and dyke formation with application to Britain, Oliver and Boyd. London, 206 p.
Badgley, C.P., 1965, Structural and tectonic principles, Harpur and Row publishers, N.Y. 521 p.
Bakliwal, P.C., 1978, Tectonic interpretation from lineament analysis using photogeophysical techniques of Ranthambhor fort area, Rajasthan, India, Proc. Vol. of 3rd Reg. Conf. on Geol. and Min. Resour. of S.E.Asia, Bankok, Thailand, pp 129–132.
Bakliwal, P.C., Ramasamy, S.M., and Ray, A.K., 1986, Lineament tectonics of proterozoic basins of Western India, Proc. Vol. Workshop on Purana Basins of Peninsular India, 29–31 Dec. 1984, Hyderabad, Goel. Soc. Ind. Mem. (in press.)
Desitter, 1956, Structural Geology, McGraw Hill, 552 p.
Harris J.F., Garrin, L. Taylor H.L., and Walper T.O. 1960, Relation of deformational fractures in sedimentary rocks to regional and local structures. Bull. of Amer. Assocn. of Petrol. Geol. V. 44 (12), pp 1853–1873.
Heman, P.J., 1961, Lineament analysis on aerail photographs emplified in the North Sturgeon Lake area, Alberta, West Canadian research publication of Geology and related sciences, Series No. 1, pp 1–20.
Bobbs, E., Bruce-Meas, D., Winthrop and Williams, F. Paul, 1976, An Outline of structural geology, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. N.Y., 571 p.
Iqbaluddin, 1979, State of stress at continental margins-Discussion, Tectonophysics, 60, pp 319–310.
Peterson, M.S. and Weiss, L.E., 1966, Experimental deformation and folding in phyllites, Bull. Geol. Soci. Amer. V. 77, pp. 343–374.
Prasad, B., 1976, Volcanic activity during Vindhyan period, Chittaurgarh district, Rajasthan, Ind. Min. 30 (4), pp 73–75.
Ramasamy, S.M., Sinha, M., and Deva Prasad, C., 1983, Micro-lineament analysis and the palaeostress environment in Ishwara Kuppam dome area, Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, Jour. Geol. Soc. Ind. V. 24 (12), pp 660–663.
Whitten, E.H., 1966, Structural geology of folded rocks, Chicago, Rand Mc Nally Geology Series.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Ramasamy, S.M., Bakliwal, P.C. & Ramana Rao, K.L.V. Use of remote sensing in lineament analysis for tectonic evolution and resource study of a part of Vindhyan Basin, Jhalawar area, India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 16, 63–71 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02992102
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02992102