Abstract
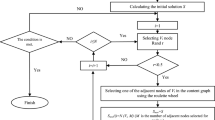
Many researchers have proven that complex networks have community structures and that most network communities are overlapping. Numerous algorithms have been proposed and used to detect non-overlapping or overlapping communities in networks. Many community-detecting algorithms are based on a clique. A clique is a subset of the nodes in the network in which every pair of nodes has an edge between them. In this paper, we propose a new algorithm that is based on a clique-to-clique similarity measure, and the label propagation to detect overlapping communities. The algorithm first finds all cliques of the network; then, it builds a new network according to a specific strategy, that specifies that in the new network, a node represents a clique found in the last step, and an edge is the link relation generated according to the strategy. The experimental results for both synthetic networks and real-world networks show that the proposed algorithm is not only effective, but also better than other algorithms in forms of the quality of results on the time efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Wasserman and K. Faust, Social Network Analysis: Methods and Applications (Cambridge University Press, London, 1994).
V. Spirin and L. A. Mirny, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 123 (2003).
B. Adamcsek et al., Bioinformatics 22, 1021 (2006).
M. Girvan and M. Newman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 7821 (2002).
G. Palla, I. Derényi, I. Farkas and T. Vicsek, Nature 435, 814 (2005).
M. E. J. Newman and M. Girvan, Phys. Rev. E 69, 026113 (2004).
H. Zhou, Phys. Rev. E 67, 061901 (2003).
S. Boccaletti et al., Phys. Rep. 424, 175 (2006).
A. Clauset, M. E. J. Newman and C. Moore, Phys. Rev. E 70, 066111 (2004).
M. E. J. Newman, Phys. Rev. E 69, 066133 (2004).
S. Fortunato, Phys. Rep. 486, 75 (2010).
Y. J. Yan, G. Yu, X. B. Yan and H. Xie, Mod. Phys. Lett. B 32, 1850405 (2018).
H. Shen, X. Cheng, K. Cai and M. B. Hu, Physica A 388, 1706 (2009).
S. Ming-Sheng, C. Duan Bing and Z. Tao, Chinese Phys. Lett. 27, 058901 (2010).
C. Lee, F. Reid, A. McDaid and N. Hurley, Tech. Rep. arXiv:1002.1827 (2010).
A. Lancichinetti, S. Fortunato and J. Kertész, New J. Phys. 11, 033015 (2009).
J. Xie, S. Kelley and B. K. Szymanski, ACM Comput. Surv. 45, 43 (2013).
J. Leskovec, K. Lang, A. Dasgupta and M. Mahoney, Internet Math. 6, 29 (2009).
U. N. Raghavan, R. Albert and S. Kumara, Phys. Rev. E 76, 036106 (2007).
Ian X. Y. Leung, P. Hui, P. Lio and J. Crowcroft, Phys. Rev. E 79, 066107 (2009).
C. Bron and J. Kerbosch, Commun. ACM 16, 575 (1973).
A. L. Traud, E. D. Kelsic, P. J. Mucha and M. A. Porter, Tech. Rep. arXiv: 0809.0690 (2008).
A. Lancichinetti, S. Fortunato and F. Radicchi, Phys. Rev. E 78, 046110 (2008).
A. Lancichinetti and S. Fortunato, Phys. Rev. E 80, 016118 (2009).
A. Lancichinetti and S. Fortunato, Phys. Rev. E 80, 56117 (2009).
V. Nicosia, G. Mangioni, V. Carchiolo and M. Malgeri, J. Stat. Mech-Theory E 2009, 03024 (2009).
S. Gregory, New J. Phys. 12, 103018 (2010).
W. W. Zachary, J. Anthropol. Res. 4, 452 (1977).
D. Lusseau et al., Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54, 396 (2003).
J. Leskovec, J. Kleinberg and C. Faloutsos, ACM Trans. KDD 1, 1 (2007).
J. Leskovec, J. Kleinberg and C. Faloutsos, ACM KDD 177, (2005).
L. Hubert and P. Arabie, J. Classif. 2, 1 (1985).
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71561013), the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20161BAB2 02055), the Social Science Planning Projects in Jiangxi Province (16TQ05), the Fund of Humanities and Social Sciences in Universities of Jiangxi Province (XW1505, JC17221, JD18083), and the Outstanding Youth Talent Support Program of JXSTNU (2015QNBJRC005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, H., Yan, Y. Detecting an Overlapping Community Structure by Using Clique-to-Clique Similarity based Label Propagation. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 75, 436–442 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.436
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.436