Abstract
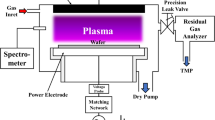
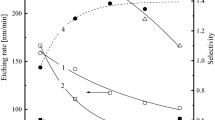
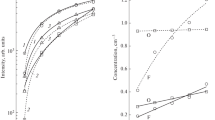
Capacitively coupled plasma reactive ion etching of silicon by injecting nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) gas was conducted, and the etching process was studied with a residual gas analyzer and an optical emission spectroscopy. During the etching of silicon by the NF3 plasma, the currents of F+ and SiF+3 ions were obtained from the residual gas analyzer. At the same time, the line intensity of fluorine was measured using optical emission spectroscopy. The ion currents of F+ and SiF+3 and the line intensity of fluorine were highest for etching at high pressure. With the results of this study, the general characteristics of reactive ion etching of silicon by using NF3 plasma were confirmed. In addition, by simply changing the flow rate of NF3, a high NF3 flow rate was found to result in a high etch rate because of the reduced residence time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Yun and G. R. J. Tynan, Appl. Phys. 89, 911 (2001).
K. Hashimoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33, 6013 (1994).
V. M. Donnelly et al., J. Appl. Phys. 55, 242 (1984).
R. C. Weast, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 70th ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1990).
S. Solomon et al., Climate Change 2007, The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I, Contribution to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2007).
K. Ino et al., IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 9, 230 (1996).
M. Konuma and E. Bauser, J. Appl. Phys. 74, 62 (1993).
J. E. Blessing et al., J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 25, 167 (2007).
J. Perrin et al., Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 10, 571 (1990).
W. H. Beattie, Appl. Spectrosc. 29, 334 (1975).
D. L. Flamm. Pure. Appl. Chem. 69, 1709 (1990).
K. Nojiri, Dry Etching Technology for Semiconductors (Springer, Switzerland, 2015).
A. Tasaka et al., J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 25, 391 (2007).
V. M. Donnelly et al., J. Appl. Phys. 55, 242 (1984).
T. Kimura and K. Hanaki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 8546 (2008).
B. N. Chapman and V. J. Minkiewicz, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 15, 329 (1978).
D. M. Manos and D. L. Flamm, Plasma Etching an Introduction (Academic Press, United States, 1989).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE) of the Republic of Korea (No. 20172010104840). Also, it was conducted using a Research Grant of Kwangwoon University in 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, HT., Kim, WJ., Shin, GW. et al. Plasma Etching of Silicon at a High Flow and a High Pressure of NF3 in Reactive Ion Etching. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 74, 1135–1139 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.74.1135
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.74.1135