Abstract
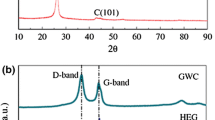
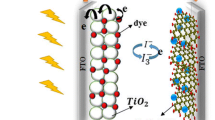
Graphene nano-sheets were prepared from natural graphite by a simple high shear exfoliation technique in suspension form and in bulk quantity. The structural properties of the graphene thus prepared were characterised by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering. BYK-multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) paste was infused into the graphene solution. UV-Vis spectroscopy was performed to know the concentration of both graphene and CNT solution. Glass microslides were used to be coated with used to be coated with the graphene-MWCNT solution and surface morphology was studied by field emission scanning electron microscopy. The study of morphology showed that the CNT’s provide better connectivity across the graphene flakes. Sheet resistance was measured by the van der Pauw method. An optimum concentration for CNT was found out for lowest sheet resistance. 3-Aminopropyl triethoxysilane (APTES) was added into the graphene-CNT composite paste to achieve better adhesion. Cell assembling was done using TiO2 coated photo-anodes, tri-iodide/iodide electrolyte solution and the graphene-CNT-APTES based counter-electrodes. APTES improves the adhesion and was able to reduce the cell-cost.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hwang, S., Batmunkh, M., et al., Chem. Phys. Chem., 2015, vol. 16, pp. 53–65.
Hamann, T.W., Jensen, R.A., Martinson, A.B.F., van Ryswyk, H., et al., Energy Environ. Sci., 2008, vol. 1, pp. 66–78.
O’Regan, B. and Gratzel, M., Nature, 1991, vol. 353, pp. 737–740.
Hinsch, A., Veurman, W., Henning Brandt, H., Jensen, K.F., et al., Chem. Phys. Chem., 2014, vol. 15, pp. 1076–1087.
Gratzel, M., et al., Nature, 2001, vol. 414, pp. 338–344.
Gratzel, M., et al., Inorg. Chem., 2005, vol. 44, no. 20, pp. 6841–6851.
Olsen, E., Hagen, G., Lindquist, S., et al., Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2000, vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 267–273.
Velten, J., Mozer, A.J., Li, D., et al., Nanotechnology, 2012, vol. 23, p. 085201.
Pang, B., Dong, L., Ma, S., Dong, H., and Yu, L., et al., RSC Adv., 2016, vol. 6, p. 41 287.
Park, H., Chang, S., Zhou, X., et al., Nano Lett., 2014, vol. 14, no. 9, pp. 5148–5154.
Xu, X., Huang, D., Wang, M., et al., Sci. Rep., 2013, vol. 3, p. 1489.
Geim, A.K., et al., Science, 2009, vol. 324, no. 5934, pp. 1530–1534.
Campos-Delgado, J., Romo-Herrera, J.M., Jia, X., et al., Nano Lett., 2008, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 2773–2778.
Scarpa, F., Adhikari, S., Srikantha Phani, A., et al., Nanotechnology, 2009, vol. 20, p. 065709.
Geim, A.K., Novoselov, K.S., et al., Nat. Mater., 2007, vol. 6, pp. 183–191.
Wu, J., Agrawal, M., Becerril, H.A., et al., ACS Nano, 2010, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 43–48.
Yung, K.C., Wu, W.M., Pierpoint, M.P., et al., Contemp. Phys., 2013, vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 233–251.
Shim, W., Kwon, Y., Jeon, S.-Y., et al., Sci. Rep., 2015, vol. 5, p. 16 568.
Paton, K.R., et al., Nat. Mater., 2014, vol. 13, pp. 624–630.
Kumar, A., Zhou, C., et al., ACS Nano, 2010, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 11–14.
Karanveer, S.A., Sivasambu, B., Khanna, A.S., et al., Nanoscale, 2015, vol. 42, pp. 17 879–17 888.
Nemala, S.S., Kartikay, P., Mallick, S., et al., J. Coll. Interface Sci., 2017, vol. 499, pp. 9–16.
Wang, G., Yang, J., Park, J., et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, vol. 112, pp. 8192–8195.
Liu, N., Luo, F., Wu, H., et al., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2008, vol. 18, pp. 1518–1525.
Saranya, K., Sivasankar, N., Subramania, A., et al., RSC Adv., 2014, vol. 4, p. 36 226.
Gao, W., et al., Graphene Oxide: Reduction Recipes, Spectroscopy, and Applications, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2015.
Beams, R., Cancado, L.G., Novotny, L., et al., J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 2015, vol. 27, p. 083 002.
Muzyka, R., Drewniak, S., Pustelny, T., et al., Materials (Basel), 2018, vol. 11, no. 7, p. 1050.
Li, Z.F., Luo, G.H., Zhou, W.P., et al., Nanotechnology, 2006, vol. 17, no. 15, pp. 3692–3698.
Dodoo-Arhin, D., Howe, R.C.T., Hu, G., et al., Carbon, 2016, vol. 105, pp. 33–41.
Devi, M., Sahu, S.R., Mukherjee, P., et al., RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5, p. 62 284.
Nemala, S.S., Kartikay, P., Mallick, S., et al., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, vol. 1, pp. 2512–2519.
Li, X., Cai, W., Jung, I., et al., ECS Trans., 2009, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 41–52.
Lotya, M., Rakovich, A., Donegan, J.F., et al., Nanotechnology, 2013, vol. 24, p. 265 703.
Roy-Mayhew, J.D., Bozym, D.J., Punckt, C., et al., ACS Nano, 2010, vol. 4, no. 10, pp. 6203–6211.
Wu, J., Lan, Z., Lin, J., et al., Chem. Rev., 2015, vol. 115, no. 5, pp. 2136–2173.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Metallurgical Engineering and Materials Science department at the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, India for providing the lab facilities required for this project, Department of Science and Technology, India, and the Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility at the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, India for characterization facilities.
Funding
The authors are grateful to the Solar Energy Research Institute for India and the United States and the National Centre for Photovoltaic Education and Research, India, for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Ratul Kumar Biswas, Nemala, S.S. & Mallick, S. Platinum and Transparent Conducting Oxide Free Graphene-CNT Composite Based Counter-Electrodes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Surf. Engin. Appl.Electrochem. 55, 472–480 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375519040021
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375519040021