Abstract
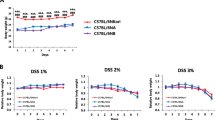
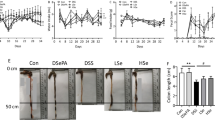
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a complex, multifactorial disorder which can be aggravated by oxidative stress. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced UC in inbred mice is the most commonly used animal-model. However, these populations lack genetic variability therefore this study aimed to establish a DSS-induced UC model in outbred ICR mice and to assess its association with the oxidant-antioxidant system. Male ICR mice were administered a 40 kDa-DSS solution (6 g/kg/day; 0.25 mL 21% DSS 4 times per day) intragastrically for 4 and 7 consecutive days (n = 5). Disease activity index (DAI) was determined daily from body weight and stool characteristics. At the end of the study, colons were collected to examine histology, myeloperoxidase activity, and expression of superoxide dismutase 1 and 2 (Sod1 and Sod2) and catalase (Cat). DSS-treated mice demonstrated daily increases in DAI score with significantly shortened colons, an indirect marker of inflammation in UC. Histological examination of DSS-treated colons revealed goblet cell loss, crypt damage, and epithelial erosion, followed by infiltration of mast cells to the mucosa with mucin depletion. Myeloperoxidase activity was elevated in the DSS-treated mice while Sod1, Sod2, and Cat were suppressed compared to controls. A DSS-induced UC model was established in ICR mice with associated oxidative stress triggering. This outbred-mouse model could prove useful for investigating the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of UC in terms of oxidant-antioxidant balance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
catalase
- DSS:
-
dextran sulfate sodium
- DAI:
-
disease activity index
- IBD:
-
inflammatory bowel disease
- MPO:
-
myeloperoxidas
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- UC:
-
ulcerative colitis
References
Akiyama S, Nesumi A, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Uehara M, Murakami A (2012) Effects of anthocyanin-rich tea “Sunrouge” on dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. BioFactors 38(3):226–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1008
Balmus IM, Ciobica A, Trifan A, Stanciu C (2016) The implications of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapies in inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and animal models. Saudi J Gastroenterol 22:3–17. https://doi.org/10.4103/1319-3767.173753
Barone M, Chain F, Sokol H, Brigidi P, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Langella P, Martin R (2018) A Versatile new model of chemically induced chronic colitis using an outbred murine strain. Front Microbiol 9:565. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00565
Basu S, Hodgson G, Katz M, Dunn AR (2002) Evaluation of role of G-CSF in the production, survival, and release of neutrophils from bone marrow into circulation. Blood 100:854–861. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V100.3.854
Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ (2007) Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. Lancet 369:1641–1657. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60751-X
Bekkering S, Torensma R (2013) Another look at the life of a neutrophil. World J Hematol 2(2):44–58. https://doi.org/10.5315/wjh.v2.i2.44
Bhattacharyya S, Dudeja PK, Tobacman JK (2009) ROS, Hsp27, and IKKβ mediate dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) activation of IkBa, NFkB, and IL-8. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15(5):673–683. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.20821
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Buffinton GD, Doe WF (1995) Depleted mucosal antioxidant defences in inflammatory bowel disease. Free Radic Biol Med 19(6):911–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(95)94362-H
Chassaing B, Aitken JD, Malleshappa M, Vijay-Kumar M (2014) Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr Protoc Immunol 104(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142735.im1525s104
Cheon JH, Kim JS, Kim JM, Kim N, Jung HC, Song IS (2006) Plant sterol guggulsterone inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells by blocking IkappaB kinase and ameliorates acute murine colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12(12):1152–1161. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mib.0000235830.94057.c6
Cho E, Shin JS, Noh YS, Cho YW, Hong SJ, Park JH, Lee JY, Lee JY, Lee KT (2011) Anti-inflammatory effects of methanol extract of Patrinia scabiosaefolia in mice with ulcerative colitis. J Ethnopharmacol 136(3):428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.04.047
Damiani CR, Benetton CA, Stoffel C, Bardini KC, Cardoso VH, Di Giunta G, Pinho RA, Dal-Pizzol F, Streck EL (2007) Oxidative stress and metabolism in animal model of colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(11):1846–1851. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.04890.x
Fang J, Seki T, Tsukamoto T, Qin H, Yin H, Liao L, Nakamura H, Maeda H (2013) Protection from inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated carcinogenesis with 4-vinyl-2, 6-dimethoxyphenol (canolol) involves suppression of oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines. Carcinogenesis 34(12):2833–2841. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgt309
Frazer KA, Murray SS, Schork NJ, Topol EJ (2009) Human genetic variation and its contribution to complex traits. Nat Rev Genet 10(4):241–251. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2554
Guan G, Lan S (2018) Implications of antioxidant systems in inflammatory bowel disease. Biomed Res Int 2018:1290179. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1290179
