Abstract
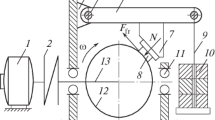
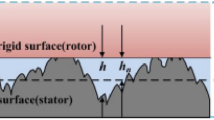
The results of an experimental study of the effect of the normal pressure in the range of 0.1–0.3MPa, a velocity of sliding of 1–100 mm/s, and a bulk temperature of 22 to–27°C on the coefficient of sliding friction of an elastomer–steel friction pair have been presented. Two types of elastomeric materials have been considered, i.e., frost-resistant rubber based on synthetic propylene oxide rubber and this rubber filled with the antifriction additive of ultrafine polytetrafluoroethylene powder in an amount of 1 weight part per 100 weight parts. The results have shown the efficiency of filling rubbers with ultrafine polytetrafluoroethylene; the coefficient of sliding friction at temperatures below–15°C decreases by more than two times.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Govorova, O.A., Vishnitskii, A.S., Chubarova, A.S., and Morozov, Yu.L., Development of weather–resistant vulcanisates with improved low–temperature and adhesion properties, Kauchuk i Rezina, 1999, no. 2, pp. 18–20.
Portnyagina, V.V., Petrova, N.N., and Zarovnyaev, B.N., Study of operability of sealing rubbers of mining equipment in extreme climatic conditions of North, Gorn. Inform.-Anal. Byull., 2014, no. 9, pp. 371–380.
Adrianova, O.A., Modificated polmernnye and elastomer tribotechnical materials for technics of North, Doctoral (Eng.) Dissertation, Moskva, 2000.
Sokolova, M.I., Elastomer nanocomposites of packing designation for extreme conditions of exploitation in the zones with cold climate, Doctoral (Eng.) Dissertation, Komsomol’sk-na-Amure, 2012.
Buznik, V.M., Fomin, V.M., and Alkhimov, A.P., Metallopolimernye nanokompozity (Metal–Polymer Nanocomposites), Novosibirsk: Sibir. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2005.
Portnyagina, V.V. and Petrova, N.N., Rubbers based on blends of propylene oxide and ultrafine polytetrafluoroethylene, Kauchuk i Rezina, 2014, no. 6, pp. 40–43.
Rezina–konstruktsionnyi material sovremennogo mashinostroeniya / (Rubber–Construction Material of Contemporary Machine Engineering. Coll. of Papers), Badenkov, P.M., Evstratov, V.F., and Reznikovskii,M.M., Eds., Moscow: Khimiya, 1967.
Schallamach, A., A theory of dynamic rubber friction, Wear, 1963, no. 6, pp. 375–382.
Grosch, K.A., Rubber friction and tire traction. Chap. 11, in The Pneumatic Tire, Gent, A.N. and Walter, J.D., Eds., Washington, D.C.: NHTSA, 2005.
Goryacheva, I.G. and Makhovskaya, Yu.Yu., Modeling of friction at different scale levels, Mechan. Solids, 2010, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 390–398.
Goryacheva, I.G. and Makhovskaya, Yu.Yu., Sliding of a wavy indentor on a viscoelastic layer surface in the case of adhesion, Mechan. Solids, 2015, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 439–450.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Morozov, N.N. Petrova, 2016, published in Trenie i Iznos, 2016, Vol. 37, No. 2, pp. 162–167.
About this article
Cite this article
Morozov, A.V., Petrova, N.N. Method of evaluating the coefficient of friction of frost-resistant sealing rubbers. J. Frict. Wear 37, 124–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068366616020124
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068366616020124