Abstract
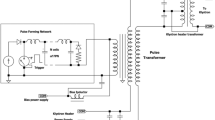
Medical linear accelerators (LINAC) for cancer treatment require pulse modulators to generate high-power pulses with a fast rise time, flat top and short duration to drive high-power magnetrons. Solid-state pulse modulators (SSPM) for medical LINACs that use high power semiconductor switches with high repetition rates, high stability and long lifetimes have been introduced to replace conventional linear-type pulse generators that use gaseous discharge switches. In this paper, the performance of a developed SSPM, which mainly consists of a capacitor charger, an insulatedgate bipolar transistor (IGBT)–capacitor stack and a pulse transformer, is evaluated with a dummy load and an X-band magnetron load. A theoretical analysis of the pulse transformer, which is a critical element of the SSPM, is carried out. The output pulse has a fast rise time and low droop, such that the modulator can drive the X-band magnetron.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. J. Karzmark, C. S. Nunan and E. Tanabe, Medical Electron Accelerators, (McGraw-Hill, NewYork, NY, 1993), p. 105.
R. G. Schonberg, H. Deruyter, W. R. Fowkes, W. A. Johnson, R. H. Miller, J. M. Potter and J. N. Weaver, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. NS-32, 5, 3234 (1985).
A. Saverskiy, H. Deruyter, M. Hernandez, A. Mishin and D. Skowbo, Portable X-band Linear Electron Accelerators for Radiographic Applications in Proceedings of 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference, (Knoxville, TN, 2005), p. 1985.
G. N. Glasoe and J. V. Lebacqz, Pulse Generators, (McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1948), p. 499.
IEEE Standard for Pulse Transformers, ANSI/IEEE Std 390-1987 (R2007), 1987.
N. R. Grossner, Transformers for Electronic Circuits, 2nd edition, (McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1983), p. 382.
S. D. Jang, Y. G. Son, J. S. Oh, Y. S. Bae, H. G. Lee, S. I. Moon, M. H. Cho and W. Namkung, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 49, S309 (2006).
P. W. Smith, Transient Electronics Pulsed Circuit Technology, (John Wiley & Sons Ltd, West Sussex, England, 2002), p. 137.
M. Akemoto, S. Gold, A. Krasynkh and R. Koontz, Pulse Transformer R&D for NLC Klystron Pulse Modulator, in Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Pulsed Power Conference (Baltimore, MD, 1997), p. 1.
A. S. Sedra and K. C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits, 4th edition, (Oxford University Press, New York, NY, 1998), p. 909.
R. Lee, IEEE Trans. Magn., Mag-13 5, 1220 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Shin, YM., Choi, YW. et al. Solid-state pulse modulator for a 1.7-MW X-band magnetron. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 64, 1267–1271 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.64.1267
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.64.1267