Abstract
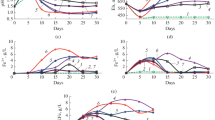
The effect of different organic compounds (glucose, fructose, ribose, glycine, alanine, pyruvate, acetate, citrate, and yeast extract) as well as of the wastes of food production (molasses, stillage, sweet whey), on the growth of iron-oxidizing acidophilic microorganisms and biooxidation of ferrous iron was studied. Representatives of the microorganisms predominating in biohydrometallurgical processes—archaea of the family Ferroplasmaceae (A. aeolicum V1T, A. cupricumulans BH2T, Acidiplasma sp. MBA-1, Ferroplasma acidiphilum B-1) and bacteria of the genus Sulfobacillus (S. thermosulfidooxidans SH 10–1, S. thermotolerans Kr1T)—were the subjects of the study. All studied strains most actively grew and oxidized ferrous iron in the presence of yeast extract, which is probably due to the presence of a large number of different growth factors in its composition, while others substrates provided growth of microorganisms and ferrous iron oxidation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, D.B., Biomining—biotechnologies for extracting and recovering metals from ores and waste materials, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 30, pp. 24–31.
Schippers, A., Microorganisms involved in bioleaching and nucleic acid-based molecular methods for their identification and quantification, in Microbial Processing of Metal Sulfides, Donati, E.R. and Sand, W., Eds., New York: Springer, 2007, pp. 3–33.
Hawkes, R.B., Franzmann, P.D., O’Hara, G., and Plumb, J.J., Ferroplasma cupricumulans sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic, acidophilic archaea isolated from an industrial-scale chalcocite bioleach heap, Extremophiles, 2006, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 525–530.
Zhou, H., Zhang, R., Hu, P., Zeng, W., Xie, Y., Wu, C., and Qiu, G., Isolation and characterization of Ferroplasma thermophilum sp. nov., a novel extremely acidophilic, moderately thermophilic archaeon and its role in bioleaching of chalcopyrite, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 105, no. 2, pp. 591–601.
Li, Q., Tian, Y., Fu, X., Yin, H., Zhou, Z., Liang, Y., Qiu, G., Liu, J., Liu, H., Liang, Y., Shen, L., Cong, J., and Liu, X., The community dynamics of major bioleaching microorganisms during chalcopyrite leaching under the effect of organics, Curr. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 63, no. 2, pp. 164–172.
van Hille, R.P., van Wyk, N., Froneman, T., and Harrison, S.T.L., Dynamic evolution of the microbial community in BIOX leaching tanks, Adv. Mater. Res., 2013, vol. 825, pp. 331–334.
Muravyov, M.I. and Bulaev, A.G., Two-step oxidation of a refractory gold-bearing sulfidic concentrate and the effect of organic nutrients on its biooxidation, Miner. Eng., 2013, vol. 45, pp. 108–114.
Golyshina, O.V. and Timmis, K.N., Ferroplasma and relatives, recently discovered cell wall-lacking archaea making a living in extremely acid, heavy metal-rich environments, Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 7, no. 9, pp. 1277–1288.
Zakharchuk, L.M., Egorova, M.A., Krasil’nikova, E.N., Tsaplina, I.A., Bogdanova, T.I., Melamud, V.S., and Karavaiko, G.I., Activity of the enzymes of carbon metabolism in Sulfobacillus sibiricus under various conditions of cultivation, Microbiology, 2003, vol. 72, no. 5, pp. 553–557.
Zakharchuk, L.M., Tsaplina, I.A., Krasil’nikova, E.N., Bogdanova, T.I., and Karavaiko, G.I., Carbon metabolism in Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, Mikrobiologiya, 1994, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 573–580.
Karavaiko, G.I., Tsaplina, I.A., Bogdanova, T.I., Krasil’nikova, E.N., and Zakharchuk, L.M., Growth and carbohydrate metabolism of sulfobacilli, Microbiology, 2001, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 245–250.
Egorova, M.A., Zakharchuk, L.M., Krasil’nikova, E.N., Tsaplina, I.A., and Bogdanova, T.I., Effect of cultivation conditions on the growth and activities of sulfur metabolism enzymes and carboxylases of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans subsp. asporogenes strain 41, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 381–387.
Vartanyan, N.S., Karavaiko, G.I., and Pivovarova, T.A., Effect of organic substances on the growth and oxidation of inorganic substrates in Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans subsp. asporogenes, Mikrobiologiya, 1990, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 411–417.
Golyshina, O.V., Pivovarova, T.A., Karavaiko, G.I., Kondrat’eva, T.F., Moore, E.R.B., Abraham, W., Lunsdorf, H., Timmis, K.N., Yakimov, M.M., and Golyshin, P.N., Ferroplasma acidiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., anacidophilic, autotrophic, ferrous-iron-oxidizing, cell-wall-lacking, mesophilic member of the Ferroplasmaceae fam. nov., comprising a distinct lineage of the Archaea, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 997–1006.
Golyshina, O.V., Yakimov, M.M., Lunsdorf, H., Ferrer, M., Nimtz, M., Timmis, K.N., Wray, V., Tindall, B.J., and Golyshin, P.N., Acidiplasma aeolicum gen. nov., sp. nov., a euryarchaeon of the family Ferroplasmaceae isolated from a hydrothermal pool, and transfer of Ferroplasma cupricumulans to Acidiplasma cupricumulans comb. Nov., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 59, no. 11, pp. 2815–2824.
Wolin, E.A., Wolin, M.J., and Wolfe, R.S., Formation of methane by bacterial extracts, J. Biol. Chem., 1963, vol. 238, no. 6, pp. 2882–2886.
Schwarzenbach, G. and Flaschka, H., Complexometric Titrations, London: Methuen, 1969.
Delaney, R.A.M., Composition, properties and uses of whey protein concentrates, J. Soc. Dairy Technol., 1976, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 91–101.
Kristiansen, B., Linden, J., and Mattey, M., Citric Acid Biotechnology, London: Taylor & Francis, 2002.
Krzywonos, M., Cibis, E., Miśkiewicz, T., and Ryznar-Luty, A., Utilization and biodegradation of starch stillage (distillery wastewater), Electron. J. Biotechnol., 2009, vol. 12, no. 1. doi 10.2225/vol12-issue1-fulltext-5
Borischewski, R.M., Keto acids as growth-limiting factors in autotrophic growth of Thiobacillus thiooxidans, J. Bacteriol., 1967, vol. 93, no. 2, pp. 597–599.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.G. Bulaev, T.V. Erofeeva, K.S. Vorobeva, G.G. Chelidze, A.A. Ramonova, 2018, published in Vestnik Moskovskogo Universiteta, Seriya 16: Biologiya, 2018, Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 178–184.
About this article
Cite this article
Bulaev, A.G., Erofeeva, T.V., Vorobeva, K.S. et al. Effect of Organic Nutrients on the Activity of Archaea of the Ferroplasmaceae Family. Moscow Univ. Biol.Sci. Bull. 73, 146–152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392518030033
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392518030033