Abstract
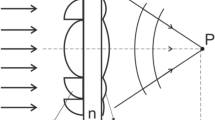
The shape of the diffractive structure of a deflecting kinoform element designed for focusing high-power laser beams with a wavelength of 10.6 µm is studied. Formulas are derived for calculating light losses induced by tilting of the incident beam, diffraction, and technological blurring of the steep slope of the structure. It is demonstrated that the height of the structure varies from the minimum to the maximum value depending on the azimuthal angle. It is found that light loss induced by shadowing due to oblique incidence of the beam is rather low (0.6–1.3%), and that caused by diffraction is smaller by an order of magnitude and can be neglected. The light losses induced by technological blurring of the slope and by deviation of the structure height from the design value (in the case of violation of the azimuthal dependence) can exceed 10%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. P. Rileey and F. N. Birkett, “A Reflection Kinoform for Use with CO2 Laser,” Opt. Acta 24 (10), 999–1009 (1977).
A. V. Goncharskii, V. A. Danilov, V. V. Popov, et al., “Solving an Inverse Problem of Laser Beam Focusing to an Arbitrary Curve,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 273, 605–608 (1983).
G. J. Swanson and W. B. Veldkamp, “Binary Lenses for Use at 10.6 Micrometers,” Opt. Eng. 24 (5), 791–795 (1985).
M. C. Hutley, R. F. Stevens, and S. J. Wilson, “The Manufacture of Blazed Zone Plates for Use in the 10 µm Spectral Region,” Opt. Eng. 30 (7), 1005–1010 (1991).
G. A. Lenkova, “Deflecting Focusing Kinoform,” Avtometriya, No. 6, 7–12 (1985).
V. Moreno, M. C. Hutley, and J. R. Tyrer, “The Manufacture of Blazed Oblique Zone Plates for Use at 10.6 µm,” in Proc. of the 2nd IEE Intern. Conf. Holographic Systems, Components and Applications, Bath, UK, September 11–13, 1989, pp. 76–79.
B. Dubik, M. Zaionts, and E. Novak, “Focusing Kinoform Mirror,” Avtometriya, No. 2, 85–88 (1990).
A. G. Poleshchuk, V. P. Koronkevich, V. P. Korol’kov, et al., “Synthesis of Diffractive Optical Elements in a Polar Coordinate System: Manufacturing Errors and their Measurement,” Avtometriya, No. 6, 42–56 (1997).
G. A. Lenkova, “Effect of the Phase Profile Depth on the Intensity Distributions in the Orders of Diffraction of a Bifocal Element,” Avtometriya, No. 5, 16–24 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © G.A. Lenkova, 2015, published in Avtometriya, 2015, Vol. 51, No. 6, pp. 32–40.
About this article
Cite this article
Lenkova, G.A. High-efficiency diffractive focusing deflecting element. Optoelectron.Instrument.Proc. 51, 560–567 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S8756699015060059
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S8756699015060059