Abstract
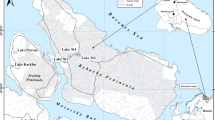
The concentration of Si, Al, Mg, K, Ca, Na, Sr, and Ba in the subcolloidal fraction of sediments at the Razdol’naya River-Amur Bay cross-section is determined using the atomic emission spectroscopy method. Computed is the mean content of studied elements in the soil and river bottom sediments (to the mixing zone). Revealed are river bottom sediments with the high concentration of macroelements corresponding to the zone of mixing of fresh river water and salt sea water. It is demonstrated that the additional accumulation of macroelements (Ca, Na, and Sr) in these sediments is associated with the formation of hydroxides of Fe and Mn and processes of sorption (Mg, Ca, Na, K, Sr, and Ba) on clay minerals (hydromica and smectites).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. V. Gordeev and A. P. Lisitsyn, “Mean Chemical Composition of Suspensions of World Rivers and Nourishment of Oceans with River Sediments,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, No. 1, 238 (1978) [in Russian].
E. T. Degens, Geochemistry of Sediments (Mir, Moscow, 1967) [Transl. from English].
J. I. Drever, The Geochemistry of Natural Waters (Mir, Moscow, 1985) [Transl. from English].
V. A. Drits and A. G. Kosovskaya, Clay Minerals: Smectites and Mixed-lattice Formations (Nauka, Moscow, 1990) [in Russian].
V. I. Zavalinskii, A. P. Nedashkovskii, S. G. Sagalaev, et al., “Nutrients and Primary Production in the Estuary of the Razdol’naya River (Amur Bay, Sea of Japan),” Biologiya Morya, No. 2, 31 (2005) [Russ. J. Mar. Biology, No. 2, 31 (2005)].
A. P. Lisitsyn, “Marginal Filter of Oceans,” Okeanologiya, No. 5, 34 (1994) [Oceanology, No. 5, 34 (1994)].
A. P. Lisitsyn, L. L. Demina, and V. V. Gordeev, “River-Sea Geochemical Barrier and Its Role in Sedimentation Pro cess,” in Ocean Biochemistry (Nauka, Moscow, 1983) [in Russian].
A. P. Lisitsyn, V. I. Lukashin, E. M. Emel’yanov, and I. B. Zverinskaya, “Aluminum,” in Geochemistry of Elements-Hydrolyzates (Nauka, Moscow, 1980) [in Russian].
V. N. Mikhailov, V. N. Morozov, E. S. Povalishnikova, et al., “Experimental Studies of River- and Seawater Mixing in the Mouth of the Danube,” Vodnye Resursy, No. 1, 27 (2000) [Water Resources, No. 1, 27 (2000)].
V. I. Osipov, V. N. Sokolov, and N. A. Rumyantseva, Microstructure of Clay Rocks (Nedra, Moscow, 1989) [in Russian].
A. I. Perel’man, Geochemistry of Elements in Hypergenesis Zone (Nedra, Moscow, 1972) [in Russian].
V. P. Petelin, Particle-Size Analysis of Marine Bottom Sediments (Nauka, Moscow, 1967) [in Russian].
D. M. Polyakov and K. I. Aksentov, “Dynamics of Accumulation of Heavy Metals by Subcolloidal Fraction of Bottom Sediments as a Result of Biochemical Processes in the Marginal Filter of the Razdol’naya River (the Amur Bay, the Sea of Japan),” Meteorol. Gidrol., No. 11 (2013) [Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol., No. 11, 38 (2013)].
D. M. Polyakov, N. D. Khodorenko, and A. A. Mar’yash, “Some Aspects of Organic Matter Accumulation by the Subcolloidal Fraction of Bottom Sediments on the “River-Sea” Barrier (the Razdol’naya River-the Amur Bay),” Vestnik DVO RAN, No. 6 (2012) [in Russian].