Gutierrez-Orozco F, Thomas-Ahner JM, Berman-Booty LD, Galley JD, Chitchumroonchokchai C, Mace T, Suksamrarn S, Bailey MT, Clinton SK, Lesinski GB, Failla ML (2014) Dietary α-mangostin, a xanthone from mangosteen fruit, exacerbates experimental colitis and promotes dysbiosis in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 58(6):1226–1238. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201300771
Halliwell B (1997) Antioxidants and human disease: a general introduction. Nutr Rev 55:S44–S52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.1997.tb06100.x
Hirata I, Yasumoto S, Toshina K, Inoue T, Nisgikawa T, Murano N, Murano M, Wang FY, Katsu K (2007) Evaluation of the effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate in suppressing inflammation in mice with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. World J Gastroenterol 13(11):1666–1671. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i11.1666
Hong J, Chung KS, Shin JS, Park G, Jang Y, Lee KT (2019) Anti-colitic effects of ethanol extract of Persea americana Mill. through suppression of pro-inflammatory mediators via NF-κB/STAT3 inactivation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice. Int J Mol Sci 20(1):E177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010177
Ishihara T, Tanaka K, Tasaka Y, Namba T, Suzuki J, Ishihara T, Okamoto S, Hibi T, Takenaga M, Igarashi R, Sato K, Mizushima Y, Mizushima T (2009) Therapeutic effect of lecithinized superoxide dismutase against colitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328(1):152–164. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.144451
Jarukamjorn K, Sakuma T, Miyaura J, Nemoto N (1999) Different regulation of the expression of mouse hepatic cytochrome P450 2B enzymes by glucocorticoid and phenobarbital. Arch Biochem Biophys 369(1):89–99. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1999.1342
Jarukamjorn K, Chatuphonprasert W, Jearapong N, Punvittayagul C, Wongpoomchai R (2019) Tetrahydrocurcumin attenuates phase I metabolizing enzyme-triggered oxidative stress in mice fed a high-fat and high-fructose diet. J Func Food 55:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.02.021
Kang Y, Xue Y, Du M, Zhu MJ (2017) Preventive effects of Goji berry on dextran-sulfate-sodium-induced colitis in mice. J Nutr Biochem 40:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.10.009
Kawabata K, Murakami A, Ohigashi H (2006) Auraptene decreases the activity of matrix metalloproteinases in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in ICR mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70(12):3062–3065. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60393
Kim M, Murakami A, Miyamoto S, Tanaka T, Ohigashi H (2010) The modifying effects of green tea polyphenols on acute colitis and inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis in male ICR mice. Biofactors 36(1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.69
Kim JJ, Shajib MS, Manocha MM, Khan WI (2012) Investigating intestinal inflammation in DSS-induced model of IBD. J Vis Exp 60:1–6. https://doi.org/10.3791/3678
Kim JE, Nam JH, Cho JY, Kim KS, Hwang DY (2017) Annual tendency of research papers used ICR mice as experimental animals in biomedical research fields. Lab Anim Res 33(2):171–178. https://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2017.33.2.171
Kim M, Chung KS, Hwang SJ, Yoon YS, Jang YP, Lee JK, Lee KT (2020) Protective effect of Cicer arietinum L. (chickpea) ethanol extract in the dextran sulfate sodium-induced mouse model of ulcerative colitis. Nutrients 12(2):E456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020456
Kitajima S, Takuma S, Morimoto S (2000) Histological analysis of murine colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium of different molecular weights. Exper Anim 49(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.49.9
Kruidenier L, Verspaget HW (2002) Review article: oxidative stress as a pathogenic factor in inflammatory bowel disease-radicals or ridiculous? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:1997–2015. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2002.01378.x
Mahler M, Bristol IJ, Leiter EH, Workman AE, Birkenmeier EH, Elson CO, Sundberg JP (1998) Differential susceptibility of inbred mouse strains to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Am J Physiol 274(3):G544–G551. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.1998.274.3.G544
Masoodi I, Tijjani BM, Wani H, Hassan NS, Khan AB, Hussain S (2011) Biomarkers in the management of ulcerative colitis: a brief review. Ger Med Sci 9:Doc03. https://doi.org/10.3205/000126
Melgar S, Karlsson A, Michaëlsson E (2005) Acute colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium progresses to chronicity in C57BL/6 but not in BALB/c mice: correlation between symptoms and inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288(6):G1328–G1338. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00467.2004
Millar AD, Rampton DS, Chander CL, Claxson AW, Blades S, Coumbe A, Panetta J, Morris CJ, Blake DR (1996) Evaluating the antioxidant potential of new treatments for inflammatory bowel disease in a rat model of colitis. Gut 39:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.39.3.407
Mosli MH, Parker CE, Nelson SA, Baker KA, MacDonald JK, Zou GY, Feagan BG, Khanna R, Levesque BG, Jairath V (2017) Histologic scoring indices for evaluation of disease activity in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 25(5):CD011256. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011256.pub2
Mulder TP, Verspaget HW, Janssens AR, de Bruin PA, Peña AS, Lamers CB (1991) Decrease in two intestinal copper/zinc containing proteins with antioxidant function in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 32(10):1146–1150. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.32.10.1146
