Abstract
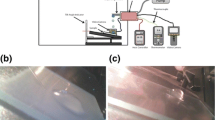
Sol–gel is a convenient method to fabricate micro-nano structures on various surfaces. In the present study, rough alumina surfaces were prepared from aluminum isopropoxide and ethyl acetoacetate and modified with low-concentration lauric acid (LA) dissolved in ethanol. The sample hydrophobicity and antiicing property were optimized by changing the rotation speed, rotation time, and coating thickness during spin-coating, and the type and concentration of surface modifier used during surface hydrophobization. Superhydrophobic surfaces were achieved with contact angle values as high as 157.6°, when 0.4-mm-thick coatings were modified with 0.4% LA dissolved in ethanol. The surface morphology of the superhydrophobic samples was shown to be rough at micro/nano-scale, which allowed them to demonstrate excellent anti-icing properties. Specifically, the optimized sample could delay the icing time and reduce the freezing temperature from 15 min and–4.1°C (for uncoated aluminum) to 65 min and–8.3°C, respectively, while also reducing the ice adhesion strength twice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, Y., Wu, Z., Su, Y., and Xu, Z., Aircraft flight characteristics in icing conditions, Prog. Aerosp. Sci., 2015, vol. 74, pp. 62–80. doi 10.1016/j.paerosci.2014.12.001
Habibi, H., Cheng, L., Zheng, H., Kappatos, V., Selcuk, C., and Gan, T.-H., A dual de-icing system for wind turbine blades combining high-power ultrasonic guided waves and low-frequency forced vibrations, Renew. En., 2015, vol. 83, pp. 859–870. doi 10.1016/j.renene.2015.05.025
Lacavalla, M., Marcacci, P., and Frigerio, A. In Forecasting and monitoring wet-snow sleeve on overhead power lines in Italy, 2015 IEEE Workshop on Environmental, Energy and Structural Monitoring Systems (EESMS), 2015, pp. 78–83.
Saito, H., Takai, K., and Yamauchi, G., Water-and icerepellent coatings, Surf. Coat. Int., 1997, vol. 80, no. 4, pp. 168–171. doi 10.1007/BF02692637
Mulherin, N.D. and Haehnel, R.B., Ice Engineering: Progress in Evaluating Surface Coatings for Icing Control at Corps Hydraulic Structures, Hanover, New Hampshire: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, 2003, vol. ERDC/CRREL TN-03-4.
Zheng, L., Li, Z., Bourdo, S., Khedir, K.R., Asar, M.P., Ryerson, C.C., and Biris, A.S., Exceptional superhydrophobicity and low velocity impact icephobicity of acetone-functionalized carbon nanotube films, Langmuir, 2011, vol. 27, no. 16, pp. 9936–9943. doi 10.1021/la201548k
Ruan, M., Li, W., Wang, B., Deng, B., Ma, F., and Yu, Z., Preparation and anti-icing behavior of superhydrophobic surfaces on aluminum alloy substrates, Langmuir, 2013, vol. 29, no. 27, pp. 8482–8491. doi 10.1021/la400979d
Gao, X. and Jiang, L., Biophysics: water-repellent legs of water striders, Nature, 2004, vol. 432, no. 7013, pp. 36–36. doi 10.1038/432036a
Shirtcliffe, N.J., McHale, G., Newton, M.I., and Zhang, Y., Superhydrophobic copper tubes with possible flow enhancement and drag reduction, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2009, vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 1316–1323. doi 10.1021/am9001937
Chen, Y., Chen, S., Yu, F., Sun, W., Zhu, H., and Yin, Y., Fabrication and anti-corrosion property of superhydrophobic hybrid film on copper surface and its formation mechanism, Surf. Interface Anal., 2009, vol. 41, no. 11, pp. 872–877. doi 10.1002/sia.3102
Wang, R., Hashimoto, K., Fujishima, A., Chikuni, M., Kojima, E., Kitamura, A., Shimohigoshi, M., and Watanabe, T., Light-induced amphiphilic surfaces, Nature, 1997, vol. 388, pp. 431–432. doi 10.1038/41233
Cao, L., Jones, A.K., Sikka, V K., Wu, J., and Gao, D., Anti-icing superhydrophobic coatings, Langmuir, 2009, vol. 25, no. 21, pp. 12444–12448. doi 10.1021/la902882b
Feng, L., Li, S., Li, Y., Li, H., Zhang, L., Zhai, J., Song, Y., Liu, B., Jiang, L., and Zhu, D., Super-hydrophobic surfaces: from natural to artificial, Adv. Mater., 2002, vol. 14, no. 24, pp. 1857–1860. doi 10.1002/adma.200290020
Kulinich, S.A. and Farzaneh, M., Ice adhesion on superhydrophobic surfaces, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, vol. 255, no. 18, pp. 8153–8157. doi 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.05.033
Guo, P., Zheng, Y., Wen, M., Song, C., Lin, Y., and Jiang, L., Icephobic/anti-icing properties of micro/nanostructured surfaces, Adv. Mater., 2012, vol. 24, no. 19, pp. 2642–2648. doi 10.1002/adma.201104412
Arianpour, F., Farzaneh, M., and Kulinich, S.A., Hydrophobic and ice-retarding properties of doped silicone rubber coatings, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, vol. 265, pp. 546–552. doi 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.11.042
Wang, Y., Xue, J., Wang, Q., Chen, Q., and Ding, J., Verification of icephobic/anti-icing properties of a superhydrophobic surface, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, vol. 5, no. 8, pp. 3370–3381. doi 10.1021/am400429q
Kulinich, S.A., Farhadi, S., Nose, K., and Du, X.W., Superhydrophobic surfaces: Are they really ice-repellent?, Langmuir, 2011, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 25–29. doi 10.1021/la104277q
