Abstract—
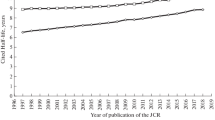
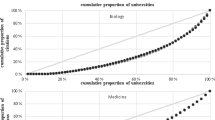
This study analyzes the half-lives of all journals from the 1997–2018 period that were included in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR): Science (JCR-SE) and Social Sciences (JCR-SSE) JCR Editions, and in some narrower branches of science specially distinguished on the basis of WoS subject categories. The findings show that the values of the Cited Half-Life (CdHL) and Citing Half-Life (CgHL) indicators are almost always positive over the entire 22-year study period and for the entire global body of journals in the JCR, individual JCR editions, and each of the specially compiled sets of All Journals and Core Journals. They confirm the long-established fact that the CdHL and CgHL depend on the branch of science and characterize that branch and demonstrate that half-life values for social sciences and humanities are generally higher than for hard sciences. A correlation between half-life values and journal impact factors and numbers of Citable Items (articles, reviews, and conference proceedings that can be cited) is clearly shown. These features of half-lives are important to consider when goal setting and forecasting the development of scientific research.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This indicator also includes cases where articles are cited in articles of the same journal.
Age stands for the difference between the publication year of the citing article and the publication year of the cited article. This definition applies to both CdHL and CgHL.
As the half-life is given according to the JCR, the year is taken as the publication year of its relevant annual issue. This rule applies to both CdHL and CgHL.
This indicator also includes cases where an article from the considered journal cites an article from the same journal.
As a matter of fact, such sets can be formed not only by subject, but also by other classification features, such as region (the journal’s country of publication) or language.
This partially explains the fact that the number of core journals may vary slightly in different years. However, the analysis shows that these differences are very small. For example, the number of core journals for the Medicine and Healthcare branch (includes 48 WoS categories) over the entire study period ranged from 1170 to 1199 journal titles, i.e., the difference between the maximum and minimum number of core journals for this branch did not reach even 2.5%.
According to the description of the Citable Items field in the JCR database, they are items that comprise the figure in the denominator of the Journal Impact Factor calculation. These items are those identified in the Web of Science as an article, review, or proceedings paper and are considered as substantive articles that contribute to the body of scholarship in a particular research field and those most likely to be cited by other articles. Other forms of journal content, such as editorial materials, letters, and meetings abstracts, are not considered as citable items. (http://help.incites.clarivate.com/incitesLiveJCR/9607-TRS).
REFERENCES
Libkind, A.N., Markusova, V.A., and Libkind, I.A., Approach for using Journal Citation Reports in determining the dynamics of half-life indicators of journals, Autom. Doc. Math. Linguist., 2020, vol. 54, pp. 174–183.
Gilyarevskii, R.S., Libkind, A.N., Bogorov, V.G., and Libkind, I.A., Calculation of a half-life period of a scientific journal in the case of incomplete data in the Journal Citation Reports, Autom. Doc. Math. Linguist., 2020, vol. 54, pp. 284–297.
Gilyarevskii, R.S., Informatsionnaya sfera: Krat. entsikl. slovar' (Information Sphere: Short Encyclopedic Dictionary), St. Petersburg: Professiya, 2016.
Arao, L.H., Veloso da Costa Santos, M.J., and Silveira Guedes, V.L., The half-life and obsolescence of the literature science area: A contribution to the understanding the chronology of citations in academic activity, Qual. Quant. Methods Libr., 2017, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 603–610.
Chant, I., New study identifies half-life of journal articles, Libr. J., 2014, vol. 139, no. 2, pp. 20–21.
Jalalifard, M., Norouzi, Y., and Isfandyari-Moghaddam, A., Analyzing web citations availability and half-life in medical journals: A case study in an Iranian university, ASLIB Proc., 2013, vol. 65, no. 3, pp. 242–261.
Gottlieb, A., The half-life of facts: Why everything we know has an expiration date, Scientist, 2012, vol. 26, no. 10, p. 67.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to Clarivate for the opportunity to use the Web of Science and Journal Citation Reports databases.
Funding
This study was performed as part of research for the state assignment to the All-Russian Institute for Scientific and Technical Information (VINITI), Russian Academy of Sciences, no. 0003-2019-0001 and was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project nos. 20-07-00014 and 20-010-00179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by A. Ovchinnikova
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
A List of Branches of Science with Corresponding WoS Categories
Medicine and Healthcare (48 WoS categories): Allergy; Andrology; Anesthesiology; Audiology & Speech-Language Pathology; Cardiac & Cardiovascular Systems; Critical Care Medicine; Dentistry, Oral Surgery & Medicine; Dermatology; Emergency Medicine; Endocrinology & Metabolism; Gastroenterology & Hepatology; Geriatrics & Gerontology; Gerontology; Health Care Sciences & Services; Health Policy & Services; Hematology; Infectious Diseases; Integrative & Complementary Medicine; Medical Ethics; Medical Informatics; Medical Laboratory Technology; Medicine, General & Internal Medicine; Legal; Research & Experimental Medicine; Nursing; Nutrition & Dietetics; Obstetrics & Gynecology; Oncology; Ophthalmology; Orthopedics; Otorhinolaryngology; Pathology; Pediatrics; Peripheral Vascular Disease; Primary Health Care; Psychiatry; Public, Environmental & Occupational Health; Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging; Rehabilitation; Respiratory System; Rheumatology; Sport Sciences; Substance Abuse; Surgery; Transplantation; Tropical Medicine; Urology & Nephrology; Veterinary Sciences.
Mathematics and Logic (7 WoS categories): Logic; Mathematics; Mathematics, Applied; Mathematics, Interdisciplinary Applications; Mechanics; Operations Research & Management Science; Statistics & Probability.
Physical Sciences (17 WoS categories): Acoustics; Astronomy & Astrophysics; Crystallography; Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences; Nanoscience & Nanotechnology; Nuclear Science & Technology; Optics; Physics, Applied; Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical; Physics, Condensed Matter; Physics, Fluids & Plasmas; Physics, Mathematical; Physics, Multidisciplinary; Physics, Nuclear; Physics, Particles & Fields; Spectroscopy; Thermodynamics.
Animals, Plants, and Viruses (6 WoS categories): Entomology; Ornithology; Parasitology; Plant Sciences; Virology; Zoology.
Computer and Information Sciences (14 WoS categories): Automation & Control Systems; Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence; Computer Science, Cybernetics; Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture; Computer Science, Information Systems; Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications; Computer Science, Software Engineering; Computer Science, Theory & Methods; Imaging Science & Photographic Technology; Information Science & Library Science; Microscopy Remote Sensing; Robotics; Telecommunications.
Historical Sciences (4 WoS categories): Archaeology; History; History & Philosophy of Science; History of Social Sciences.
About this article
Cite this article
Gilyarevskii, R.S., Libkind, A.N., Libkind, I.A. et al. The Obsolescence of Cited and Citing Journals: Half-Lives and Their Connection to Other Bibliometric Indicators. Autom. Doc. Math. Linguist. 55, 152–165 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0005105521040026
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0005105521040026