Abstract
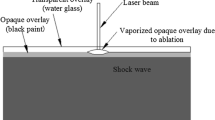
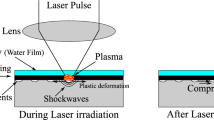
Laser shock forming is an innovative technology in which a laser shock wave induces a flexural deformation of a thin plate. Naturally, the technology of laser shock forming cannot increase the curvature of the plates indefinitely and its possibilities have limits, especially for thick plates. This article investigates the maximum convex flexural curvature of a plate that can be achieved using the technology of laser shock forming by successively increasing its main characteristics: the laser spot overlap factor, the number of repetitive laser pulses, and the intensity of laser power density. The resulting flexural torque and bending curvature are calculated from the average residual stresses obtained by the finite element method. The proposed method for predicting the plate curvature can effectively predict the flexural behavior of the plate. This allows one to plan the process of laser shock forming properly.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Peng, Y., Chen, J., Yang, L., and Wang, Y., Study on elongation after shot peen forming for integral panel of large aircraft, Aeronaut. Manuf. Technol., 2017, vol. 57, no. 9, p. 97.
Hu, Yo., Luo, M., and Yao, Z., Increasing the capability of laser peen forming to bend titanium alloy sheets with laser-assisted local heating, Mater. Des., 2016, vol. 90, no. 90, pp. 364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.128
Zhou, W.F., Ren, X.D., Wang, C.C., Yang, X.Q., and Larson, E.A., Residual stress induced convex bending in laser peen formed aluminum alloy, J. Laser Appl., 2018, vol. 30, no. 1, p. 12001. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.5012962
Hu, Y.X. and Yao, Z.Q., Fem simulation of residual stresses induced by laser shock with overlapping laser spots, Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.), 2008, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1006-7191(08)60029-0
Behera, A., Sahu, P.S., and Patel, S.K., Application of Taguchi methodology for optimization of process parameters in laser bending of Al sheet, Mater. Today: Proc., 2020, vol. 26, no. 26, pp. 2323–2327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.500
Hu, Yo., Xu, X., Yao, Z., and Hu, J., Laser peen forming induced two way bending of thin sheet metals and its mechanisms, J. Appl. Phys., 2010, vol. 108, no. 7, p. 73117. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3486218
Hu, Yo., Han, Ye., Yao, Z., and Hu, J., Three-dimensional numerical simulation and experimental study of sheet metal bending by laser peen forming, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2010, vol. 132, no. 6, p. 61001. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4002585
Luo, M., Hu, Yo., Hu, L., and Yao, Z., Efficient process planning of laser peen forming for complex shaping with distributed eigen-moment, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020, vol. 279, p. 116588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116588
Sagisaka, Yo., Kamiya, M., Matsuda, M., and Ohta, Yu., Thin-sheet-metal bending by laser peen forming with femtosecond laser, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2010, vol. 210, no. 15, pp. 2304–2309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.08.025
Xiao, X., Li, Yo., Sun, Ya., Zhao, P., Li, Ya., and Gao, G., Prediction of peen forming stress and curvature with dynamic response of compressively prestressed target, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, vol. 29, pp. 3079–3091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04851-5
Yang, Yu., Lu, Yi., Qiao, H., Zhao, J., Sun, B., Wu, J., and Hu, X., The effect of laser shock processing on mechanical properties of an advanced powder material depending on different ablative coatings and confinement medias, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2021, vol. 117, nos. 7–8, pp. 2377–2385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07080-9
Sun, B., Qiao, H., and Zhao, J., Accurate numerical modeling of residual stress fields induced by laser shock peening, AIP Adv., 2018, vol. 8, no. 9, p. 95203. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5039674
Zhu, R., Zhang, Y.K., Sun, G.F., Li, F., Zhang, S.B., and Ni, Z.H., Numerical simulation of residual stress fields in three-dimensional flattened laser shocking of 2024 aluminum alloy, Chin. J. Lasers, 2017, vol. 44, no. 8, p. 0802007.
Hu, Yo. and Grandhi, R., Efficient numerical prediction of residual stress and deformation for large-scale laser shock processing using the eigenstrain methodology, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, vol. 206, no. 15, pp. 3374–3385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.01.050
Hfaiedh, N., Peyre, P., Song, H., Popa, I., Ji, V., and Vignal, V., Finite element analysis of laser shock peening of 2050-T8 aluminum alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2015, vol. 70, pp. 480–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2014.05.015
Sakhvadze, G.Z., Finite element simulation of hybrid additive technology using laser shock processing, J. Mach. Manuf. Reliab., 2023, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 170–177. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1052618823020073
Sakhvadze, G.Z., Influence of biomimetic laser shock peening on the crack resistance and residual fatigue life of aluminum alloys, Russ. Eng. Res., 2022, vol. 42, no. Suppl. 1, pp. S33–S39. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X23010240
Sakhvadze, G.Z., Modeling of laser shock processing technology using an artificial neural network to determine the mechanical properties of the Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy, J. Mach. Manuf. Reliab., 2022, vol. 51, no. 8, pp. 831–839. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1052618822080167
Chen, D., Cheng, Z.Q., Cunningham, P.R., and Xiong, J., Fatigue life prediction of 2524-T3 and 7075-T62 thin-sheet aluminium alloy with an initial impact dent under block spectrum loading, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1096, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 1096–1113. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13416
Vukelić, S., Kysar, J.W., and Lawrence Yao, Y.L., Grain boundary response of aluminum bicrystal under micro scale laser shock peening, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2013, vol. 46, nos. 18–19, pp. 3323–3335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2009.04.021
Mylavarapu, P., Bhat, C., Perla, M.K.R., Banerjee, K., Gopinath, K., and Jayakumar, T., Identification of critical material thickness for eliminating back reflected shockwaves in laser shock peening—A numerical study, Opt. Laser Technol., 2021, vol. 142, p. 107217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107217
Hu, Yo. and Yao, Z., Overlapping rate effect on laser shock processing of 1045 steel by small spots with Nd:YAG pulsed laser, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2008, vol. 202, no. 8, pp. 1517–1525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2007.07.008
Cao, Yu., Feng, A., and Hua, G., Influence of interaction parameters on laser shock wave induced dynamic strain on 7050 aluminum alloy surface, J. Appl. Phys., 2014, vol. 116, no. 15, p. 775. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4898689
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by G. Dedkov
About this article
Cite this article
Sakhvadze, G.Z. Finite-Element Modeling of Laser Shock Forming Technology. J. Mach. Manuf. Reliab. 52, 500–508 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3103/S105261882305014X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S105261882305014X