Abstract
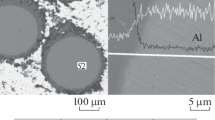
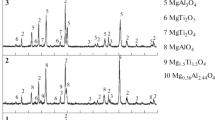
Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) in the Ni–Al–Ti–B system has been carried out. The aim of the study is to obtain, in one process step, a composite material with a ceramic and intermetallic framework and a developed porous structure in combustion mode from the boron–titanium–large nickel-clad aluminum granules powder system pressed by successive batch compaction method. The synthesis process is characterized by a stage nature, in which a highly exothermic reaction between titanium and boron form a boride matrix with developed open porosity and acts as a “chemical furnace” to maintain the reaction in the clad granules, in which nickel aluminides appeared. The aluminide melt impregnates the porous diboride matrix. The synthesis stages are reflected in the thermograms of the process. The final structure of the product has a multiscale porosity, a characteristic feature of which is large round pores (~100–160 μm in diameter) whose location corresponds to the position of clad granules in the initial powder system. Small (0.1–5.0 μm) and some average-sized (up to 15 μm) diboride matrix pores are filled with nickel aluminides. The resulting material has a composite structure of the type of interpenetrating frameworks—ceramic (TiB2) and aluminide (NiAl, Ni3Al). The diboride matrix is formed by chaotically oriented hexagonal small crystals predominantly 0.2–1.0 μm across in size. At the boundaries with macropores, crystal diboride grains increase in size up to 2–6 μm in diameter and 0.5–2.0 μm in thickness, acquiring a more pronounced platelike shape. The main size of intermetallic interlayers filling the pores between the diboride crystal grains is ~0.2–1.0 μm.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Borovinskaya, I.P., On the regulation of the composition, structure and properties of SHS-products, in Kontseptsiya razvitiya SVS kak oblasti nauchno-tekhnicheskogo progressa. Sbornik (Concept of Development of SHS as a Field of Scientific-Technical Progress. Collection of Articles), Merzhanov, A.G., Ed., Chernogolovka: Territoriya, 2003.
Maznoi, A.S. and Kirdyashkin, A.I., Influence of initial parameters of reacting systems on the porosity structure of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis products, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 2014, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 60–67. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508214010079
Andriyanov, D.I., Amosov, A.P., and Samboruk, A.R., Influence of granulation of powder charge of titanium-boron on regularities of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of porous material, Key Eng. Mater., 2016, vol. 685, pp. 500–504. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.685.500
Ponomarev, M.A., Loryan, V.E., Kochetov, N.A., and Merzhanov, A.G., SHS in preliminary structured compacts: I. Ni-Al blends, Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 2013, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 193–201. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386213040043
Ponomarev, M.A., Loryan, V.E., Shchukin, A.S., and Merzhanov, A.G., SHS in preliminary structured compacts: II. Ti-2B and Ti-Al blends, Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 2013, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 202–209. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386213040055
Ponomarev, M.A. and Loryan, V.E., Synthesis of porous composite materials via combustion of a mixture of titanium, VT6 alloy, and amorphous boron powders, Inorg. Mater., 2018, vol. 54, no. 8, pp. 772–778. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168518080150
Ponomarev, M.A. and Loryan, V.E., Synthesis of composite material in Al-Ti-B system during combustion of titanium and boron powders and aluminum-clad granules of VT6 alloy, Inorg. Mater.: Appl. Res., 2019, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 1204–1212. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113319050241
Hyjek, P., Sulima, I., and Jaworska, L., Application of SHS in the manufacture of (NiAl/Ni3Al)/TiB2 composite, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2019, vol. 50, no. 8, pp. 3724–3735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05306-w
Camurlu, H.E. and Maglia, F., Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of ZrB2 or TiB2 reinforced Ni–Al composite powders, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, vol. 478, nos. 1–2, pp. 721–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.11.139
Bhaumik, S.K., Divakar, C., Rangaraj, L., and Singh, A.K., Reaction sintering of NiAl and TiB2–NiAl composites under pressure, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, vol. 257, no. 2, pp. 341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(98)00862-4
Li Ma, Hong Zhi Cui, Li Li Cao, Fang Lei Teng, Ning Cui, and Lei Liu, The synthesis of porous TiC–TiB2–NiAl composites by SHS, Adv. Mater. Res., 2013, vols. 634–638. pp. 2110–2118. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.634-638.2110
