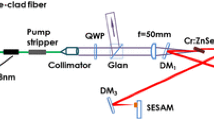
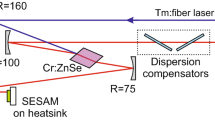
Abstract
By using split-step Fourier method, we conducted the simulation of pulse formation in two SESAM mode-locked lasers. One is a conventional laser with the SESAM at the cavity end. The other is constructed by moving the SESAM of the conventional laser to the middle of the cavity. In the laser with the SESAM in the middle of the cavity, since the pulse meets the SESAM twice during one round-trip, the pulse shaping also occurs twice by the saturable absorption induced at the SESAM. For this reason, in net positive dispersion regime, the chirped-pulse propagating in the laser with the SESAM in the middle of the cavity was shorter than the chirped-pulse that experiences the pulse shaping per one round-trip by the SESAM in the conventional laser. In the operation regime of net negative dispersion, the soliton-like pulse shaping is a more dominant process in pulse shortening than the pulse shaping by the SESAM, therefore, there was no big difference between the steady-state pulse profiles of both lasers regardless of the SESAM position. However, it was found that the pulse contrast is better and the initial pulse changes to a steady-state pulse faster when the SESAM is in the middle of the cavity than at the cavity end. Since the enhanced cavity loss by the SESAM in the middle of the cavity suppresses pulse destabilization more effectively, it is demonstrated that the pulse stability against cw generation is better in the laser with the SESAM in the middle of the cavity than at the cavity end.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Matos et al., Opt. Lett. 29, 1683 (2004).
K. Sugioka and Y. Cheng, Light Sci. Appl. 3, e149 (2014).
Y. Liu et al., Opt. Express 15, 18103 (2007).
S. Yefet and A. Pe’er, Appl. Sci. 3, 694 (2013).
J. Herrmann, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 11, 498 (1994).
H. A. Haus, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 6, 1173 (2000).
D.H. Song et al., Laser Phys. Lett. 10, 065003 (2013).
T. Brabec, C. Spielmann, P. F. Curley and F. Krausz, Opt. Lett. 17, 1292 (1992).
J. Herrmann, Opt. Commun. 98, 111 (1993).
H. A. Haus, J. G. Fujimoto and E. P. Ippen, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 8, 2068 (1991).
U. Keller et al., IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2, 435 (1996).
E. Sorokin, N. Tolstik, K. I. Schaffers and I. T. Sorokina, Opt. Express 20, 28947 (2012).
D. H. Sutter et al., Appl. Phys. B 70, S5 (2000).
R. L. Fork, E. Martinez and J. P. Gordon, Opt. Lett. 9, 150 (1984).
S. Naumov et al., New J. Phys. 7, 216 (2005).
J. Ma et al., Opt. Express 25, 14968 (2017).
S. Dewald et al., Opt. Lett. 31, 2072 (2006).
P. Dombi et al., Opt. Express 17, 20598 (2009).
S-H. Kwon, D. H. Song, I. S. Kim and D-K. Ko, Opt. Laser Technol. 133, 106560 (2021).
M. Gong, H. Yu, X. Wushouer and P. Yan, Laser Phys. Lett. 5, 514 (2008).
A. Laurain et al., Proc. SPIE 10515, 105150H (2018).
O. Shtyrina et al., J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 26, 346 (2009).
C. Brandus and T. Dascalu, Opt. Laser Technol. 111, 452 (2019).
V. L. Kalashnikov et al., New J. Phys. 7, 217 (2005).
Y. H. Cha, J. M. Han and Y. J. Rhee, Appl. Phys. B 74, S283 (2002).
M. Tokurakawa and A. Shirakawa, Opt. Express 23, 26288 (2015).
D. H. Song, S. I. Hwang and D-K. Ko, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 61, 730 (2012).
R. Paschotta et al., Appl. Phys. B 73, 653 (2001).
F. X. Kärtner, J. A. der Au and U. Keller, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 4, 159 (1998).
F. X. Kaärtner, I. D. Jung and U. Keller, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2, 540 (1996).
C. Spielmann, P. F. Curley, T. Brabec and F. Krausz, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 30, 1100 (1994).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (Grant No. NRF-2015R1A5A1009962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, SH., Ko, DK. Pulse Formation and Stability of a SESAM Mode-locked Laser Depending on the SESAM Position. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 77, 1153–1158 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.1153
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.1153