Farhadi, S., Farzaneh, M., and Kulinich, S.A., Antiicing performance of superhydrophobic surfaces, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, vol. 257, no. 14, pp. 6264–6269. doi 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.02.057
Kulinich, S.A., Honda, M., Zhu, A., Rozhin, A.G., and Du, X.W., The icephobic performance of alkylgrafted aluminum surfaces, Soft Matter., 2015, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 856–861. doi 10.1039/C4SM02204A
Xue, C.-H., Jia, S.-T., Zhang, J., and Ma, J.-Z., Largearea fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces for practical applications: an overview, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2016, vol. 11, p. 033002. doi 10.1088/1468- 6996/11/3/033002
Qian, B. and Shen, Z., Fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces by dislocation-selective chemical etching on aluminum, copper, and zinc substrates, Langmuir, 2005, vol. 21, no. 20, pp. 9007–9009. doi 10.1021/la051308c
Shibuichi, S., Yamamoto, T., Onda, T., and Tsujii, K., Super water-and oil-repellent surfaces resulting from fractal structure, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1998, vol. 208, no. 1, pp. 287–294. doi 10.1006/jcis.1998.5813
Baldacchini, T., Carey, J.E., Zhou, M., and Mazur, E., Superhydrophobic surfaces prepared by microstructuring of silicon using a femtosecond laser, Langmuir, 2006, vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 4917–4919. doi 10.1021/la053374k
Ma, M., Mao, Y., Gupta, M., Gleason, K.K., and Rutledge, G.C., Superhydrophobic fabrics produced by electrospinning and chemical vapor deposition, Macromolecules, 2005, vol. 38, no. 23, pp. 9742–9748. doi 10.1021/ma0511189
Lu, H., Gao, K., and Chu, W., Determination of tensile stress induced by dezincification layer during corrosion for brass, Corr. Sci., 1998, vol. 40, no. 10, pp. 1663–1670. doi 10.1016/S0010-938X(98)00063-8
Laforte, J., Allaire, M., and Laflamme, J., State-ofthe- art on power line de-icing, Atm. Res., 1998, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 143–158. doi 10.1016/S0169-8095(97)00057-4
Fu, Q., Wu, X., Kumar, D., Ho, J.W., Kanhere, P.D., Srikanth, N., Liu, E., Wilson, P., and Chen, Z., Development of sol–gel icephobic coatings: Effect of surface roughness and surface energy, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, vol. 6, no. 23, pp. 20685–20692. doi 10.1021/am504348x
Ayres, J., Simendinger, W., and Balik, C., Characterization of titanium alkoxide sol–gel systems designed for anti-icing coatings, II: Mass loss kinetics, J. Coat. Technol. Res., 2007, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 473–481. doi 10.1007/s11998-007-9055-7
Tang, Y., Zhang, Q., Zhan, X., and Chen, F., Superhydrophobic and anti-icing properties at overcooled temperature of a fluorinated hybrid surface prepared via a sol–gel process, Soft Matter, 2015, vol. 11, no. 22, pp. 4540–4550. doi 10.1039/C5SM00674K
Zhang, S. and Dreizin, E.L., Reaction interface for heterogeneous oxidation of aluminum powders, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, vol. 117, no. 27, pp. 14025–14031. doi 10.1021/jp402990v
Shi, M., Xi, J., Wang, H., and Wu, X., A translucent and superhydrophobic surface prepared with a sol–gel method based on alumina nanoparticles, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol., 2008, vol. 22, nos. 3–4, pp. 311–318. doi 10.1163/156856108X295419
Wang, S., Song, Y., and Jiang, L., Microscale and nanoscale hierarchical structured mesh films with superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties induced by long-chain fatty acids, Nanotechnology, 2006, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 015103. doi 10.1088/0957- 4484/18/1/015103
Wang, S., Feng, L., and Jiang, L., One-step solutionimmersion process for the fabrication of stable bionic superhydrophobic surfaces, Adv. Mater., 2006, vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 767–770. doi 10.1002/adma.200501794
Dakhakhni, T.H., Raouf, G.A., and Qusti, S.Y., Evaluation of the toxic effect of the herbicide 2,4-D on rat hepatocytes: An FT-IR spectroscopic study, Eur. Biophys. J., 2015, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1–10.
Lummerstorfer, T. and Hoffmann, H., IR reflection spectra of monolayer films sandwiched between two high refractive index materials, Langmuir, 2004, vol. 20, no. 16, pp. 6542–6545. doi 10.1021/la0492916
Tao, Y.T., Structural comparison of self-assembled monolayers of n-alkanoic acids on the surfaces of silver, copper, and aluminum, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, vol. 115, no. 10, pp. 4350–4358. doi 10.1021/ja00063a062
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, M., Wang, J.W., Liu, Q.L. et al. Superhydrophobic and anti-icing properties of sol–gel prepared alumina coatings. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 57, 638–645 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821216060122
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821216060122