Abstract
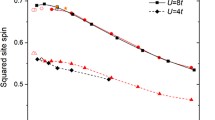
We study quantum phase transitions of an ionic Hubbard model in two dimensions. The ionic Hubbard model explains the quantum states of strongly correlated electrons under the influence of checkerboard-type alternating chemical potentials. For a given amplitude of the alternating potentials Δ, we obtain quantum ground states as we tune the local repulsive energy U between a spin-up electron and a spin-down electron by using an exact diagonalization method of a modified Lanczos algorithm. The system undergoes a quantum phase transition from a band insulator to a Mott insulator as U increases at half-filling. We find the signature of a quantum phase transition by investigating the behavior of ground-state energies and that of double occupancies for the size of L × L = 4 × 4, which was the largest possible lattice in this work. We compare our results with those of quantum Monte Carlo simulations employing the Hirsch-Fye algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. von Klitzing, G. Dorda and M. Pepper, Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 494 (1980)
C. Tsui, H. L. Stormer and A. C. Gossard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 1559 (1982).
J. G. Bednorz and K. A. Müller, Z. Phys. B 64, 189 (1986).
M. Z. Hasan and C. L. Kane, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3045 (2010).
M. C. Gutzwiller, Phys. Rev. Lett. 10, 159 (1963).
J. Kanamori, Prog. Theor. Phys. 30, 275 (1963).
J. Hubbard, Proc. R. Soc. A 276, 237 (1963).
E. Dagotto, Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 763 (1994).
E. H. Lieb and F. Y. Wu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 20, 1445 (1968); Erratum, ibid. 21, 192 (1968).
W. Metzner and D. Vollhardt, Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 324 (1989).
J. Spalek and A. M. Olés, Physica B 86-88, 375 (1977).
J. Hubbard and J. B. Torrance, Phys. Rev. Lett. 47, 1750 (1981).
E. R. Gagliano, E. Dagotto, A. Moreo and F. C. Alcaraz, Phys. Rev. B 34, 1677 (1986).
E. Dagotto, A. Moreo, F. Ortolani, D. Poilblanc and J. Riera, Phys. Rev. B 45, 10741 (1992).
S. Sachdev, Quantum Phase Transitions (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1999).
D. Baeriswyl and W. von D. Linden, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 5, 999 (1991).
K. Bouadim, N. Paris, F. Hébert, G. G. Batrouni and R. T. Scalettar, Phys. Rev. B 76, 085112 (2007).
B. Martinie, arXiv:1002.0325 (2013).
L. Craco, P. Lombardo, R. Hayn, G. I. Japaridze and E. Müller-Hartmann, Phys. Rev. B 78, 075121 (2008).
J. E. Hirsch and R. M. Fye, Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 2521 (1986).
http://openmp.org.
http://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/non-commercial- software-download.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, J., Lee, JW. Exact diagonalization and quantum Monte Carlo study of an ionic Hubbard model in two dimensions. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 70, 494–498 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.70.494
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.70.494