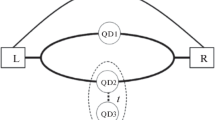
Abstract
The decoherence mechanism of an electron interferometer is studied by using a serial quantum dot and ring device. By coupling a quantum dot to a quantum ring (closed-loop electron interferometer), we were able to observe both Coulomb oscillations and Aharonov-Bohm interference simultaneously. The coupled device behaves like an ordinary double quantum dot at zero magnetic field while the conductance of the Coulomb blockade peak is modulated by the electron interference at finite magnetic fields. By injecting one electron at a time (by exploiting the sequential tunneling of a quantum dot) into the interferometer, we were able to study the visibility of the electron interference at non-zero bias voltage. The visibility was found to decay rapidly as the electron energy was increased, which was consistent with the recently reported result for an electron interferometer. However, the lobe pattern and the sudden phase jump became less prominent. These results imply that the lobe pattern and the phase jump in an electron interferometer may be due to electron interactions inside the interferometer, as is predicted by the theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. Meirav, M. A. Kastner and S. J. Wind, Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 771 (1990).
L. P. Kouwenhoven, D. G. Austing and S. Tarucha, Rep. Prog. Phys. 64, 701 (2001).
A. Yacoby, M. Heiblum, V. Umansky, H. Shtrikman and D. Mahalu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 3149 (1994).
Y. Ji, Y. Chung, D. Sprinzak, M. Heiblum, D. Mahalu and H. Shtrikman, Nature 422, 415 (2003).
F. H. L. Koppens et al., Nature 442, 766 (2006).
J. R. Petta et al., Science 309, 2180 (2005).
D. Goldhaber-Gordon, H. Shtrikman, D. Mahalu, D. Abusch-Magder, U. Meirav and M. A. Kastner, Nature 391, 157 (1998).
S. De Franceschi, S. Sasaki, J. M. Elzerman, W. G. van der Wiel, S. Tarucha and L. P. Kouwenhoven, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 878 (2001).
W. G. van der Wiel et al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 1 (2003).
M. Seo, H. K. Choi, S-Y. Lee, N. Kim, Y. Chung, H-S. Sim, V. Umansky and D. Mahalu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 046803 (2013).
I. Neder, M. Heiblum, Y. Levinson, D. Mahalu and V. Umansky, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 016804 (2006).
S-C. Youn, H-W. Lee and H-S. Sim, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 196807 (2008).
E. V. Sukhorukov and V. V. Cheianov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 156801 (2007).
A. Yacoby, R. Schuster and M. Heiblum, Phys. Rev. B 53, 9583 (1996).
A. Fuhrer et al., Nature 413, 822 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, M., Chung, Y. Transport properties of a quantum dot and a quantum ring in series. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 72, 138–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.72.138
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.72.138