Murthy S, Flanigan A (1999) Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease. In: Morgan DW, Marshall LA (eds) In vivo models of inflammation. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 205–236
Naito Y, Takagi T, Yoshikawa T (2007) Neutrophil-dependent oxidative stress in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 41:18–36. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.2007003
Nishiyama Y, Kataoka T, Yamato K, Taguchi T, Yamaoka K (2012) Suppression of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by radon inhalation. Mediat Inflamm 2012:239617. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/239617
Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ (2012) Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 380(9853):1606–1619. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60150-0
Pavlick KP, Laroux FS, Fuseler J, Wolf RE, Gray L, Hoffman J, Grisham MB (2002) Role of reactive metabolites of oxygen and nitrogen in inflammatory bowel disease. Free Radic Biol Med 33(3):311–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00853-5
Pengkumsri N, Suwannalert P, Sivamaruthi BS, Wongpoomchai R, Sirisattha S, Tammasakchai A, Taya S, Sirilun S, Peerajan S, Chaiyasut C (2015) Molecular, histological, and anti-oxidant evaluation of colitis induction in rats by different concentration of dextran sodium sulfate (5 kDa). Int J Pharm Sci 7(12):283–287. https://innovareacademics.in/journals/index.php/ijpps/article/view/9356
Perše M, Cerar A (2012) Dextran sodium sulphate colitis mouse model: traps and tricks. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:10–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/718617
Pervin M, Hasnat A, Lim JH, Lee YM, Eun Kim O, Um BH, Lim BO (2016) Preventive and therapeutic effects of Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) extract against DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by regulation of antioxidant and inflammatory mediators. J Nutr Biochem 28:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.10.006
Ribeiro AL, Shimada AL, Hebeda CB, de Oliveira TF, de Melo Loureiro AP, Filho Wdos R, Santos AM, de Lima WT, Farsky SH (2011) In vivo hydroquinone exposure alters circulating neutrophil activities and impairs LPS-induced lung inflammation in mice. Toxicology 288(1–3):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.05.009
Seo S, Shin JS, Lee WS, Rhee YK, Cho CW, Hong HD, Lee KT (2017) Anti-colitis effect of Lactobacillus sakei K040706 via suppression of inflammatory responses in the dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice model. J Func Foods 27:256–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.12.045
Singh S, Graff LA, Bernstein CN (2009) Do NSAIDs, antibiotics, infections, or stress trigger flares in IBD? Am J Gastroenterol 104(5):1298–1313. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.15
Stevceva L, Pavli P, Buffinton G, Wozniak A, Doe WF (1999) Dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis activity varies with mouse strain but develops in lipopolysaccharide-unresponsive mice. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1746.1999.01806.x
Tamaki H, Nakamura H, Nishio A, Nakase H, Ueno S, Uza N, Kido M, Inoue S, Mikami S, Asada M, Kiriya K, Kitamura H, Ohashi S, Fukui T, Kawasaki K, Matsuura M, Ishii Y, Okazaki K, Yodoi J, Chiba T (2006) Human thioredoxin-1 ameliorates experimental murine colitis in association with suppressed macrophage inhibitory factor production. Gastroenterology 131(4):1110–1121. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.023
Tatiya-aphiradee N, Chatuphonprasert W, Jarukamjorn K (2019) Anti-inflammatory effect of Garcinia mangostana Linn. pericarp extract in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced superficial skin infection in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 111:705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.142
Wallace JL, MacNaughton WK, Morris GP, Bech PL (1989) Inhibition of leukotriene synthesis markedly accelerates healing in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 96(1):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(89)90760-9
Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK (2007) Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 448(7152):427–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06005
Xiao HT, Lin Cy, Ho DH, Peng J, Chen Y, Tsang SW, Wong M, Zhang XJ, Zhang M, Bian ZX (2013) Inhibitory effect of the gallotannin corilagin on dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine ulcerative colitis. J Nat Prod 76(11):2120–2125. https://doi.org/10.1021/np4006772
Yao J, Wang JY, Liu L, Li YX, Xun AY, Zeng WS, Jia CH, Wei XX, Feng JL, Zhao L, Wang LS (2010) Anti-oxidant effects of resveratrol on mice with DSS-induced ulcerative colitis. Arch Med Res 41(4):288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2010.05.002
Acknowledgements
Nitima Tatiya-aphiradee acknowledges the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. program, Thailand Research Fund for the scholarship (PhD0008/2559). The authors thank Dr. Glenn Borlace, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen University for English language assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Employment of leadership
None declared.
Honorarium
None declared.
Conflict of interest
The funding organization(s) played no role in the study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the report for publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatiya-aphiradee, N., Chatuphonprasert, W. & Jarukamjorn, K. Oxidative stress exacerbates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in ICR mice. Biologia 75, 2063–2071 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00524-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00524-9