Abstract
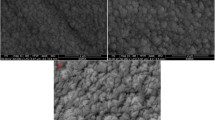
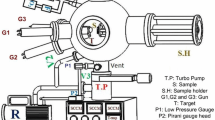
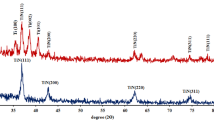
Hydrogenated amorphous carbon films (a-C:H or DLC) exhibit high hardness, low friction coefficient, and high wear resistance. Variations in the tribological properties were studied for amorphous carbon films fabricated by using closed-field unbalanced magnetron sputtering with TiC thin films as an adhesive layer. The a-C, a-C:Ti, and TiC/a-C nano-composite films were prepared using closed-field unbalanced magnetron sputtering with graphite and titanium as targets. Various structures of Ti-doped a-C and TiC interlayers under the amorphous carbon (a-C) film were examined to improve the tribological properties, and characteristic changes in the nano-composite structure were observed. The structure of the nano-composite film showed improved tribological properties, including high hardness, low friction coefficient, low surface roughness, and good adhesion of the a-C thin films. With a Ti-doped a-C film in a laminated structure, the tribological properties were improved to a high hardness value of >28.5 GPa, a high elastic modulus of >250 GPa, and a smooth surface with a roughness of <0.1 nm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Donnet, Surf. Coat. Technol. 80, 151 (1996).
C-P. Klages and R. Memming, Mater. Sci. Forum 52/53, 609 (1989).
K. Bewilogua et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 127, 224 (2000).
A. A. Voevodin et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 73, 185 (1995).
D. P. Monaghan et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 60, 525 (1993).
A. Ander, Phys. Rev. E 55, 969 (1997).
J. Robertson, Diam. Relat. Mater. 3, 361 (1994).
A. A. Voevodin, M. A. Capano and S. J. P. Laube, Thin Solid Films 298, 107 (1998).
D. Beeman, J. Silverman, R. Lynds and M. R. Anderson, Phys. Rev. B 5, 4951 (1972).
N. Popovic et al., Thin Solid Films 459, 286 (2004).
J. Bulir et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 708 (2005).
K. Yamamoto and K. Matsukado, Tribol. Int. 39, 1609 (2006).
V. Kulikovsky et al., Diam. Relat. Mater. 10, 1076 (2001).
Š. Meškinis et al., Vacuum 80, 1007 (2006).
D. Sheeja, B. K. Tay, C. Q. Sun and Y. Q. Fu, J. Mater. Sci. 38, 421 (2003).
C-L. Chang and D-Y. Wang, Diam. Relat. Mater. 10, 1528 (2001).
K. Bewilogua, R. Wittorf and H. Thomsen, Thin Solid Films 447–448, 142 (2004).
Y. T. Pei, D. Galvan and J. Th. M. De Hosson, Acta Mater. 53, 4505 (2005).
B. Yang et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 5812 (2006).
X. L. Peng, Z. H. Barber and T. W. Clyne, Surf. Coat. Technol. 138, 23 (2001).
Y. Liu, A. Erdemir and E. I. Meletis, Surf. Coat. Technol. 86–87, 564 (1996).
Y-Y. Chang, D-Y. Wang, C-H. Chang and W. T. Wu, Surf. Coat. Technol. 184, 349 (2004).
M. I. Jones et al., Diam. Relat. Mater. 8, 457 (1999).
N. Ali et al., Thin Solid Films 515, 59 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research funds from Chosun University, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y.S., Kim, NH. TiC/a-C Nano-Composite Films Fabricated by Using Closed-Field Unbalanced Magnetron Sputtering for Biomedical Applications. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 75, 380–384 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.380
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.380