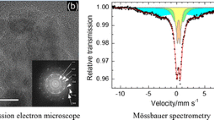
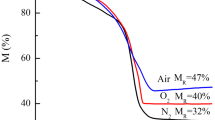
Abstract—Iron nanoparticles are obtained by reducing iron(III) chloride with sodium borohydride in aqueous solutions at room temperature without using stabilizing agents. The obtained samples are characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis, low-temperature adsorption of argon, and transmission electron microscopy. The effect of the concentration of reagent solutions, the molar ratio of reagents, and exposure to ultrasound and inert atmosphere (Ar) on the size and composition of the resulting particles is found. Depending on the conditions of borohydride reduction of iron salts in an aqueous solution, both agglomerates of iron nanoparticles (5–50 nm) of 200 nm or larger and individual iron nanoparticles of 1 to 20 nm in size can be obtained. The presence and concentration of wustite and magnetite in the composition of the obtained particles mainly depend on the concentration of the reducing agent.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Zha, S., Cheng, Y., Gao, Y., and Chen, Z., Chem. Eng. J., 2014, vol. 255, p. 141.
Kazusaka, A., Suzuki, H., and Toyoshima, I., J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1983, vol. 4, p. 150.
Messele, S.A., Bengoa, C., Stuber, F., Fortuny, A., Fabregat, A., and Font, J., Desalin. Water Treat., 2016, vol. 57, p. 5155.
Aich, N., Su, C., Kim, I., and Masoud, A., Application of nanozerovalent iron for water treatment and soil remediation: Emerging nanohybrid approach and environmental implications, in Iron Nanomaterials for Water and Soil Treatment, London: Taylor & Francis, 2018, ch. 4.
Mahdy, S.A., Raheed, Q.J., and Kalaichelvan, P.T., Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res., 2012, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 578.
Groiss, S., Selvaraj, R., Varadavenkatesan, T., and Vinayagam, R., J. Mol. Struct., 2017, vol. 1128, p. 572.
Stefaniuk, M., Oleszczuk, P., and Ok, Y.S., Chem. Eng. J., 2016, vol. 287, p. 618.
Vitta, Y., Piscitelli, V., Fernandez, A., Gonzalez-Jimenez, F., and Castillo, J., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2011, vol. 512, nos. 1–3, p. 96.
Mukherjee, R., Kumar, R., Sinha, A., Lama, Y., and Saha, A.K., Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 46, no. 5, p. 443.
Huyen, N.T.T., Nhung, N.H., Thanh, L., Khanh, P.D., Lam, T.D., and Son, H.A., VietnamJ. Chem., 2018, vol. 56, no. 2, p. 226.
Saranya, S., Vijayarani, K., and Pavithra, S., Indian J. Pharm. Sci., 2017, vol. 5, no. 4, p. 688.
Panţuru, R., Jinescu, G., Panţuru, E., Filcenco-Olteanu, A., and Rădulescu, R., Sci. Bull. - Univ. “Politeh.” Bucharest,Ser. B, 2010, vol. 72, no. 4, p. 207.
Yuvakkumar, R., Elango, V., Rajendran, V., and Kannan, N., Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct., 2011, vol. 6, no. 4, p. 1771.
Ravikumar, K.V.G., Dubey, S., Pulimi, M., Chandrasekaran, N., and Mukherjee, A., J. Mol. Liq. A, 2016, vol. 224, p. 589.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 16-13-10365.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Zhukova
About this article
Cite this article
Vernaya, O.I., Peisikova, A.V., Fuki, M.K. et al. Effect of the Conditions the Reaction on the Formation of Iron Nanoparticles during the Reduction of Iron(III) Ions with Sodium Borohydride. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 74, 326–329 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0027131419060142
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0027131419060142