Wei, N., Cui, H., Ma, L., Song, X., Liu, W., and Hou, N., Porous TiC–TiB2–NiAl composites and effect of NiAl contents on pore structure and microstructure, Powder Metall., 2015, vol. 58, pp. 273–280. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743290115Y.0000000007
Heng Zhang and He-Guo Zhu, In situ synthesis of TiB2/NiAl composite, Proc. 2nd Annual Int. Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 2016), Wuhan, 2016, Atlantis Press, 2016, pp. 31–135. https://doi.org/10.2991/ame-16.2016.22
Guo, J.T. and Xing, Z.P., Investigation of NiAl-TiB2 in situ composites, J. Mater. Res., 1997, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1997.0151
Yi, H.C., Varma, A., Rogachev, A.S., and McGinn, P.J., Gravity-induced microstructural nonuniformities during combustion synthesis of intermetallic-ceramic composite materials, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1996, vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 2982–2985. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie950750v
Mukasyan, A.S., Pelekh, A., Varma, A., and Rogachev, A.S., Effects of gravity on combustion synthesis in heterogeneous gasless systems, AIAA J., 1997, vol. 35, no. 12, pp. 1821–1828. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.13757
Merzhanov, A.G., Thermally coupled SHS reactions, Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 2011, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 61–63. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386211010109
Mukasyan, A.S., Lau, C., and Varma, A., Gasless combustion of aluminum particles clad by nickel, Combust. Sci. Technol., 2001, vol. 170, no. 1, pp. 67–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/00102200108907850
Lapshin, O.V. and Ovcharenko, V.E., A mathematical model of high-temperature synthesis of nickel aluminide Ni3Al by thermal shock of a powder mixture of pure elements, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 1996, vol. 32, no. 3. pp. 299–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01998460
Gasparyan, A.G. and Shteinberg, A.S., Macrokinetics of reaction and thermal explosion in Ni and Al powder mixtures, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 1988, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 324–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750616
Korchagin, M.A., Filimonov, V.Y., Smirnov, E.V., and Lyakhov, N.Z., Thermal explosion of a mechanically activated 3Ni-Al mixture, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 2010, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 41–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10573-010-0007-7
Rosenband, V. and Gany, A., Thermal explosion synthesis of a magnesium diboride powder, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 2014, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 653–657. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508214060057
Larina, T.V., Perminov, V.P., Sosnov, A.N., and Neronov, V.A., Methods of production of aluminum and magnesium borides, Geo-Siberia, 2007, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 109–112. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.201403468
Popov, D.A., Ogorodov, D.V., and Trapeznikov, A.V., Alternative sources of boron-containing raw materials for the Al-B ligatures production (review), Tr. Vseross. Inst. Aviats. Mater., 2015, no. 10, pp. 41–47. https://doi.org/10.18577/2307-6046-2015-0-10-7-7
Azatyan, T.S., Mal’tsev, V.M., Merzhanov, A.G., and Seleznev, V.A., Combustion wave propagation mechanism in titanium-boron mixtures, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 1980, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 163–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00740195
Kirdyashkin, A.I., Maksimov, Yu.M., and Merzhanov, A.G., Effects of capillary flow on combustion in a gas-free system, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 1981, vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 591–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00784246
Andreev, V.A., Levashov, E.A., Mal’tsev, V.M., and Khavskii, N.N., Characteristics of capillary mass transfer in a combustion wave in multicomponent heterogeneous systems, Combust., Explos., Shock Waves, 1988, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 189–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749186
Ponomarev, M.A., Shcherbakov, V.A., and Shteinberg, A.S., Combustion patterns of thin layers of Ti-B powder mixture, Dokl. Akad. Nauk, 1995, vol. 340, no. 5, pp. 642–645.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by V. Selikhanovich
About this article
Cite this article
Ponomarev, M.A., Loryan, V.E. Synthesis of Porous Composite Material with the Combustion of Titanium and Boron Powders and Nickel-Clad Aluminum Granules. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 61, 716–724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220060176
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220060176