P. Ya. Tishchenko, V. I. Zvalinskii, and O. V. Shevtsova, “Hydrochemical Studies of the Razdol’naya River-Amur Bay Estuary,” in The State of Marine Ecosystems Affected by River Runoff (Dal’nauka, Vladivostok, 2005) [in Russian].
G. S. Bien, D. E. Contois, and W. H. Thomas, “The Removal of Soluble Silica from Fresh Water Entering the Sea,” Geochim. et cosmochim. acta, No. 1, 14 (1958).
P. E. Biscaye, “Mineralogy and Sedimentation of Recent Deep-sea Clay in the Atlantic Ocean and Adjacent Seas and Oceans,” J. Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer., No. 7, 76 (1965).
F. Frascari, M. Frignani, P. Giordani, et al., “Sedimentological and Geochemical Behavior of Heavy Metals in the Area near the Po River Delta,” Mem. Soc. Geol. It., 27 (1984).
A. Gunnars, S. Blomqvist, P. Johansson, and C. Andersson, “Formation of Fe(III) Oxyhydroxide Colloids in Freshwaters and Brackish Seawater, with Incorporation of Phosphate and Calcium,” Geochim. et cosmochim. acta, No. 5, 66 (2002).
J. Hosokawa, K. Ochshima, and N. Kondo, “On the Concentration of the Dissolved Chemical Elements in the Estuary of the Chkugogawa River,” J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jap., No. 1, 26 (1970).
W. A. House, F. H. Denison, M. S. Watwick, and B. V. Zhmud, “Dissolution of Silica and the Development of Concentration Profiles in Fresh Sediments,” Appl. Geochem., 15 (2000).
A. A. Levinson, B. Hitchon, and S. W. Reeder, “Major Element Composition of the Mackenzie River at Norman Wells,” Geochim. et cosmochim. acta, No. 1, 33 (1969).
P. S. Liss and M. J. Pointon, “Removal of Dissolved Boron and Silicon during Estuarine Mixing of Sea and River Waters,” Geochim. et cosmochim. acta, 37 (1973).
D. A. Livingstone, Chemical Composition of Rivers and Lakes: Data of Geochemistry (US Covt. Print. Off., Washington, 1963).
J. L. Mackenzie and R. M. Garrels, “Silica in Sea Water. Control by Silicate Minerals,” Science, 155 (1955).
A. Monako, “Sur Quelgues Phenomenes d’Echangesioniques duas les Suspensions Argileuses au Contact de l’Eau de Mer,” C. r. Acad. Sci., No. 14, D270 (1970).
R. Y. Ning, “Discussion of Silica Speciation, Fouling, Control and Maximum Reduction,” Desalination, 151 (2002).
K. L. Russel, “Geochemistry and Halmirolis of Clay Minerals. Rio Ameca; Mexico,” Geochim. et cosmochim. acta, 34 (1970).
E. R. Sholkovitz, “The Flocculation of Dissolved Fe, Mn, Al, Cu, Ni, Co, and Cd during Estuarine Mixing,” Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett., No. 2, 41 (1978).
M. Tanaka and K. Takahashi, “Estuarine. Ionised Silica in the Estuary of a River as Supply to Seawater: Identification and Ionization Efficiency of Silica Species by FAB-MS,” Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 121–122 (2013).
R. Wallast, G. Billen, and F. Mackenzie, “Behavior of Mercury in Natural Systems and Its Global Cycle,” Ecolog. Loxicol. Res. (1976).
R. Wollast, “The Silica Problem,” in The Sea, Vol. 5 (Wiley-Intersci., N. Y., 1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.M. Polyakov, A.V. Mozherovskii, A.A. Mar’yash, 2014, published in Meteorologiya i Gidrologiya, 2014, No. 10, pp. 79–88.
About this article
Cite this article
Polyakov, D.M., Mozherovskii, A.V. & Mar’yash, A.A. Geochemical aspects of accumulation of macroelements in the subcolloidal fraction of bottom sediments at the Razdol’naya River-Amur Bay cross-section (the Sea of Japan). Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 39, 697–704 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068373914100070
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068373914100070